What is Quantitative Research?
Definition of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a systematic approach to investigating phenomena by gathering numerical data that can be analyzed using statistical methods. This type of research design is crucial in various fields, including social sciences, natural sciences, and business. When exploring the types of quantitative research designs, it’s essential to understand that these approaches aim to answer research questions, test hypotheses, and establish relationships among variables through objective measurements and analyses.
The primary goal of quantitative research is to generalize findings from a sample to a larger population, making it a powerful tool for researchers seeking to draw broad conclusions. Unlike qualitative research, which focuses on descriptive data, quantitative research methods rely heavily on numerical data and statistical analysis to draw conclusions. As we delve deeper into the types of quantitative research designs, we’ll see how each approach contributes to this overarching methodology.
Struggling with dissertation statistics? Best Dissertation Writers offers specialized statistical analysis help! Our expert statisticians will guide you through complex data analysis, ensuring accurate results and clear interpretations. Don’t let numbers hold you back—click now for professional statistical support!
Importance of Quantitative Research in Social Sciences
The importance of quantitative research in social sciences cannot be overstated, particularly when considering the various types of quantitative research designs available to researchers.
- These research methods provide a structured way to collect and analyze data, allowing social scientists to test theories, identify patterns, and make predictions about human behavior and social phenomena.
- By employing different types of quantitative research designs, researchers can address complex social issues with a degree of objectivity and precision that qualitative methods alone may not achieve. For instance, experimental designs in quantitative research enable the investigation of cause-and-effect relationships, while correlational designs help uncover associations between variables.
- The ability to generalize findings from a sample to a larger population makes quantitative research particularly valuable in informing policy decisions and social interventions.
- Moreover, the replicability of quantitative studies enhances the reliability and validity of research findings, contributing to the cumulative nature of scientific knowledge in social sciences.
Key Characteristics of Quantitative Research
When examining the types of quantitative research designs, it’s crucial to understand the key characteristics that define this approach to research.
- Quantitative research is distinguished by its focus on numerical data, statistical analysis, and the use of structured research methods. One of the primary features of quantitative research designs is their emphasis on objectivity and the ability to test hypotheses. Researchers using these methods aim to minimize bias and produce results that can be replicated by other scientists.
- Another essential characteristic of the various types of quantitative research designs is their reliance on large sample sizes. This aspect allows for greater generalizability of findings to broader populations. The research process in quantitative studies typically follows a linear path, starting with a research question or hypothesis, followed by data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Validity and reliability are crucial concepts in all types of quantitative research designs. Validity ensures that the research measures what it intends to measure, while reliability refers to the consistency of results over time. These factors contribute to the robustness of quantitative research methods.
- Furthermore, quantitative research often involves the use of standardized instruments, such as surveys or questionnaires, to gather data. This standardization allows for comparisons across different studies and facilitates the accumulation of knowledge in a particular field.
As we explore the specific types of quantitative research designs, we’ll see how these characteristics manifest in various approaches to conducting research.
What are the Types of Quantitative Research Designs?
