What is a Purposive Sample?
- Purposive sampling is a non-probability sampling method where researchers select participants based on specific characteristics that align with the research objectives.
- This form of sampling involves choosing individuals who are believed to provide the most relevant information in answering the research question.
- Purposive sampling is widely used in qualitative research because it allows researchers to focus on specific cases that are most likely to provide deep, insightful data.
- Unlike random sampling, where participants are selected at random, purposive sampling deliberately targets specific individuals or groups, making it a type of sampling used to address particular aspects of a study.
Expert Dissertation Help
Get professional assistance from Best Dissertation Writers to craft a high-quality dissertation that meets all academic standards. Let us guide you through the process with expert writing, research, and editing services.
Definition and Importance of a Purposeful Sample
- Purposive sampling refers to the intentional selection of participants who meet certain criteria, ensuring that the sample directly relates to the research question.
- The importance of purposive sampling lies in its ability to focus on the richness of the data rather than the representativeness of the sample.
- Researchers use purposive sampling when they want to gather specific qualitative data collection from a particular subset of people who are likely to have in-depth knowledge on the subject of study.
- A key reason for using this type of sampling is that it supports the goals of qualitative method research, where the emphasis is on understanding the depth and context of a phenomenon.
- It can involve various forms of purposive sampling, such as homogeneous sample, which targets participants with similar characteristics, or typical case sample, which focuses on average cases that represent common experiences.
How Purposive Sampling Differs from Other Sampling Methods
- Purposive sampling differs from random sampling, which selects participants purely by chance, often without regard to the research question.
- In contrast to probability sampling, which aims to give every individual an equal chance of being selected, purposive sampling is a non-probability sampling method that selects participants based on specific criteria that are relevant to the study’s aims.
- While random sampling is often used in quantitative research to ensure statistical representativeness, purposive sampling is more suited for qualitative data collection and analysis, as it allows for a targeted, in-depth exploration of a specific phenomenon.
- One type of purposive sampling is extreme case sampling, where researchers intentionally select participants who have experienced unusual or extreme cases, providing a deeper understanding of the range of experiences related to the research topic.
- Convenience sample, another form of sampling, often involves choosing readily available participants, which can be less focused than purposive sampling but still provides relevant insights for some types of research studies.
Applications of Purposive Sampling in Qualitative Research
- Purposive sampling is often used in qualitative research to target specific groups or individuals who have the knowledge or experience relevant to the research question.
- It is especially helpful in qualitative data collection when the researcher aims to understand particular perspectives, behaviors, or experiences that are directly tied to the research objectives.
- By focusing on certain types of participants, such as those within a homogeneous sample or those involved in extreme case sampling, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the complexities surrounding a phenomenon.
- Purposive sampling is valuable in studies where a typical case sample is needed to represent an average or common experience, which can help in identifying trends or patterns within a specific context.
- This type of purposeful sampling is particularly effective in qualitative method research where the aim is to generate rich, detailed data that offers insight into social, psychological, or cultural phenomena.
