Introduction
A systematic literature review (SLR) is a comprehensive and structured way to identify, evaluate, and synthesize existing research relevant to a particular research question or topic.
Conducting a systematic literature review holds several key importance across various fields and disciplines:
- Identification of Knowledge Gaps: Systematic literature reviews help identify gaps in current knowledge by synthesizing existing research. By systematically gathering and analyzing relevant studies, researchers can identify areas where further research is needed.
- Evidence-Based Decision Making: Systematic reviews provide a comprehensive summary of the available evidence on a particular topic or research question. Policymakers, practitioners, and other stakeholders can use this synthesized evidence to make informed decisions and develop evidence-based policies, guidelines, and interventions.
- Reducing Bias: The systematic approach to searching, selecting, and synthesizing literature minimizes bias in the review process. By using predefined criteria for study inclusion and transparent methods for data extraction and analysis, systematic reviews aim to reduce the risk of bias and enhance the reliability of the findings.
- Maximizing Efficiency: Systematic reviews help researchers avoid duplicating efforts by identifying and synthesizing existing research. By summarizing the current state of knowledge on a topic, systematic reviews enable researchers to build upon existing evidence and focus their efforts on areas where further research is warranted.
- Synthesizing Heterogeneous Evidence: Systematic reviews can synthesize evidence from diverse sources, including primary research studies, grey literature, and expert opinions. By synthesizing evidence from different types of studies and sources, systematic reviews provide a more comprehensive understanding of a topic than individual studies alone.
- Quality Assessment: Systematic reviews often include an assessment of the quality of included studies, such as risk of bias assessment or evaluation of study methodology. This helps readers evaluate the strength of the evidence and the reliability of the findings.
- Informing Research Priorities: Systematic reviews can help inform research priorities by identifying areas where further research is needed or where existing evidence is insufficient or conflicting. Researchers, funders, and policymakers can use the findings of systematic reviews to prioritize research efforts and allocate resources effectively.
Unlock your academic potential and secure top grades effortlessly by placing your order with our trusted dissertation and thesis writers who are dedicated to crafting impeccable research papers tailored to your requirements.
At Best Dissertation Writers, we have a list of competent and dedicated writers to help you with all your dissertation writing needs, including the systematic literature review.
A systematic literature review follows a structured organization comprising introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion sections.
Here is a typical structure and template for conducting a systematic literature review:
Chapter 1: Introduction
Research Background
In the background information section of a systematic literature review, you should include:
- Contextual information about the research topic or problem.
- Brief overview of the importance and relevance of the topic.
- Explanation of why the review is necessary.
- Description of any existing theories or frameworks relevant to the topic.
- Identification of any key concepts or terms relevant to the review.
- Overview of previous research or literature related to the topic.
- Discussion of any controversies or debates in the literature.
Research Problem/Problem statement
In the research problem/problem statement section of a systematic literature review, you should include:
- Clear statement of the research problem
- Explanation of why the research problem is important or relevant.
- Description of any gaps or deficiencies in current knowledge.
- Identification of the scope and boundaries of the review.
- Justification for conducting a systematic literature review to address the research problem.
- Explanation of how the review will contribute to the existing literature or fill gaps in knowledge.
Purpose and Significance of the Review
In this section, you should include the follow:
- Statement of the overall purpose or objective of the review.
- Explanation of why the topic is important or relevant.
- Identification of the specific research questions or objectives addressed by the review.
- Justification for conducting a systematic literature review rather than a traditional narrative review.
- Description of the potential contributions of the review to the field or literature.
- Explanation of how the findings of the review may inform practice, policy, or future research.
- Discussion of any gaps or deficiencies in current knowledge that the review aims to address.
- Statement of the significance of the review in advancing understanding or knowledge in the field.
Research aim
When writing the research aim for your systematic literature review, it’s important to clearly and concisely articulate the primary objective or purpose of your study. You can find more details on how to formulate your research aim here.
Research Questions
When writing research questions for a systematic literature review, it’s important to consider several key points to ensure they are well-formulated and appropriate for guiding your review effectively. You can find more details on how to formulate your research questions here. Here are the key points to note:
- Clarity and Specificity: Ensure that your research questions are clear, specific, and focused on addressing a particular aspect of the topic.
- Relevance: Ensure that your research questions are relevant to the objectives or goals of the review and address important gaps or issues in the existing literature.
- Feasibility: Consider the feasibility of answering the research questions given the available resources, time constraints, and scope of the review.