Overview of the 4 Types of Quantitative Research
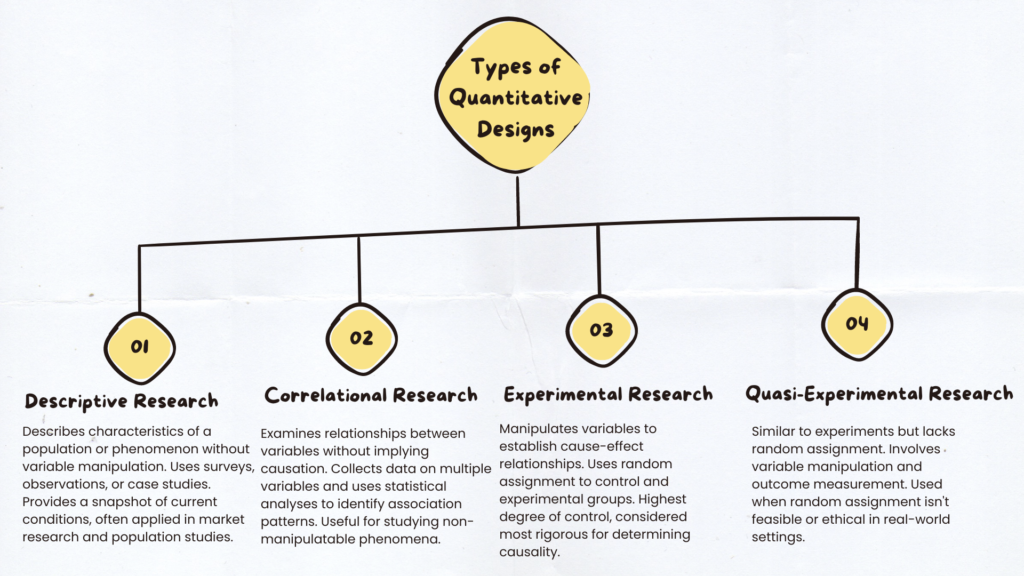
When discussing the types of quantitative research designs, it’s important to recognize that there are four main categories: descriptive, correlational, experimental, and quasi-experimental. Each of these types of quantitative research designs serves a specific purpose and is suited to different research questions and objectives.
- Descriptive research designs aim to describe characteristics of a population or phenomenon without manipulating variables.
- Correlational research seeks to identify relationships between variables without implying causation.
- Experimental research, considered the gold standard among the types of quantitative research designs, involves manipulating variables to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- Quasi-experimental designs share similarities with true experiments but lack random assignment of participants to groups.
Understanding these different types of quantitative research designs is crucial for researchers to choose the most appropriate method for their study. Each design has its strengths and limitations, and the choice depends on the research question, available resources, and ethical considerations. As we delve deeper into each of these types of quantitative research designs, we’ll explore their unique features and applications.
Differences Between Descriptive and Correlational Research
When comparing types of quantitative research designs, it’s essential to understand the distinctions between descriptive and correlational approaches. Descriptive research aims to accurately describe a phenomenon without manipulating variables, often using surveys or observational methods. It’s frequently used in market research and population studies.
Correlational research, on the other hand, examines relationships between variables without implying causation. While both are non-experimental types of quantitative research designs, correlational studies go a step further by analyzing associations between variables. However, neither can establish causality, which is a key limitation of these types of quantitative research designs compared to experimental methods.
Experimental vs. Quasi-Experimental Research Designs
Among the types of quantitative research designs, experimental and quasi-experimental approaches are often compared due to their similarity in structure. Experimental designs, considered the most rigorous of the types of quantitative research designs, involve random assignment of participants to control and experimental groups, allowing researchers to establish causality.
Quasi-experimental designs, while similar, lack this random assignment. This key difference affects the internal validity of the research. Both types of quantitative research designs involve manipulating variables and measuring outcomes, but quasi-experimental designs are often used when random assignment is not feasible or ethical, making them valuable alternatives in certain research contexts.
Affordable Dissertation Writing Help
Feeling overwhelmed by your dissertation? Best Dissertation Writers is here to help! Our experienced writers will assist you at every stage, from proposal to final draft. Don’t delay your graduation—contact us today and take the first step towards completion!
What is Descriptive Research Design?
Definition of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design is one of the fundamental types of quantitative research designs used to describe characteristics of a population or phenomenon. This approach aims to answer “what” questions rather than “why” or “how” questions. Among the types of quantitative research designs, descriptive research is used to provide a snapshot of the current state of affairs. It involves collecting data through various methods such as surveys, observations, or case studies. Unlike other types of quantitative research designs, descriptive research does not manipulate variables or establish causality. Instead, it focuses on accurately depicting the subject of study, making it a valuable tool for initial explorations of research topics.
Characteristics of Descriptive Research
When examining the types of quantitative research designs, descriptive research stands out for its unique characteristics.
- Unlike other types of quantitative research designs, descriptive studies do not test hypotheses or manipulate variables. Instead, they aim to provide a comprehensive, accurate description of a phenomenon or population.