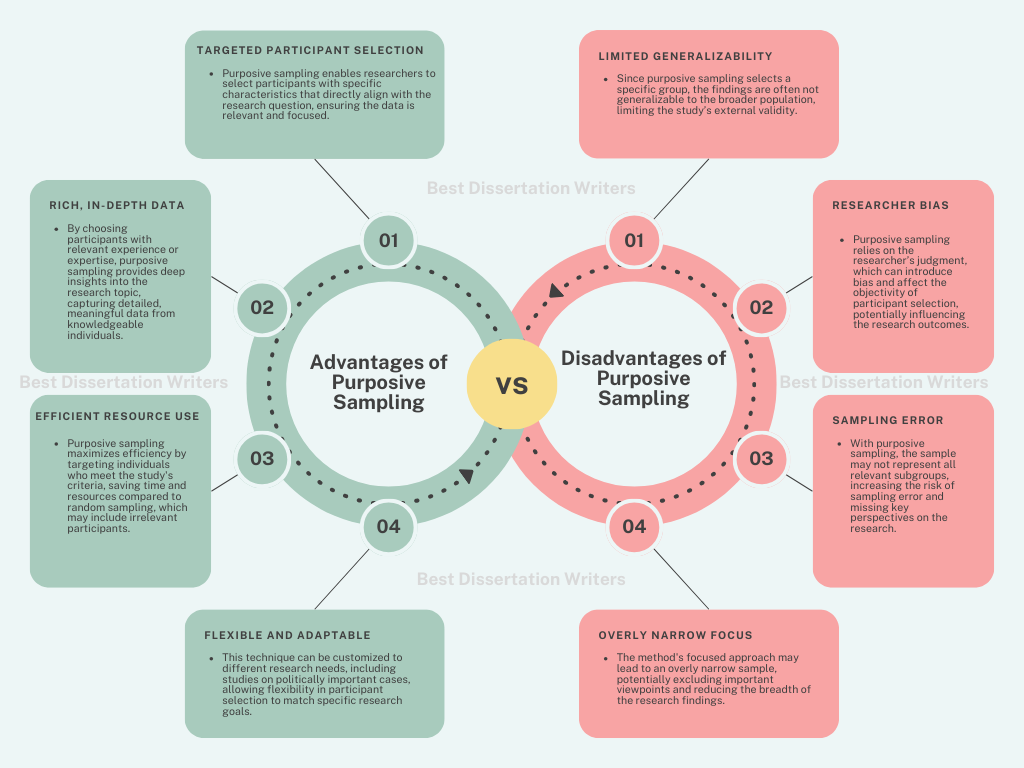
What Are the Advantages of Purposive Sampling?
- Purposive sampling is a targeted sampling strategy for qualitative research where participants are selected based on their relevance to the specific research question.
- One key advantage of purposive sampling is that it allows researchers to focus on individuals or groups who can provide deep insights into the research aims, which is ideal for qualitative studies.
- Purposive sampling ensures that the sampling process directly aligns with the goals of the study, leading to more accurate and relevant data for the researcher’s investigation.
Benefits of Using a Purposeful Sample in Research
- Purposive sampling allows researchers to select a sample size that is not overly large but sufficient for qualitative research. This makes it more manageable and focused.
- Since purposive sampling involves selecting a sample based on specific criteria, it enhances the use of purposeful sampling to gather data that is highly relevant to the research question.
- The sampling approach ensures that participants have a rich understanding or experience related to the study, which is particularly beneficial in mental health services research or exploratory research.
- By focusing on the appropriate sample, researchers avoid the need for random selection, making purposive sampling more effective in obtaining targeted data that directly addresses the research aims.
- Researchers can apply different forms of purposeful sampling, such as quota sampling or extreme case sampling, depending on the needs of the study.
When to Use Purposive Sampling
- Purposive sampling is particularly useful when the research requires detailed and specific insights into a well-defined group or phenomenon.
- It is often used in exploratory research, where the goal is to understand a topic or phenomenon from a few, highly knowledgeable perspectives.
- When conducting research on politically important cases or specific subgroups, purposive sampling allows the researcher to focus on the most relevant individuals, ensuring a deep understanding of the subject matter.
- This sampling strategy is also beneficial in mixed method implementation research, where qualitative data from a targeted sample is complemented by quantitative methods.
Comparing Advantages and Disadvantages of Purposive Sampling
- Purposive sampling is beneficial in ensuring that the sample directly fits the research objectives; however, it is prone to research bias because the selection is not random.
- Unlike convenience sampling, which selects participants based on ease, purposive sampling focuses on relevance to the research question, leading to more meaningful data but potentially at the cost of generalizability.
- Purposive sampling can provide sufficient qualitative data, but the sample size for purposive sampling is often smaller, which may not always be ideal for larger-scale studies.
- Purposive sampling and convenience sampling both involve selecting a sample based on non-random methods, but purposive sampling offers more control over who is selected, ensuring that the sample aligns closely with the data collection method and research focus.
- Despite its advantages, purposive sampling is prone to researcher bias, as the selection criteria are subjective and based on the researcher’s judgment. Therefore, it is important to manage this risk through transparency in the sampling process and clear selection criteria.
High-Quality Essay Writing Services
Struggling with your essay? Trust Best Dissertation Writers to deliver well-researched, properly structured, and insightful essays that align with your academic goals. Reach out now for top-notch essay writing services.
What Are the Disadvantages of Purposive Sampling?
- Purposive sampling is a widely used technique in qualitative research for selecting participants based on specific characteristics that are central to the research question. However, it has several disadvantages that researchers need to consider when using this approach.
