What is a Narrative Review?
- A narrative review is a type of literature review that summarizes and interprets findings from the scientific literature on a specific topic.
- The goal of a narrative review is to provide an overview of the existing literature and describe patterns and trends in published research studies.
- A narrative review may be noncomprehensive, focusing on a topic of interest chosen by the review authors.
- Unlike a systematic review, a narrative review does not follow rigid inclusion and exclusion criteria, but instead relies on analyzing and interpreting the literature to offer insights.
- The narrative review provides description and interpretation of data, allowing educators and researchers to understand the body of knowledge within a field and identify factors that may shape future research.
Why and When to Choose a Narrative Review?
- A narrative review is ideal when the goal is to develop a qualitative understanding rather than perform a systematic comparison of studies.
- Choose a narrative review when exploring broad or emerging research questions, where the scope of evidence is diverse or theoretical.
- This type of review is useful when synthesizing insights from relevant literature that does not lend itself to meta-analysis.
- A narrative review allows reviewers to discuss perspectives and experiences informed by published research and to establish a theoretical foundation.
- Narrative literature reviews provide context for your research, helping researchers to describe trends, synthesize information, and guide future research directions.
- Although narrative reviews may lack statistical precision, they remain crucial for review types that promote understanding of a topic.

Differences Between a Systematic Review and a Narrative Review
- A systematic review and a narrative review differ in their structure, rigor, and purpose.
- A systematic review follows strict guidelines, detailed search strategies, and clear inclusion and exclusion criteria. In contrast, a narrative review allows flexible selection and appraisal of studies.
- The systematic review and a narrative differ in analysis—systematic reviews often include meta-analysis, while a narrative review focuses on narrative synthesis of available evidence.
- A systematic review uses databases like PubMed (PMC), while a narrative review may include grey literature or traditional literature.
- Review authors conducting a narrative review emphasize the description and interpretation of findings, rather than quantitative aggregation.
- Both review types enrich the body of knowledge, but narrative reviews provide flexibility to interpret and analyze literature in context.
Differences Between a Narrative Review and a Scoping Review
- A narrative review and a scoping review differ mainly in their scope and purpose. A scoping review maps existing literature across large areas, while a narrative review narrows focus to a specific topic.
- A narrative review analyzes and synthesizes key themes, while a systematic review and a scoping review both involve structured literature search methods.
- Narrative reviews may include a broad range of research studies, while scoping reviews systematically collect peer-reviewed and grey literature.
- A narrative review provides description and interpretation, while a scoping review identifies research gaps and factors that may influence study design.
- Use a narrative review for qualitative synthesis, and a scoping review for mapping typology of reviews.
- Both review forms complement each other as part of the research process.
Narrative Review Help
- Expertly written syntheses by Best Dissertation Writers
- Comprehensive literature search support
- Accurate data analysis and reporting
Free Expert Consultation
- Personalized advice tailored to you
- Clear guidance before project start
- No-cost expert topic evaluation
How to Formulate Research Questions in a Narrative Review
- Defining a strong research question is central to a narrative review.
- The research question should align with the topic of interest, guiding literature search and analysis and interpretation.
- Authors should also ensure the narrative review captures patterns and trends within published research and links them to a clear theoretical framework.
- A good narrative review question considers factors that may affect study results, population, and setting.
- Research guides suggest refining the research question using frameworks such as PICO or SPIDER for qualitative reviews.
- Well-defined research questions help reviewers conduct a comprehensive review of the literature and ensure the narrative review provides understanding of a topic and contributes to future research.
- Example of a Narrative Review Research Question: “How do stress management interventions influence the mental health and job performance of healthcare professionals in high-pressure clinical environments?”
- This narrative review question is qualitative in nature.
- It allows the review authors to explore published research, grey literature, and traditional literature reviews.
- It provides description and interpretation rather than statistical results, aligning perfectly with the purpose of a narrative literature review.
