Introduction
A literature search strategy is a systematic plan or approach used to identify relevant research studies and literature on a particular topic. It involves identifying and selecting appropriate databases, developing search terms and keywords, applying filters and limits, and executing the search process. The goal of a literature search strategy is to comprehensively and efficiently retrieve relevant literature that addresses the research question or objectives.
Developing a search strategy is essential for systematic literature reviews and meta-analyses as it ensures comprehensive coverage of the literature, minimizes bias, enhances transparency and reproducibility, optimizes efficiency, identifies relevant studies, and upholds rigor and quality in the review process.
At Best Dissertation Writers, we have developed a versatile and adaptable platform enabling students from across the world to connect with skilled professionals for assistance with their challenging writing tasks, such as systematic literature review dissertation services.
What are the components of a literature search strategy?
Key components of a literature search strategy include:
Identification of Databases
You should first identify the databases to use when performing your literature search. Identification of databases for literature search is essential in research to ensure comprehensiveness, access to diverse perspectives, minimization of bias, validation of findings, coverage of grey literature, and adherence to methodological standards, particularly in systematic literature reviews. Therefore, you need to determine which academic databases, repositories, or sources are most relevant to the topic of interest.
Identification of databases for literature search is crucial in research for several reasons:
- Comprehensiveness: Different databases cover various disciplines, journals, and publication types. Identifying multiple databases ensures a more comprehensive search, capturing a wider range of relevant literature on the research topic.
- Access to Different Disciplines: Research topics in nursing often intersect with multiple disciplines, such as medicine, psychology, sociology, and public health. Searching databases from different fields ensures access to diverse perspectives and a broader pool of literature relevant to the research question.
- Depth of Coverage: Each database may index different journals and publications, resulting in variations in coverage and depth of content. By searching multiple databases, researchers increase the likelihood of identifying relevant studies that may not be indexed in other databases.
- Minimization of Bias: Relying on a single database for literature search increases the risk of bias, as it may prioritize certain types of publications or sources over others. Searching multiple databases helps minimize bias and ensures a more balanced and inclusive representation of the literature.
- Validation of Findings: Finding consistent results across multiple databases strengthens the validity and reliability of the findings. It provides reassurance that the conclusions drawn from the literature search are robust and not solely reliant on the characteristics of a single database.
- Coverage of Grey Literature: Some databases specialize in indexing grey literature, such as conference proceedings, dissertations, and reports, which may not be available through traditional academic databases. Identifying and searching relevant databases for grey literature enhances the comprehensiveness of the literature search.
- Requirement of Systematic Reviews: In systematic literature reviews, it is often a requirement to search multiple databases to ensure that the search is comprehensive and transparent. Identifying databases upfront helps meet these methodological standards and enhances the credibility of the review.
What are the common databases for nursing research studies/literature?
There are several databases that you can use for your nursing research studies and literature. Some of the most popular ones include:
- PubMed/MEDLINE: PubMed is a free search engine maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) that provides access to MEDLINE, which is a comprehensive database of biomedical literature. It covers a wide range of nursing journals and is a primary resource for nursing research.
- CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature): CINAHL is a specialized database for nursing and allied health literature. It indexes a vast array of nursing journals, books, dissertations, conference proceedings, and more, making it an essential resource for nursing research.
- EMBASE: EMBASE is a biomedical and pharmacological database that covers a broader range of journals and includes more European and non-English language content compared to PubMed/MEDLINE. It is particularly useful for nursing research that involves pharmacology or international perspectives.
- PsycINFO: PsycINFO is a database maintained by the American Psychological Association (APA) that covers psychology and related disciplines. It includes a significant amount of literature relevant to psychiatric nursing, mental health, and behavioral science.
- Scopus: Scopus is a multidisciplinary database that covers a wide range of scientific literature, including nursing. It offers extensive coverage of journals, conference proceedings, and patents, making it a valuable resource for interdisciplinary research.
- Web of Science: Web of Science is another multidisciplinary database that provides access to scholarly literature across various disciplines, including nursing. It offers citation indexing and analysis tools, allowing researchers to track citations and identify influential articles.
- ProQuest Nursing & Allied Health Source: ProQuest Nursing & Allied Health Source is a comprehensive database that provides access to a diverse collection of nursing and allied health literature. It includes journals, dissertations, conference proceedings, and more, covering a wide range of topics in nursing research.
All of these databases provide you with a wealth of literature and resources for nursing research studies, including peer-reviewed journals, conference abstracts, systematic reviews, and grey literature. It is recommendable that you use a combination of these databases to ensure comprehensive coverage and access to relevant literature on your research topics.
Selection of Search Terms and Keywords
The selection of search terms and keywords is a crucial step in developing a literature search strategy for your systematic literature review research. It involves identifying and choosing specific words, phrases, and concepts that accurately represent the topic of interest and are likely to retrieve relevant literature from databases. You should consider synonyms, variations, and related terms to capture a broad range of relevant literature.