- While purposive sampling ensures targeted selection based on the research objectives, it may not provide a representative sample of the entire population, which could limit the generalizability of findings.
Common Limitations of the Purposive Sampling Technique
- Purposive sampling relies on the researcher’s judgment to select participants, which may introduce research bias. The selection process is subjective, and the choices made by the researcher may inadvertently favor certain perspectives or experiences, limiting the diversity of the sample.
- The goal of purposive sampling is to gather data from participants who are believed to have insights that are relevant to the research question. However, the subjective nature of the selection process means that important perspectives may be overlooked, leading to an incomplete understanding of the phenomenon being studied.
- Purposive sampling may not be ideal for studies where a more diverse or representative sample is needed. Unlike random sampling, which provides a more balanced and generalized sample, purposive sampling focuses on specific cases, which could result in a skewed or unbalanced dataset.
Sampling Error and Bias in Purposive Sampling
- Purposive sampling is prone to research bias because it involves selecting participants based on the researcher’s criteria rather than random selection. This bias can lead to findings that are not generalizable or that reflect only the views of a specific subgroup.
- The sampling approach to purposive sampling can sometimes result in sampling errors because the sample may not accurately reflect the wider population. This issue arises when the participants selected are too similar to each other (as in homogeneous sampling), limiting the diversity of the data.
- Purposive sampling is also susceptible to sampling error, especially if the research design and methodology do not adequately account for the need for a broad range of experiences or opinions. For example, when purposive sampling is used to focus on politically important cases, the sample may not capture other relevant viewpoints, leading to a narrow perspective.
Challenges in Implementation Research with Purposive Sampling
- In implementation research, where the goal is to understand how interventions or strategies work in practice, purposive sampling can be challenging because the participants selected may not represent the full range of experiences or outcomes.
- For mixed method studies, combining qualitative and quantitative data, purposive sampling may not always align with the research objectives when the sample size is too small or too narrowly defined.
- The types of purposive sampling—such as homogeneous sampling, which selects participants with similar characteristics—may not be suitable for all research designs. When researchers are attempting to explore a broad range of perspectives, using purposive sampling could limit the ability to understand diverse views on the issue.
- Additionally, purposive sampling is not well suited for situations where random sampling is used because it does not provide an equal chance for all members of the population to be included, affecting the rigor of the findings.
What Are the Different Types of Purposive Sampling Methods?
- Purposive sampling is a technique widely used in qualitative research where participants are selected based on specific characteristics that are relevant to the research question.
- There are various types of purposive sampling, each serving a specific purpose depending on the nature of the research question and the objectives of the research.
- These methods allow researchers to focus on a specific group that is believed to provide the most relevant data, making purposive sampling a useful tool for in-depth exploration of complex topics.
Understanding Maximum Variation Sampling
- Maximum variation sampling is a type of purposive sampling that involves selecting participants who represent a broad range of perspectives or characteristics.
- This approach is used when the researcher wants to capture the diversity of experiences within a population, ensuring that all possible variations of a phenomenon are considered.
- Purposive sampling will vary depending on the specific research focus. For example, in studies exploring politically important cases, maximum variation sampling ensures that different viewpoints are represented, enriching the data.
- The goal of this sampling technique is to identify the extremes within the data, which allows the researcher to understand the full spectrum of experiences related to the research question.
Exploring Critical Case Sampling
- Critical case sampling is a form of purposive sampling that involves selecting cases that are especially important for understanding the research phenomenon.
- This type of sampling focuses on cases that are likely to yield the most significant insights, even if they are few in number.
- Researchers using critical case sampling identify critical cases that are central to understanding the objectives of the research, ensuring that the data collected will be highly relevant to the research question.
- Purposive sampling is to identify these critical cases, as they provide key information that could impact the overall findings or help validate the research hypotheses.
- For example, in mental health services research, a critical case might involve a patient with a unique set of circumstances that offers insights into how mental health interventions work in specific situations.
Expert Sampling: When and How to Use It
- Expert sampling is a type of purposive sampling where participants are selected based on their expertise or specialized knowledge in a particular area.
- This method is used when the researcher needs insight from individuals who have deep knowledge or experience relevant to the research topic.