- One key feature of this type of quantitative research design is its flexibility in data collection methods. Researchers may use surveys, questionnaires, or observational techniques to gather information. Another characteristic is the potential for both quantitative and qualitative data collection, although the analysis typically involves quantitative methods.
- Descriptive research often serves as a foundation for other types of quantitative research designs. It can generate hypotheses for future studies and provide valuable insights into research problems.
However, like all types of quantitative research designs, it has limitations. Descriptive research cannot establish causality or explain why phenomena occur, which is important to consider when choosing among the various types of quantitative research designs for a study.
Applications of Descriptive Research in Market Research
Among the various types of quantitative research designs, descriptive research finds extensive application in market research. This type of quantitative research design is particularly useful for understanding consumer behavior, market trends, and product performance.
In market research, descriptive studies often involve surveys to gather data on customer preferences, buying habits, or satisfaction levels. For example, a company might use this type of quantitative research design to describe the demographic characteristics of its target market or to measure brand awareness.
Descriptive research in market research can also involve observational methods. For instance, researchers might observe and record customer behavior in a retail setting. This application of descriptive research design provides valuable insights that can inform marketing strategies and product development.
While other types of quantitative research designs might be used to test specific hypotheses about market behavior, descriptive research offers a broad overview that can guide further, more focused studies. Its ability to provide a comprehensive picture of market conditions makes it an essential tool in the repertoire of market researchers.
Limitations of Descriptive Research
While descriptive research is valuable among the types of quantitative research designs, it has notable limitations.
- Unlike other types of quantitative research designs, descriptive studies cannot establish causality or explain why phenomena occur.
- They provide a snapshot of a situation but cannot predict future outcomes or changes over time.
- Additionally, this type of quantitative research design may be subject to respondent bias, especially when using self-reported data.
- Descriptive research also lacks the control over variables that experimental types of quantitative research designs offer.
Despite these limitations, when used appropriately and in conjunction with other types of quantitative research designs, descriptive research remains a crucial tool in the researcher’s arsenal.
What is Correlational Research?
Understanding Correlational Research Design
Correlational research design is one of the key types of quantitative research designs used to explore relationships between variables without manipulating them. Unlike experimental types of quantitative research designs, correlational studies do not attempt to establish causality. Instead, this type of quantitative research design aims to determine the strength and direction of associations between two or more variables.
Researchers using correlational designs collect data on multiple variables and use statistical analyses to identify patterns of relationship. While it’s less controlled than some other types of quantitative research designs, correlational research is valuable for studying phenomena that cannot be experimentally manipulated and for generating hypotheses for future experimental studies.
Applications and Examples of Correlational Research
Correlational research, as one of the types of quantitative research designs, finds applications across various fields. In psychology, for example, this type of quantitative research design might be used to study the relationship between stress levels and academic performance. In economics, researchers might use correlational designs to examine the association between education levels and income.
- An example of correlational research in health sciences could involve studying the relationship between exercise frequency and blood pressure. Unlike experimental types of quantitative research designs, the researcher wouldn’t manipulate exercise levels but would collect data on both variables from a sample of participants.
- In business, this type of quantitative research design might be applied to explore the correlation between employee satisfaction and productivity. While other types of quantitative research designs might be needed to establish causality, correlational studies can provide valuable insights into potential relationships between variables.
It’s important to note that while correlational research is one of the types of quantitative research designs that can identify relationships, it cannot determine cause and effect. This limitation distinguishes it from experimental types of quantitative research designs.
Correlation vs. Causation in Research
When discussing types of quantitative research designs, it’s crucial to understand the distinction between correlation and causation. Correlational research, one of the types of quantitative research designs, identifies relationships between variables but cannot establish causality. For instance, a correlation between ice cream sales and crime rates doesn’t mean one causes the other. In contrast, experimental types of quantitative research designs can establish causation by manipulating variables and controlling for confounding factors.
