What Is a Thematic Literature Review?
- A thematic literature review is a type of literature review that organises and analyses existing research based on themes or patterns rather than chronological order.
- This review of literature helps synthesise key findings, identify trends, and offer a comprehensive overview of relevant literature across academic papers and journal articles.
- Structuring a thematic review matters because a clear literature review structure enhances coherence, shows understanding of research methodologies, and ensures a logical writing process.
- A well-structured thematic literature review allows scholars to write a literature review that highlights themes within the broader context of a specific research question.

How to Organise and Write a Thematic Literature Review
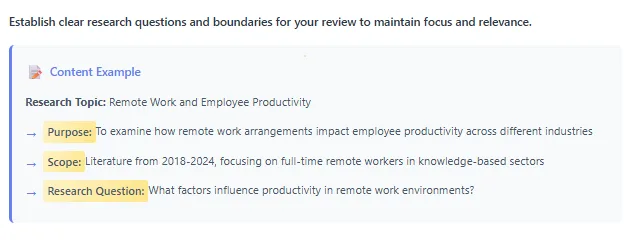
Step 1: Define the Purpose and Scope of Your Literature Review
- Begin by clarifying why you are writing the thematic literature review and what your research question or thesis seeks to address.
- The purpose determines how you structure your literature review, what methodology fits best (qualitative, quantitative, or methodological mix), and what themes or topics are most relevant.
- Provide a comprehensive overview of existing knowledge, highlighting key findings and gaps the literature review might explore.
- Clearly define your research scope—whether your review follows a chronological approach, thematic approach, or a combination for a balanced review of literature.
Step 2: Gather and Analyse Academic Papers Thematically
- Conduct a literature search using databases of published research, academic papers, and journal articles.
- Collect relevant sources that align with your specific research question or research project.
- Reviewing literature requires identifying research methodologies, epistemology, and theoretical approaches used by scholars in the field.
- Group the literature thematically by identifying common themes, trends, or conceptual frameworks.
- Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each research article, noting how each theme or category contributes to existing research.
- Maintain a bibliography or citation list to ensure proper citation style consistency when writing the literature review.

Step 3: Identify Common Themes and Patterns
- The thematic literature review focuses on recognising themes or patterns across diverse sources.
- Identify themes within your relevant literature by comparing key findings and conceptual similarities.
- Use a thematic approach to organise content — for example, group studies by methodology, findings, or theoretical stance.
- Recognising themes or topics helps synthesise information, making your literature review presents a clear way of understanding existing knowledge.
- The review helps connect literature by theme, showing how various pieces together create a cohesive overview of your research area.

Step 4: Structure Your Literature Review Around Themes
- Structure and write your thematic literature review around themes, not authors or publication dates.
- Each theme or category should include:
- Overview of research: Summarise existing literature related to that theme.
- Critical synthesis: Discuss research methodologies, strengths and weaknesses, and gaps.
- Link to research question: Show how the theme informs your specific research.
- This way to organise ensures your literature review reads cohesively and provides a roadmap for the reader.
- Incorporate qualitative insights, chronological background, and methodological diversity to demonstrate depth.
- The structure of your literature review should logically transition between themes or topics for a smooth writing process.

Step 5: Write a Well-Structured and Cohesive Review
- Start with an introduction that outlines the purpose, scope, and structure of your literature review.
- Use headings and subheadings to create a clear way for readers to follow your thematic organisation.
- When writing the literature review, ensure each paragraph focuses on one theme and ends with synthesis—how that theme connects to others.
- Maintain consistent citation style, integrating references to relevant literature accurately.
- Use concise language and ensure your review might offer insights across various research articles and theoretical approaches.
- Keep paragraphs organised around themes, highlighting key findings that support your research project or thesis.

Step 6: Revise, Refine, and Ensure Logical Flow
- After drafting, revise your thematic literature review to enhance logical flow and cohesion.
- Check whether each theme builds towards your research question and aligns with the broader context of your academic research.
- Ensure your review provides a comprehensive overview rather than isolated summaries.
