Introduction
Data extraction in systematic literature reviews and meta-analyses is a critical process that involves systematically collecting relevant information from included studies to address the research question or objective of the review.
Data extraction involves collecting, recording, and organizing relevant information from included studies to facilitate analysis and synthesis of the evidence. By following standardized procedures and ensuring accuracy and consistency in data extraction, researchers can produce reliable and valid findings that inform evidence-based practice and decision-making.
At Best Dissertation Writers, we have developed a versatile and adaptable platform enabling students from across the world to connect with skilled professionals for assistance with their challenging writing tasks, such as systematic literature review dissertation services.
Key Steps Involved in Data Extraction Process
Here are the key steps involved in data extraction:
- Develop Data Extraction Form: Before data extraction begins, researchers should develop a standardized data extraction form or template. This form typically includes fields for capturing relevant information from each included study, such as study characteristics, methods, results, and key findings. The form should be designed to align with the research question and objectives of the review.
- Define Variables of Interest: Researchers should clearly define the variables of interest to be extracted from each study. These variables may include study characteristics (e.g., study design, sample size, duration), intervention/exposure details (e.g., type of intervention, dosage), outcome measures (e.g., primary and secondary outcomes), and any additional data relevant to the review.
- Conduct Data Extraction: Using the predefined data extraction form, researchers systematically extract data from each included study. This involves carefully reviewing the full text of the study and recording relevant information in the appropriate fields of the extraction form. Data extraction may be conducted independently by two or more reviewers to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Resolve Discrepancies: In cases where discrepancies or uncertainties arise during data extraction, reviewers should resolve these issues through discussion or consultation with a third reviewer. Consensus should be reached on any discrepancies to ensure consistency and accuracy in the extracted data.
- Verify Accuracy: After completing data extraction for all included studies, researchers should verify the accuracy and completeness of the extracted data. This may involve cross-checking the extracted data against the original study documents to ensure that all relevant information has been captured accurately.
- Manage Data: Once data extraction is complete, researchers should organize and manage the extracted data in a systematic manner. This may involve summarizing the data, entering it into a database or spreadsheet, and performing any necessary data cleaning or formatting to prepare it for analysis.
- Document Process: It is important to document the data extraction process, including details such as who conducted the extraction, any discrepancies or issues encountered, and how they were resolved. This documentation helps ensure transparency and reproducibility of the review process.
Literature Matrix/Data Extraction Matrix/Evidence Table
A literature matrix, also known as a data extraction matrix or evidence table, is a structured framework used in systematic reviews to organize and synthesize information extracted from included studies. It serves as a tool for systematically recording and comparing key characteristics and findings of each study, facilitating the analysis and synthesis of evidence.
The literature matrix typically consists of rows and columns, with each row representing an individual study included in the review and each column representing different categories or variables of interest. The specific content and format of the literature matrix may vary depending on the research question, objectives, and characteristics of the included studies, but common elements often include:
- Study Identification: Information about each study, such as author(s), publication year, study title, and citation details, is typically recorded to identify and reference the study.
- Study Characteristics: Key characteristics of each study, such as study design, sample size, population characteristics, intervention/exposure details, comparator/control group, outcome measures, follow-up duration, and setting, are recorded to provide context and describe the included studies.
- Results/Data: Relevant findings or data extracted from each study, such as effect estimates, measures of association, statistical significance, qualitative themes, or other pertinent results, are recorded to summarize the key findings of the study.
- Quality Assessment: Information about the methodological quality, risk of bias, or quality appraisal of each study, such as assessment criteria, scores, or ratings, may be recorded to evaluate the reliability and validity of the evidence.
- Notes/Comments: Additional notes, comments, or observations about each study, such as strengths, limitations, or noteworthy findings, may be recorded to provide context or insights into the interpretation of the evidence.
Including these characteristics in your systematic review helps to provide a comprehensive summary of the included studies, allowing readers to assess the relevance, quality, and applicability of the evidence to your research question and clinical practice. Adjust the list of characteristics as needed based on the specific requirements of your review and the types of studies included.
Example of Literature Matrix/Data Extraction Matrix/Evidence Table
With the research question of a nursing systematic literature review which states:
“Among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, what is the effectiveness of nurse-led educational interventions compared to standard care in improving self-management behaviors and glycemic control?” The following is an example of a complete literature matrix;
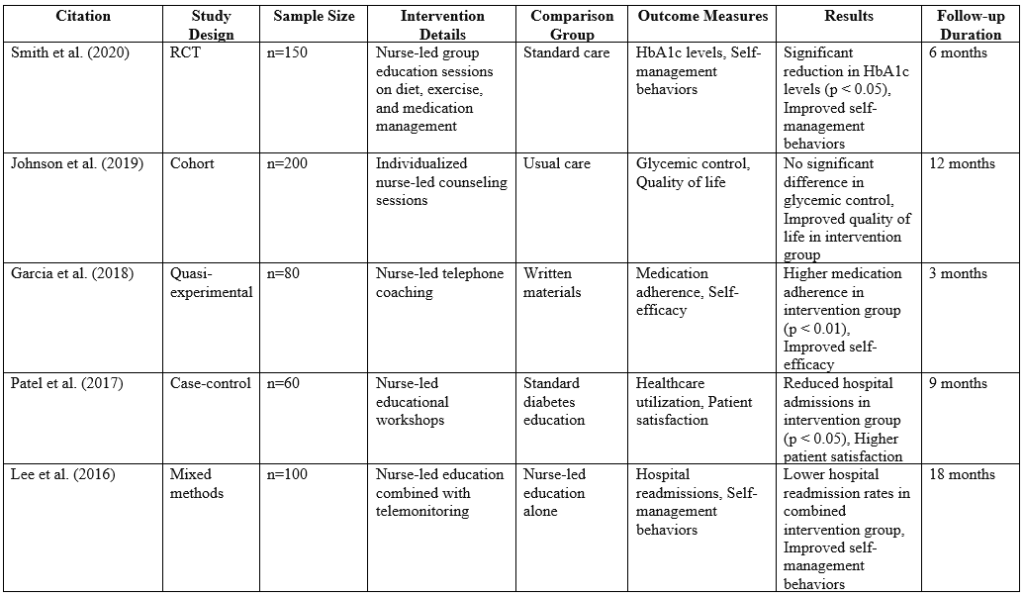
The table shows an example of a simplified literature matrix table for a systematic literature review on the effectiveness of nurse-led educational interventions compared to standard care in improving self-management behaviors and glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Please note that this example includes only a subset of potential data elements for illustration purposes, and you may need to customize the table further based on your specific research question and inclusion/exclusion criteria.
Summary
A data extraction matrix or table in a systematic literature review and meta-analysis is a structured framework used to organize and synthesize information extracted from included studies. It typically consists of rows representing individual studies and columns representing key categories such as study design, sample size, intervention details, comparator, outcome measures, results, quality assessment, and notes/comments. The matrix facilitates systematic recording and comparison of study characteristics and findings, enabling researchers to analyze and synthesize evidence effectively. It promotes consistency, transparency, and reproducibility in the review process by providing a standardized format for documenting extracted data. Additionally, the data extraction matrix serves as a valuable tool for quality assessment, facilitating the evaluation of study quality and risk of bias. Overall, the matrix plays a crucial role in synthesizing evidence from multiple studies to inform evidence-based practice and decision-making.