This key difference highlights why researchers must choose appropriate types of quantitative research designs based on their research questions. While correlation can suggest possible causal relationships, only certain types of quantitative research designs, particularly experimental ones, can confirm causation.
Ready to excel in your dissertation? Let Best Dissertation Writers guide you to success! Our expert team will help you craft a compelling, well-researched thesis that stands out. Don’t struggle alone—click now to start your journey towards academic excellence!
How to Conduct Experimental Research?
Steps in Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design, one of the most rigorous types of quantitative research designs, follows a structured process. The first step in this type of quantitative research design is formulating a hypothesis. Next, researchers identify and define variables – independent, dependent, and control. They then design the experiment, ensuring random assignment of participants to groups.
Data collection follows, often using standardized measures. Finally, researchers analyze the data using statistical methods to test the hypothesis. Unlike other types of quantitative research designs, experimental research allows for the manipulation of variables and establishment of causality. This systematic approach distinguishes experimental designs from other types of quantitative research designs and contributes to their high internal validity.
Understanding Variables in Experimental Research
- In experimental research, one of the key types of quantitative research designs, understanding variables is crucial. Unlike some other types of quantitative research designs, experimental studies involve manipulating variables to observe their effects.
- The independent variable is the factor that researchers manipulate in an experiment. For example, in a study on the effect of study time on test scores, study time would be the independent variable. The dependent variable is what researchers measure to see the effect of the independent variable. In this case, test scores would be the dependent variable.
- Control variables are factors that researchers keep constant across all conditions to ensure they don’t influence the results. This level of control is a defining feature of experimental types of quantitative research designs.
- Understanding these variables and their relationships is essential for designing and interpreting experimental studies. It’s this precise control and manipulation of variables that sets experimental designs apart from other types of quantitative research designs and allows researchers to establish causality.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Experimental Research
Experimental research, among the various types of quantitative research designs, offers several benefits.
- One of the main advantages of this type of quantitative research design is its ability to establish causality. By manipulating variables and controlling for confounding factors, experiments can demonstrate cause-and-effect relationships more conclusively than other types of quantitative research designs.
- Another benefit is the high internal validity of experimental studies. The controlled environment minimizes the influence of extraneous variables, ensuring that observed effects are due to the manipulated variable.
However, like all types of quantitative research designs, experimental research has drawbacks.
- One limitation is potentially low external validity. The controlled setting may not reflect real-world conditions, making it challenging to generalize findings.
- Ethical considerations can also limit the applicability of experimental designs. Some variables cannot be manipulated for ethical reasons, restricting the use of this type of quantitative research design in certain contexts.
Despite these limitations, experimental research remains one of the most powerful types of quantitative research designs for establishing causal relationships and testing hypotheses.
How is Data Collected in Quantitative Research?
Common Data Collection Methods
Data collection is a crucial aspect of all types of quantitative research designs. The methods used can vary depending on the specific type of quantitative research design employed.
- Surveys and questionnaires are commonly used across various types of quantitative research designs. They allow researchers to collect large amounts of data efficiently. In experimental types of quantitative research designs, standardized tests or measurements are often used to gather data on dependent variables.
- Observational methods can be employed in descriptive or correlational types of quantitative research designs. These might involve structured observation protocols to ensure consistency in data collection.
- Some types of quantitative research designs may utilize existing databases or secondary data sources. This approach is common in large-scale studies or when primary data collection is not feasible.
Regardless of the type of quantitative research design, it’s crucial that data collection methods are reliable, valid, and appropriate for the research question. The choice of data collection method can significantly impact the quality and generalizability of results across different types of quantitative research designs.
Surveys as a Tool for Data Collection
Surveys are a versatile tool used across various types of quantitative research designs. In descriptive research, one of the common types of quantitative research designs, surveys can provide a snapshot of population characteristics. For correlational studies, another type of quantitative research design, surveys can collect data on multiple variables to examine relationships.
Even in experimental types of quantitative research designs, surveys might be used to gather additional data about participants. The flexibility of surveys makes them adaptable to different research needs. However, researchers must be aware of potential biases in survey data. Regardless of the type of quantitative research design, ensuring survey validity and reliability is crucial. When properly designed and implemented, surveys can be a powerful data collection method across different types of quantitative research designs.