- Edit for clarity, accuracy, and consistency in citation, ensuring every research article is properly referenced.
- Reflect on the epistemology and methodological assumptions guiding your literature review, ensuring they fit your theoretical framework.
- A well-polished thematic literature review demonstrates mastery of the writing process and contributes significantly to your research paper or thesis.

Thematic Literature Review Example
- The thematic literature review example focuses on improving nurse handoff communication to enhance patient safety.
- It demonstrates how to organise literature thematically around four key themes: standardised frameworks, interprofessional collaboration, technology use, and organisational culture.
- The review synthesises existing research to reveal common patterns, strengths and weaknesses, and gaps in current evidence.
- It shows how a structured thematic approach offers a comprehensive overview of relevant literature.
- The example highlights how a well-structured thematic literature review supports evidence-based nursing practice and enhances understanding of communication, teamwork, and safety outcomes.
Topic: Enhancing Nursing Handoff Communication and Patient Safety through Structured Approaches
Introduction
Effective communication during nursing handoff is fundamental to ensuring continuity of care and patient safety. Miscommunication between shifts often results in adverse events such as medication errors, falls, and pressure injuries. A thematic literature review provides a comprehensive overview of existing research examining interventions that improve the quality, safety, and consistency of nurse handoff communication. This review identifies three major themes: (1) structured communication frameworks and team training, (2) barriers and facilitators influencing handover quality, and (3) the relationship between safety attitudes and clinical outcomes. Organising the literature thematically allows for a cohesive synthesis of diverse findings across contexts and methodologies.
Theme 1: Structured Communication Frameworks and Team Training
A consistent theme across the literature is the effectiveness of structured communication frameworks and interprofessional team training in reducing miscommunication. Neville, Miltner, and Shirey (2021) conducted a quasi-experimental study that implemented clinical team training combined with a structured handoff tool. Their intervention significantly improved teamwork scores and reduced communication breakdowns during patient transfers. This study underscores those effective handoffs rely not only on information exchange but also on shared situational awareness within the clinical team.
Similarly, Hada and Coyer (2021) provided evidence through an integrative review that structured, standardised handover tools—such as SBAR (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation)—contribute to measurable improvements in patient outcomes, including decreased fall rates and fewer medication administration errors. The authors identified that embedding structured communication tools into routine nursing practice creates a consistent framework that reduces ambiguity and cognitive load during information transfer.
Desmedt et al. (2021) reinforced this finding through a systematic review of systematic reviews, which revealed that structured handoff protocols consistently enhance information completeness, timeliness, and comprehension. Their meta-synthesis of multiple healthcare disciplines showed that standardisation promotes accountability and decreases omission of critical data. Collectively, these studies emphasise that structured communication, supported by team-based education, provides a foundation for safe and reliable handoffs across healthcare settings.
Theme 2: Barriers and Facilitators Influencing Handover Quality
The second theme focuses on the contextual and interpersonal factors that shape the quality of nursing handovers. Pun (2021) explored factors associated with nurses’ perceptions of handover quality in Hong Kong, finding that effective communication skills and environmental support were strong predictors of high-quality handovers. The study revealed that overcrowded wards, time pressure, and inconsistent information flow were common barriers to effective shift transitions. Importantly, nurses with formal communication training reported greater confidence and perceived clarity in their handoffs.
Desmedt et al. (2021) also noted that organisational culture and workflow interruptions frequently compromise handover quality. The presence of hierarchical barriers can deter junior nurses from seeking clarification, leading to fragmented information exchange. Meanwhile, Hada and Coyer (2021) highlighted that engagement from leadership and continuous audit feedback are crucial facilitators for sustaining high-quality handover practices.
From a broader safety perspective, Afaya, Konlan, and Kim (2021) investigated barriers to reporting medication administration errors among nurses. While not limited to handoffs, their findings reflect systemic communication challenges within nursing teams. Fear of blame, inadequate reporting systems, and lack of organisational transparency discourage open dialogue about safety incidents. Addressing these cultural barriers is therefore integral to improving the quality of both communication and patient outcomes during shift transitions. This theme demonstrates that even well-designed communication frameworks may fail without supportive environmental and cultural conditions. Sustainable improvement requires combining standardised tools with a psychologically safe environment that values continuous learning and transparent reporting.