- Scope: Ensure that your research questions are neither too broad nor too narrow in scope. They should be focused enough to guide your search and analysis effectively but also comprehensive enough to capture relevant literature.
- Alignment with Objectives: Ensure that your research questions align with the overall objectives or goals of the review as stated in the introduction.
- Consideration of Variables: If applicable, ensure that your research questions consider relevant variables such as population characteristics, interventions/exposures, comparisons, outcomes, and time frames (PICO(T) framework for quantitative reviews, PICO framework for qualitative reviews).
You want your systematic literature review dissertation to be completed? Please place an order with us and our team of writers will deliver to you a high-quality and plagiarism-free research paper.
Chapter 2: Methodology
Methodological Approach
In this section, you should include the follow:
- Description of the overall research design, i.e., systematic literature review.
- Explanation of why a systematic approach is chosen over other review methods.
- Discussion of any potential limitations or biases in the review process and how they will be addressed.
- Explanation of how the review will adhere to established guidelines or standards for systematic literature reviews in the field.
- Statement of any ethical considerations related to the conduct of the review, if applicable.
Literature Search Strategy
In this section, you should include the follow:
- Description of the databases and sources searched (e.g., PubMed, Web of Science, Google Scholar).
- Explanation of any specific search terms or keywords used, including any synonyms or variations.
- Description of any search filters or limits applied (e.g., publication date, language, study type).
- Explanation of any additional search methods used (e.g., hand-searching reference lists, contacting experts).
- Statement of how the search strategy was developed and refined (e.g., consultation with librarians or subject experts).
- Description of any efforts made to ensure the comprehensiveness and reproducibility of the search (e.g., use of search logs, documentation of search strings).
- Discussion of any challenges or limitations encountered during the search process and how they were addressed.
- Statement of how duplicates were managed and removed from the search results.
- Overview of the search timeframe and any updates or modifications made to the search strategy.
- Discussion of any potential biases in the search strategy and how they were minimized.
- Statement of adherence to established guidelines or standards for conducting systematic literature reviews in the field.
Eligibility Criteria
In this section, you should include the follow:
- Description of the criteria used to determine the eligibility of studies for inclusion in the review.
- Explanation of the inclusion criteria specifying the characteristics that studies must possess to be included (e.g., study design, population, intervention/exposure, outcomes).
- Explanation of the exclusion criteria specifying the characteristics that studies must lack to be included (e.g., irrelevant topic, inappropriate study design).
- Statement of any restrictions on publication status (e.g., published articles only, inclusion of grey literature).
- Description of any restrictions on language or geographical location.
- Explanation of any criteria for study quality or risk of bias assessment.
- Discussion of how the eligibility criteria were developed and refined, including any consultation with stakeholders or subject experts.
- Statement of how the eligibility criteria were applied during the screening and selection process.
- Overview of any pilot testing or calibration exercises conducted to ensure consistency in applying the eligibility criteria.
- Discussion of any challenges or limitations encountered when applying the eligibility criteria and how they were addressed.
- Statement of adherence to established guidelines or standards for defining eligibility criteria in systematic literature reviews.
Literature Quality Assessment
In this section, you should include the follow:
- Explanation of the rationale for assessing the quality of included studies.
- Description of the criteria or tools used for assessing study quality (e.g., risk of bias assessment tools, quality assessment scales).
- Explanation of how each component of study quality was assessed (e.g., randomization, blinding, sample size).
- Discussion of any subjective judgments involved in the quality assessment process and how they were mitigated.
- Statement of whether quality assessment was conducted independently by multiple reviewers, and if so, how discrepancies were resolved.
- Overview of any efforts made to ensure the reliability and validity of the quality assessment process (e.g., training of reviewers, calibration exercises).
- Description of how the results of the quality assessment were used in the analysis and interpretation of the findings.
- Discussion of any limitations or challenges encountered during the quality assessment process and how they were addressed.
- Explanation of how the quality assessment findings were synthesized or presented in the review (e.g., summary tables, narrative description).
- Statement of adherence to established guidelines or standards for assessing study quality in systematic literature reviews.
Literature Search Results
In this section, you should include the follow:
- Total number of records identified through the initial database search.
- Description of any additional records identified through other sources (e.g., hand-searching reference lists, contacting experts).
- Number of duplicates removed during the screening process.
- Total number of records screened based on title and abstract.
- Number of records excluded at the title and abstract screening stage and reasons for exclusion.
- Number of full-text articles assessed for eligibility.