Choosing the Right Data Collection Method
Selecting the appropriate data collection method is crucial across all types of quantitative research designs. The choice depends on several factors, including the research question, the type of quantitative research design being used, and practical considerations like time and resources.
- For descriptive types of quantitative research designs, surveys or observational methods might be most appropriate. Correlational designs might use surveys or existing databases to collect data on multiple variables.
- Experimental types of quantitative research designs often require more controlled data collection methods, such as standardized tests or measurements. These methods allow for precise quantification of the dependent variable.
- Researchers must also consider the reliability and validity of the data collection method. Different types of quantitative research designs may require different levels of measurement precision.
- Practical factors like sample size, budget, and time constraints also influence the choice of data collection method. For instance, online surveys might be chosen for large-scale studies across various types of quantitative research designs due to their efficiency.
- Ultimately, the goal is to choose a method that aligns with the research objectives and the specific type of quantitative research design being employed.
How to Choose the Right Quantitative Research Design?
Factors to Consider in Choosing a Research Design
Selecting the appropriate type of quantitative research design is a critical decision in any research project. Several factors influence this choice:
- Research Question: The nature of the research question often dictates which of the several types of quantitative research designs is most suitable. For example, a question seeking to test a hypothesis might require an experimental design.
- Variables: The ability to manipulate variables or randomly assign participants influences whether a true experimental design is feasible.
- Resources: Time, budget, and available tools can impact the choice between different quantitative research design types.
- Ethical Considerations: Some research questions may not be ethically investigated using certain types of designs, e.g., randomly assigning participants to harmful conditions.
- Desired Outcomes: Whether the research is used to understand correlations or establish causality affects the design choice.
- Existing Knowledge: The current state of research in the field can guide whether a descriptive, correlational, or experimental approach is most appropriate.
Understanding these factors helps researchers choose the most suitable design for their quantitative research study.
Aligning Research Questions with Research Designs
In quantitative and qualitative research, aligning research questions with appropriate designs is crucial. For quantitative research, this alignment ensures that the chosen method can effectively answer the research question and collect quantitative data that will yield meaningful results.
Different types of research questions necessitate different approaches. For instance:
- Descriptive questions (e.g., “What is the current state of…?”) often align with descriptive research designs.
Questions about relationships between variables (e.g., “Is there a correlation between…?”) typically require correlational designs.
Questions seeking to establish cause-and-effect relationships (e.g., “What is the effect of… on…?”) usually demand experimental or quasi-experimental designs. - Research guides at universities often emphasize this alignment, highlighting how the research method used should directly address the research question. By carefully matching questions to designs, researchers can ensure their study’s validity and reliability. This alignment is a fundamental step in how to conduct quantitative research effectively.
Combining Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches
In modern research, combining qualitative and quantitative research approaches has become increasingly common. This mixed-methods approach allows researchers to harness the strengths of both qualitative and quantitative research methodologies, providing a more comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena.
Quantitative research design types offer statistical rigor and generalizability, while qualitative methods provide depth and context. For example, a research project might use surveys to collect quantitative data on a large scale, followed by in-depth interviews to explore the reasons behind the patterns observed in the survey data.
This combination can be particularly useful when:
- Initial quantitative findings raise new questions that qualitative methods can explore
- Qualitative research is used to generate hypotheses that quantitative studies can then test
- Complex research questions require both breadth and depth of understanding
While quantitative approaches focus on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative types of research can provide rich, descriptive data that necessarily reflect the nuanced experiences of participants. By integrating both, researchers can develop a more holistic view of their subject matter.
Time is running out on your dissertation deadline! Don’t panic—Best Dissertation Writers is here to help. Our efficient, high-quality writing services will get you back on track. Don’t risk your academic future—reach out now and let us turn your stress into success!