Theme 3: Safety Attitudes and Patient Outcomes
The final theme emerging from the literature concerns the relationship between nurses’ safety attitudes and measurable patient outcomes. Alanazi, Sim, and Lapkin (2022) conducted a systematic review that synthesised evidence linking nurses’ perceptions of safety culture to rates of adverse events in acute-care hospitals. Their analysis showed that positive safety attitudes correlated strongly with reduced patient harm, lower mortality rates, and enhanced staff wellbeing. Nurses who felt empowered to communicate concerns during handoff were more likely to prevent near misses and errors.
These findings align closely with those of Neville et al. (2021), who observed that team training not only improved communication skills but also fostered mutual trust and accountability among nurses. A robust safety culture therefore acts as a catalyst that enhances the effectiveness of structured handoff systems. In parallel, Afaya et al. (2021) highlighted that promoting open discussion about medication errors contributes to a positive safety climate. When nurses are encouraged to disclose mistakes without fear of reprisal, teams can identify systemic weaknesses and improve future handoffs. Collectively, these studies show that improving handover communication cannot be isolated from broader safety attitudes within the clinical environment. Enhancing teamwork, transparency, and mutual respect ultimately leads to better patient outcomes.
Thematic Synthesis and Implications
Synthesising these themes within a thematic literature review illustrates that structured frameworks, supportive culture, and positive safety attitudes are mutually reinforcing components of effective handoff communication. Structured tools such as SBAR provide the necessary scaffolding, but successful implementation depends on team competence and organisational readiness. Barriers such as time constraints, poor leadership, and blame culture can erode these benefits, highlighting the need for multi-level interventions that address both system design and human behaviour.
Moreover, the literature suggests that sustainability requires integrating education and reflective practice into daily workflow. Continuous training helps maintain communication competence, while data feedback from audits encourages adherence to structured protocols. The review helps demonstrate that improving handoff communication is not a single intervention but an evolving process shaped by teamwork, leadership, and safety culture. From a methodological standpoint, most included studies employed integrative and systematic review methodologies, combining both qualitative and quantitative data. This enhances the comprehensive overview of evidence while identifying research gaps, such as the limited exploration of digital communication tools and cross-cultural differences in handover practices.
Conclusion
This thematic literature review demonstrates that improving nurse handoff communication requires an integrated and multifaceted approach. Structured communication frameworks enhance clarity and reduce errors, while team training strengthens collaboration and mutual understanding among healthcare professionals. However, successful implementation depends on addressing barriers such as time constraints, inconsistent practices, and organisational culture. Promoting a positive safety climate encourages open communication, accountability, and continuous learning, which are essential for sustaining effective handover practices.
References
- Afaya, A., Konlan, K. D., & Kim Do, H. (2021). Improving patient safety through identifying barriers to reporting medication administration errors among nurses: an integrative review. BMC health services research, 21(1), 1156-1164. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12913-021-07187-5
- Alanazi, F. K., Sim, J., & Lapkin, S. (2022). Systematic review: Nurses’ safety attitudes and their impact on patient outcomes in acute‐care hospitals. Nursing open, 9(1), 30-43. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/nop2.1063
- Desmedt, M., Ulenaers, D., Grosemans, J., Hellings, J., & Bergs, J. (2021). Clinical handover and handoff in healthcare: a systematic review of systematic reviews. International Journal for Quality in Health Care, 33(1), 170-182. https://academic.oup.com/intqhc/article-abstract/33/1/mzaa170/6039082
- Hada, A., & Coyer, F. (2021). Shift‐to‐shift nursing handover interventions associated with improved inpatient outcomes—Falls, pressure injuries and medication administration errors: An integrative review. Nursing & health sciences, 23(2), 337-351. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/nhs.12825
- Neville, B., Miltner, R. S., & Shirey, M. R. (2021). Clinical team training and a structured handoff tool to improve teamwork, communication, and patient safety. The Journal for Healthcare Quality (JHQ), 43(6), 365-373. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34734920/
- Pun, J. (2021). Factors associated with nurses’ perceptions, their communication skills and the quality of clinical handover in the Hong Kong context. BMC nursing, 20(1), 95-99. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12912-021-00624-0
Tips to Structure and Write a High-Quality Literature Review
- Use a thematic approach to structure your literature review for clarity and depth.