- Purposive and convenience sampling both rely on the researcher’s ability to select participants, but expert sampling specifically targets individuals with specific, high-level knowledge.
- The objective of expert sampling is to gain perspectives from those who are recognized as experts in the research question and the type of investigation being conducted. This can help enrich the findings and offer a more informed perspective on the subject.
- In some cases, expert sampling is used to gather data from professionals or practitioners in the field, such as in a study on the implementation of new technologies or public health strategies.
- Overall, the types of purposive sampling exist to suit different research needs, with each method offering a distinct way to gather relevant and insightful data. Researchers choose the most appropriate purposive sampling method based on the characteristics relevant to the research and the nature of the research question.
How to Effectively Use Purposive Sampling in Research?
- Purposive sampling is a valuable qualitative sampling method that allows researchers to intentionally select participants who are most relevant to the research question.
- To effectively use purposive sampling, it’s essential to follow a structured approach that aligns with the study’s goals, ensuring targeted and insightful data collection.
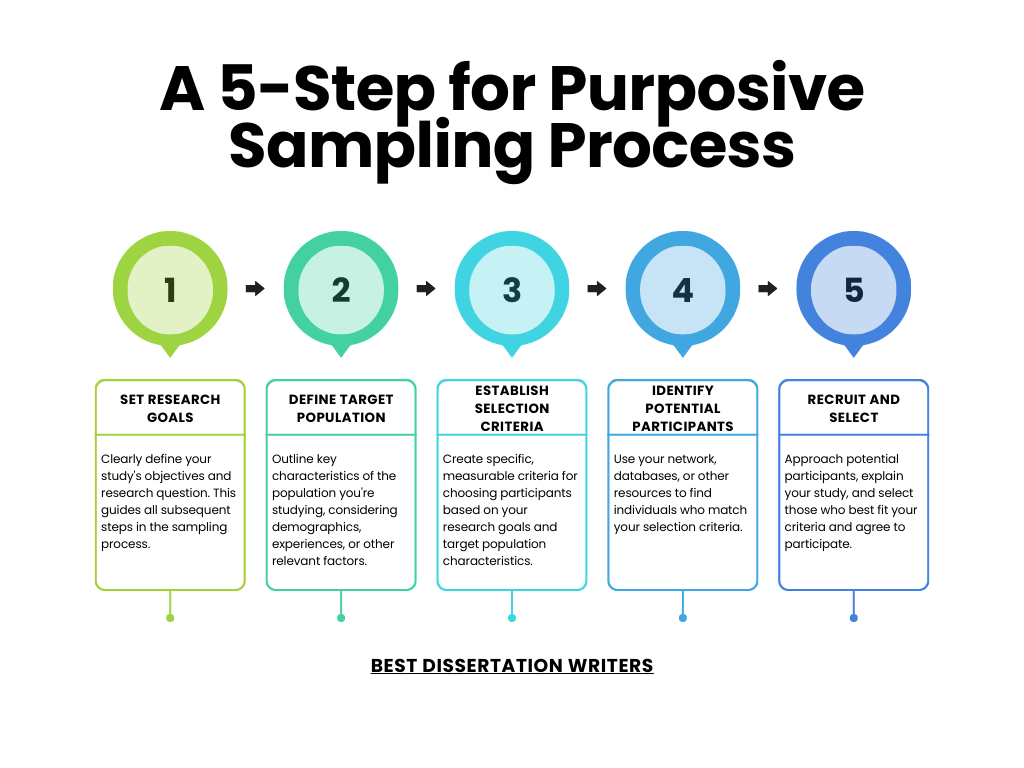
5 Steps for Implementing Purposive Sampling in Qualitative Research
- Step 1: Define the Research Question and Objectives
- The first step in implementing purposive sampling is to clearly define the research question and the specific objectives of the research.
- Understanding the goals of the study helps in selecting participants who have the characteristics relevant to the research. For example, in studies examining politically important cases, participants must have a direct connection to political issues.
- Step 2: Identify the Key Characteristics for Selection
- Determine the characteristics participants must have to provide valuable insights into the research topic.
- For example, homogeneous sampling involves selecting participants with similar attributes or experiences, which helps explore specific issues in-depth within a group.
- Step 3: Select Participants Based on Relevance
- Use purposive sampling to carefully select individuals or groups who meet the predefined criteria, ensuring the data collected is closely aligned with the research objectives.