Develop a list of search terms, keywords, and phrases that accurately represent the concepts or aspects of the topic being researched. Consider synonyms, variations, and related terms to capture a broad range of relevant literature. A well-designed literature search strategy is essential for conducting a systematic and comprehensive review of the literature, enabling researchers to identify and access relevant studies that contribute to the evidence base on a particular topic.
Boolean Operators
Boolean operators are essential in nursing literature searches for several reasons:
- Precision: Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) help refine search queries to ensure precision in retrieving relevant literature. Using AND narrows down search results by requiring all specified terms to be present, while using OR broadens search results by retrieving articles that contain any of the specified terms.
- Flexibility: Boolean operators offer flexibility in constructing search queries to accommodate different combinations of search terms and concepts. This flexibility allows researchers to customize search queries based on the complexity and specificity of the research topic, ensuring that relevant literature is captured.
- Complex Search Queries: Nursing research topics often involve multiple concepts and variables that need to be explored simultaneously. Boolean operators enable researchers to construct complex search queries that incorporate multiple search terms, concepts, and criteria, allowing for a more thorough and comprehensive literature search.
- Optimization of Search Results: By using Boolean operators strategically, researchers can optimize search results to retrieve articles that are most relevant to their research question or objectives. This helps streamline the literature search process and facilitates the identification of high-quality evidence that aligns with the research needs.
- Reduction of Noise: Boolean operators can help reduce noise in search results by excluding irrelevant terms or concepts using the NOT operator. This ensures that search results are focused on the specific aspects of the research topic and minimize the inclusion of irrelevant or tangential literature.
You should always use Boolean operators (e.g., AND, OR, NOT) to combine search terms and refine search results. For example, using “diabetes” AND “nursing intervention” will retrieve articles that contain both terms, while using “diabetes” OR “type 2 diabetes” will retrieve articles that contain either term.
Truncation and Wildcards
Truncation and wildcards play a crucial role in enhancing the effectiveness and efficiency of literature searches in nursing research. Truncation, typically denoted by an asterisk (*) or other symbols, allows researchers to search for variations of a word root, capturing all possible endings and forms of a term. This is particularly useful in nursing research, where terminology can vary widely across different contexts and disciplines. By using truncation, researchers can broaden their search queries to encompass all relevant variations of a term, ensuring that no relevant literature is overlooked due to differences in spelling or word endings.
Wildcards, such as question marks (?), provide additional flexibility by substituting for one or more characters within a word. This allows researchers to account for variations in spelling or word morphology, further expanding the scope of their search queries. Together, truncation and wildcards enable researchers to conduct comprehensive literature searches that capture a wide range of relevant articles and evidence, enhancing the robustness and completeness of their research findings in nursing.
You should also use truncation () and wildcards (?) to capture variations of search terms and expand search results. For example, using “diabet” will retrieve articles containing terms such as “diabetes,” “diabetic,” or “diabetics.”
Example of a Literature Search Strategy for a Nursing Systematic Literature Review
The types of keywords and search terms included in your literature search strategy are determined by the nature of research question, aim or objective you have developed. For example, if the research question that you are addressing in your systematic literature review is
“Among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, what is the effectiveness of nurse-led educational interventions compared to standard care in improving self-management behaviors and glycemic control?”
You will be required to develop a literature search strategy that will allow identification and selection of studies or other forms of literature works which provide evidence about the defined research phenomenon or problem. This section provides a detailed literature search strategy for retrieving appropriate evidence that can be used to answer the research question “Among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, what is the effectiveness of nurse-led educational interventions compared to standard care in improving self-management behaviors and glycemic control?”
You can use similar strategy, but redefine it to suit your research problem, phenomenon or research question.
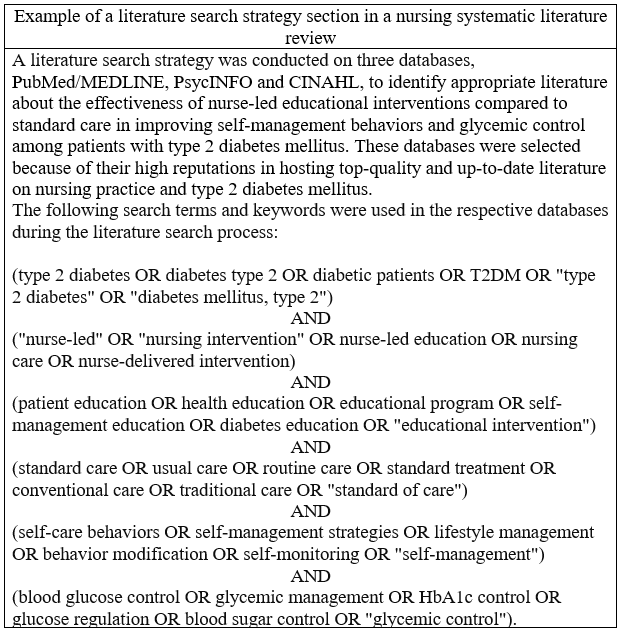
The literature search strategy provided in the example above will help you ensure that all relevant literature related to nurse-led educational interventions, standard care, self-management behaviors, and glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus is captured. Adjustments can be made based on specific database requirements or additional terms identified during the search process.