Conclusion: The Power and Limitations of Quantitative Research Designs
As we’ve explored the various types of quantitative research designs, it’s clear that these methods play a crucial role in advancing our understanding across numerous fields. From descriptive studies that paint a picture of current conditions to experimental designs that establish causality, each type of quantitative research offers unique strengths.
Quantitative research is often used to understand large-scale trends, test hypotheses, and generate statistically significant findings that can be generalized to broader populations. The ability to conduct quantitative research and analyze data using descriptive statistics and more advanced techniques allows researchers to uncover patterns and relationships that might not be apparent through casual observation.
However, it’s important to recognize that quantitative research design types also have limitations. They may not capture the full complexity of human experiences or the nuanced contexts in which phenomena occur. Additionally, correlational research cannot establish causation, a limitation that researchers must always keep in mind when interpreting results.
To address these limitations, many researchers opt for mixed-methods approaches, combining qualitative and quantitative methodologies. This integration allows for a more comprehensive exploration of research questions, leveraging the strengths of both approaches.
As research evolves, new methods to choose from and innovative ways to collect quantitative data continue to emerge. From online surveys to big data analysis, the toolkit available to quantitative researchers is expanding, opening up new possibilities for investigation.
Understanding the types of quantitative research designs is essential for anyone engaged in or evaluating research. Whether you’re a student navigating research guides at university, a professional conducting a research project, or simply a critical consumer of research findings, recognizing the strengths, limitations, and appropriate applications of different quantitative approaches is key. By thoughtfully selecting and implementing these designs, researchers can continue to push the boundaries of knowledge and answer new research questions across diverse fields of study.
FAQs about Types of Quantitative Research Designs
What are the 4 types of quantitative research design?
The four main types of quantitative research design are descriptive, correlational, experimental, and quasi-experimental. Descriptive research involves collecting data to describe characteristics of a population or phenomenon. Correlational research examines relationships between variables without manipulation. Experimental research design for quantitative studies involves manipulating variables and using a control group to establish causality. Quasi-experimental research is similar to experimental but lacks random assignment. Each research type serves different purposes in quantitative studies, e.g., descriptive for surveys, experimental for testing hypotheses.
What are the 5 quantitative research designs?
The five quantitative research designs commonly recognized are descriptive, correlational, experimental, quasi-experimental, and causal-comparative. Descriptive research involves observing and describing a phenomenon. Correlational research examines relationships between variables. Experimental research design for quantitative studies manipulates variables and uses a control group. Quasi-experimental lacks random assignment but still manipulates variables. Causal-comparative research involves comparing groups to understand cause-effect relationships. Each type serves different research purposes and involves specific methods to collect and analyze research data, e.g., surveys for descriptive studies or controlled experiments for experimental research.
What are the seven 7 types of quantitative research?
The seven types of quantitative research include descriptive, correlational, experimental, quasi-experimental, causal-comparative, survey, and longitudinal. Descriptive research describes phenomena. Correlational examines relationships between variables. Experimental research design for quantitative studies uses control groups and manipulation. Quasi-experimental lacks random assignment. Causal-comparative compares groups. Survey research involves large-scale data collection. Longitudinal studies observe changes over time. Each type involves specific methods to collect research data and serves different purposes, e.g., surveys for public opinion or experiments for testing hypotheses. These designs contrast with types of qualitative research in their approach and data analysis methods.
What are the 10 types of quantitative research with examples?
The ten types of quantitative research include: 1) Descriptive (e.g., population surveys), 2) Correlational (e.g., studying relationship between stress and academic performance), 3) Experimental (e.g., drug trials with control group), 4) Quasi-experimental (e.g., comparing teaching methods in existing classes), 5) Causal-comparative (e.g., comparing smokers vs non-smokers), 6) Survey (e.g., customer satisfaction studies), 7) Longitudinal (e.g., tracking health over decades), 8) Cross-sectional (e.g., comparing age groups), 9) Cohort (e.g., following a group of people born in the same year), and 10) Case-control (e.g., comparing disease cases with healthy controls). Each research type involves specific methods to collect and analyze research data.