- Number of full-text articles excluded and reasons for exclusion.
- Total number of studies included in the systematic review.
- Characteristics of the included studies (e.g., study design, population, interventions/exposures, outcomes).
- Summary of any challenges or limitations encountered during the search process.
- Statement of adherence to established guidelines or standards for reporting search results in systematic literature reviews.
- The literature search results can be included in a PRISMA diagram.
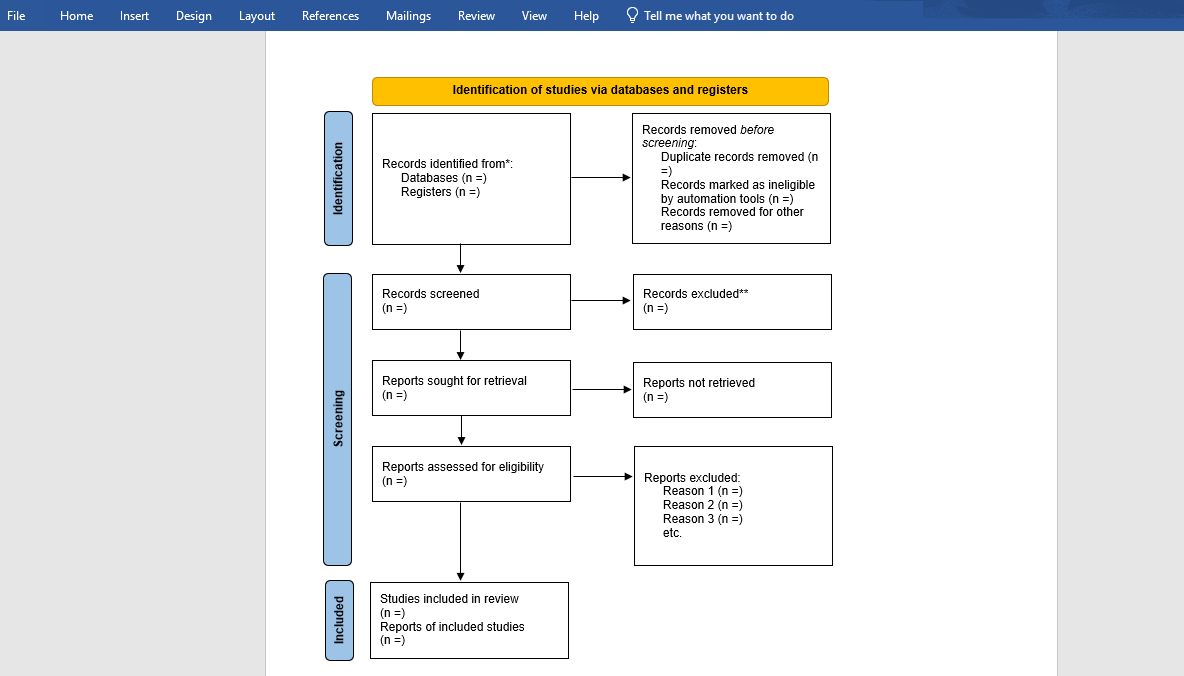
PRISMA Flowchart for systematic literature review
You want your systematic literature review dissertation to be completed? Please place an order with us and our team of writers will deliver to you a high-quality and plagiarism-free research paper.
Chapter 3: Results
Here is how you can structure the results chapter of your systematic literature review in point form:
Introduction to Results
- Briefly introduce the purpose of the results chapter.
- Explain how the results will be presented and organized.
Summary of Search Results
- Provide an overview of the literature search process.
- Summarize the number of records identified, screened, and included in the review.
- Mention any duplicates removed during the screening process.
Characteristics of Included Studies
- Present descriptive statistics of the included studies.
- Include information such as study design, sample size, population characteristics, intervention/exposure, outcomes measured, and study settings.
- Use tables or figures to summarize key characteristics.
Synthesis of Findings
- Present the main findings of the included studies.
- Organize findings based on themes, categories, or key concepts identified during data analysis.
- Use tables, charts, or diagrams to illustrate trends, patterns, or relationships among the studies.
Subgroup Analyses or Sensitivity Analyses (if applicable)
- Present any subgroup analyses or sensitivity analyses conducted.
- Highlight any subgroup differences or variations in study findings.
Additional Analyses (if applicable)
- Include any additional analyses performed, such as subgroup analyses, meta-regression, or sensitivity analyses.
- Discuss the rationale and implications of these additional analyses.