- Purposive sampling provides a focused approach, helping researchers gather rich, detailed data from participants who are most likely to provide relevant insights.
- Step 4: Collect Data Using Qualitative Methods
- Once the sample is selected, collect qualitative data through interviews, focus groups, or observations.
- Ensure the data collection methods allow participants to share their perspectives on the research question, helping to gain deeper insights into the study’s objectives.
- Step 5: Analyze Data for Relevant Patterns
- Analyze the data with the aim of identifying key themes, patterns, or relationships that address the research question.
- The analysis should focus on understanding the perspectives on the research gathered from the purposively selected sample, using appropriate qualitative analysis techniques.
Research Design Considerations for Purposive Sampling
- Purposive sampling should align with the overall research design. Researchers must ensure that the sampling approach fits the study’s methodology and aims.
- For example, in exploratory research, purposive sampling helps identify specific individuals who have in-depth knowledge of the topic under investigation.
- The research design must also address how purposive sampling integrates with the study’s goals, ensuring that the selected participants provide valuable insights into the research question.
- Also, researchers must consider the sample size for purposive sampling to ensure the data gathered is comprehensive enough to answer the research questions effectively.
Integrating Purposive Sampling with Other Research Methods
- Purposive sampling can be combined with other methods like random sampling or convenience sampling for a more robust research design.
- For example, a purposive sampling approach can be used to select key informants, while random sampling might be used to gather data from a broader population for comparative analysis.
- This sampling strategy allows for triangulation of data, increasing the validity and depth of the findings by incorporating diverse perspectives.
- Sampling politically important cases is one such example where purposive sampling can be combined with other methods to ensure that critical cases are thoroughly investigated while also capturing a broader view.
By following these steps and integrating purposive sampling with other methods, researchers can effectively collect targeted data that addresses their specific research objectives and provides meaningful insights into their study.
Examples of Purposive Sampling in Qualitative Research
- Purposive sampling is a key method in qualitative research, as it allows researchers to select participants who meet specific criteria relevant to the research question. Here are a few examples where purposive sampling is used to gather targeted data that aligns with the study’s goals.
Case Studies Utilizing a Purposive Sample
- In a study exploring mental health services research, purposive sampling may be used to select individuals who have received specific treatments or have unique experiences with mental health services.
- Researchers might target patients who have experienced particular treatments for mental health conditions, ensuring that participants’ insights are directly related to the research question.
- Another example is a case study examining politically important cases. Here, purposive sampling can be used to select experts or individuals who have direct involvement in the political case being studied, offering in-depth perspectives on the issue.
Analyzing the Impact of Sampling Strategies on Research Outcomes
- The effectiveness of purposive sampling depends largely on how well the sample aligns with the research objectives. The sampling approach can significantly influence the outcomes of the research.
- If the research seeks to understand specific experiences or phenomena (such as homogeneous sampling, which focuses on selecting participants with similar characteristics), purposive sampling helps researchers gain targeted insights that might not be achieved through random sampling.
- However, purposive sampling is not without its drawbacks. Since it does not provide a representative sample of the entire population, the findings may lack generalizability. Sampling error can occur if the sample is too narrowly defined, or if the researcher’s judgment is influenced by bias, which can skew the results.
Stress-Free Academic Writing
Make your academic journey smoother with Best Dissertation Writers. Our team offers personalized dissertation and essay writing services, ensuring high-quality work delivered on time. Let us help you achieve your academic success today!
Real-World Applications of Purposeful Sampling Techniques
- Purposive sampling is often used in fields where deep, detailed understanding is crucial, such as healthcare research or education studies. For example:
- In education research, purposive sampling can be applied to select teachers who specialize in certain areas, such as special education, ensuring that the insights gathered are specific to that niche.
- In business research, companies may use purposive sampling to select participants who are decision-makers or key stakeholders, ensuring that the data collected is relevant to the organization’s strategic goals.
- Researchers studying the effects of social interventions might use purposive sampling to identify participants who have directly experienced the intervention, providing data that is both relevant and insightful.
Purposive sampling offers several advantages for qualitative research, particularly in case studies, healthcare, and education. However, it’s important to carefully design the sampling strategy to avoid bias and ensure that the findings are meaningful and relevant to the research question.