- Synthesize relevant literature rather than summarising it.
- Combine qualitative insights and chronological context to provide a comprehensive overview.
- Maintain consistent citation style and list all relevant sources in your bibliography.
- Ensure your thematic literature review is well-structured, logically ordered, and connected to your research question.
- Always organise the content thematically for greater cohesion and academic credibility.
Common Mistakes When Writing the Literature Review
- Listing studies chronologically instead of organising them thematically.
- Failing to synthesise and merely summarising existing research.
- Ignoring methodological differences and research methodologies in the literature available.
- Weak structure or unclear themes within the review of literature.
- Using inconsistent citation style or omitting relevant literature.
- Neglecting the broader context, which makes the review might lack depth.
- A poor structure and write process prevents readers from seeing the connections across themes or topics in your thematic literature review.
Final Thoughts on Writing a Thematic Literature Review
- A thematic literature review offers a clear way to connect existing research and identify themes across diverse sources.
- When you structure and write with purpose, your review provides a comprehensive overview of academic research within the broader context of your research question.
- This beginner’s guide helps you write a thematic literature review that is well-structured, methodologically sound, and academically compelling.
- By following these ways to structure your literature, you create a review helps readers navigate themes or patterns in a concise, organised, and cohesive manner.
Why Choose Our Dissertation Experts
- Experienced academic writing experts
- 100% original, plagiarism-free content
- Timely delivery with quality assurance
Why Choose Our Review Specialists
- Comprehensive database research
- Accurate synthesis of key evidence
- Structured, academically compliant reviews
FAQs About Thematic Literature Reviews
What are examples of themes in a literature review?
Examples of themes in a thematic literature review include leadership styles in nursing, technology adoption in healthcare, mental health interventions, and communication in multidisciplinary teams. A literature review organised thematically helps identify patterns, gaps, and relationships across studies, offering a clear and structured understanding of the relevant literature within a specific research area.
What is the difference between chronological and thematic literature review?
A chronological literature review organises studies by publication date, showing how research evolves over time, while a thematic literature review groups findings around common themes or topics. The thematic approach provides deeper analysis by connecting ideas across periods, making it ideal for identifying trends, gaps, and theoretical developments within the review of literature.
What is meant by thematic review?
A thematic review is a type of literature review that organises and analyses research articles based on recurring themes or concepts rather than time sequence. This method allows researchers to synthesise findings, highlight common themes, and develop a comprehensive overview of existing knowledge within a specific topic, improving the overall structure of the literature review.
What is an example of thematic approach?
An example of a thematic approach is organising a literature review on patient safety into themes such as communication errors, teamwork, and technology-based interventions. Instead of listing studies chronologically, the review is structured thematically to connect related ideas and synthesise research effectively, offering a more cohesive understanding of trends and insights across the relevant literature.
Read More About Thematic Literature Review and Analysis
Discover how to structure your research effectively with our example of thematic literature review and explore a detailed thematic literature review sample to understand the key elements of a high-quality review. Learn how to organise your paper step by step using our thematic literature review outline and check out a practical thematic literature review example to see how themes connect across studies. Understand how researchers identify key patterns with our guide on thematic content analysis and explore the connection between theme in qualitative content analysis and thematic analysis for deeper research insights. See how technology enhances research accuracy in our guide on AI thematic analysis, view a real thematic analysis example to learn how to code and interpret qualitative data effectively, and compare methods in our comprehensive breakdown of content analysis vs thematic analysis to choose the right approach for your study.