You want your systematic literature review dissertation to be completed? Please place an order with us and our team of writers will deliver to you a high-quality and plagiarism-free research paper.
Chapter 4: Discussion
Here is how you can structure the discussion chapter of your systematic literature review in point form:
Introduction to Discussion
- Briefly introduce the purpose of the discussion chapter.
- Explain how the discussion will address the implications of the findings and contribute to the understanding of the research topic.
Interpretation of Findings
- Interpret and discuss the meaning and significance of the results obtained from the systematic literature review.
- Analyze the main findings in relation to the research question or objective.
- Identify any patterns, trends, or relationships among the studies.
Comparison with Previous Literature
- Compare and contrast the findings of your review with those of previous studies or existing literature.
- Discuss how your findings align with or diverge from previous research.
- Identify areas of agreement or disagreement with existing literature.
Explanation of Contradictory Findings
- Address any contradictory findings or unexpected results identified in the review.
- Explore possible explanations for discrepancies among the studies.
- Discuss potential sources of bias or variability that may have influenced the results.
Strengths and Limitations
- Discuss the strengths and limitations of the systematic literature review.
- Highlight methodological strengths, such as rigorous search strategies and transparent selection criteria.
- Acknowledge any limitations, such as publication bias or heterogeneity among included studies.
Implications for Practice
- Discuss the practical implications of the findings for clinical practice, policy development, or decision-making.
- Consider how the results can inform healthcare practices, interventions, or guidelines.
- Discuss the potential benefits or challenges of implementing the findings in real-world settings.
Implications for Research
- Identify areas for future research based on the gaps or limitations identified in the review.
- Suggest potential research questions or directions for further investigation.
- Discuss how future studies can build upon the findings of the systematic literature review.
Conclusion
- Summarize the main findings and key points discussed in the discussion chapter.
- Reiterate the significance of the findings in addressing the research question or objective.
- Offer final reflections on the implications of the systematic literature review for practice, research, and policy.
Recommendations
- Provide recommendations for stakeholders, policymakers, or researchers based on the implications of the systematic literature review.
- Highlight actionable steps or strategies for addressing the issues identified in the review.
You want your systematic literature review dissertation to be completed? Please place an order with us and our team of writers will deliver to you a high-quality and plagiarism-free research paper.
References
- List all the references cited in the review following a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
Appendices Section
Here is how you can structure the appendices section of your systematic literature review in point form:
Appendix A: Search Strategy
- Provide a detailed description of the search strategy used to identify relevant studies.
- Include search terms, databases searched, date of search, and any filters or limits applied.
- Present the complete search strings used for each database.
Appendix B: PRISMA Flow Diagram
- Include a PRISMA flow diagram depicting the flow of information through the different phases of the systematic literature review process (e.g., identification, screening, eligibility, inclusion).
Appendix C: Study Selection Criteria
- List the inclusion and exclusion criteria used to screen and select studies for inclusion in the review.
- Specify the criteria for study design, population, interventions/exposures, outcomes, language, publication status, and date range.
Appendix D: Data Extraction Form
- Provide a copy of the data extraction form used to extract relevant information from included studies.
- Include the variables or data items extracted, as well as any coding or categorization schemes used.
Appendix E: Quality Assessment Tools
- Include copies of the quality assessment tools or scales used to assess the methodological quality and risk of bias of included studies.
- Provide instructions for using the tools and scoring criteria.
Appendix F: List of Included Studies
- Present a comprehensive list of all studies included in the systematic literature review, along with relevant study characteristics (e.g., author, title, year of publication, study design).
Appendix G: Characteristics of Included Studies
- Provide detailed tables or summaries presenting the characteristics of included studies.
- Include information such as study design, sample size, population characteristics, interventions/exposures, outcomes measured, and study settings.
Appendix H: Quality Assessment Results
- Present the results of the quality assessment conducted for included studies.
- Include tables or summaries displaying the quality assessment scores or ratings for each study.
Appendix I: Additional Analyses (if applicable)
- Include any additional analyses conducted as part of the systematic literature review (e.g., subgroup analyses, sensitivity analyses).
- Provide tables, figures, or detailed descriptions of the additional analyses performed.
Appendix J: Other Supporting Information
- Include any other supporting information deemed relevant or useful for readers.
- This may include supplementary tables, figures, data visualizations, or detailed methodological explanations.
You want your systematic literature review dissertation to be completed? Please place an order with us and our team of writers will deliver to you a high-quality and plagiarism-free research paper.