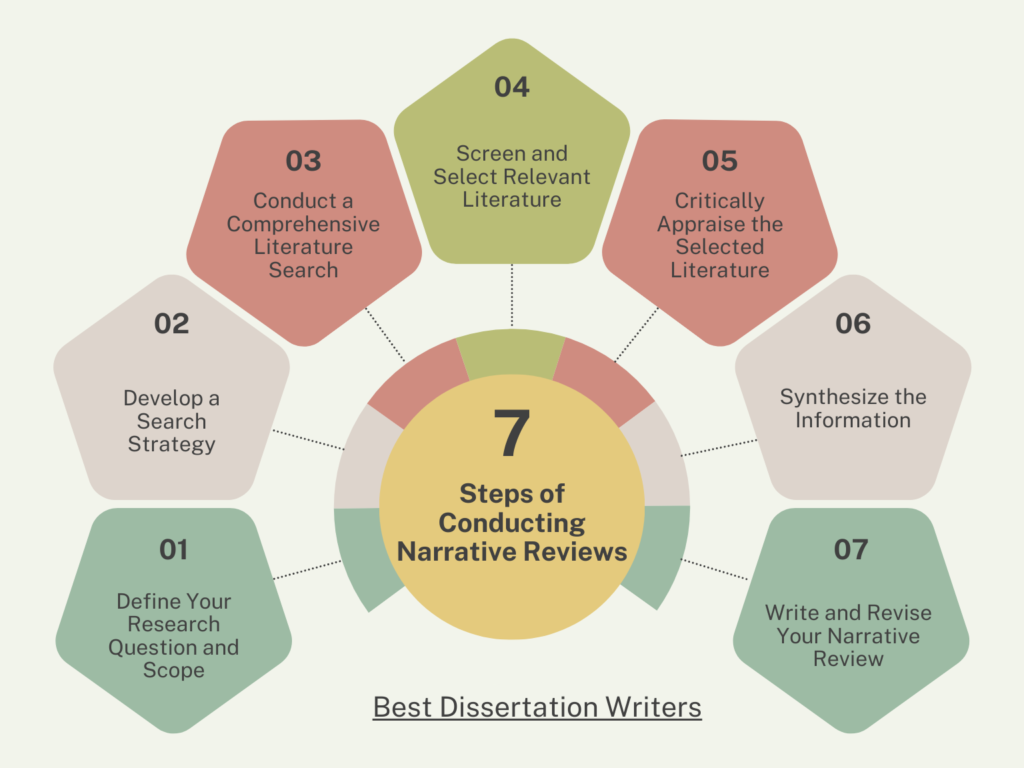
How to Conduct a Narrative Review in 7 Easy Steps
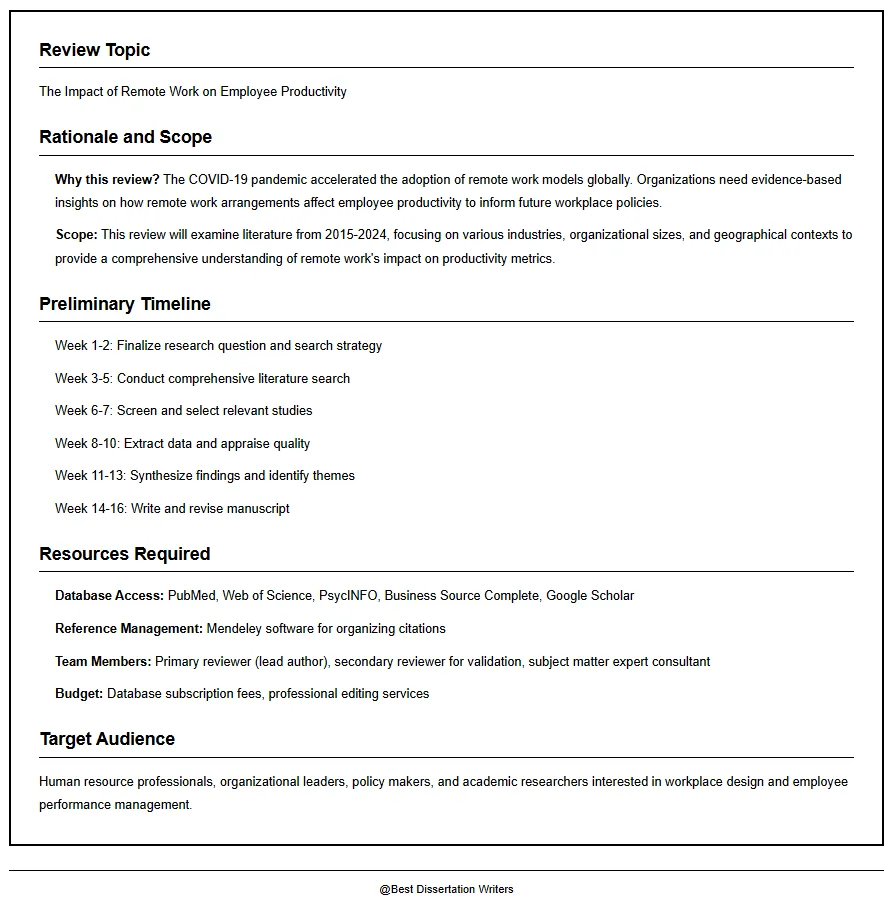
Step 1: Plan the Narrative Review
- Begin the narrative review by outlining its scope, topic of interest, and rationale.
- Decide whether your narrative review will be a critical review, traditional literature review, or meta-narrative review—the main subtypes of narrative reviews.
- The author team or review authors should include experts to ensure best practice in analysis and synthesis.
- Planning helps determine whether the review may inform policy, theory, or educators and researchers.
- Align your structure with the RAMESES publication standards to ensure methodological clarity.
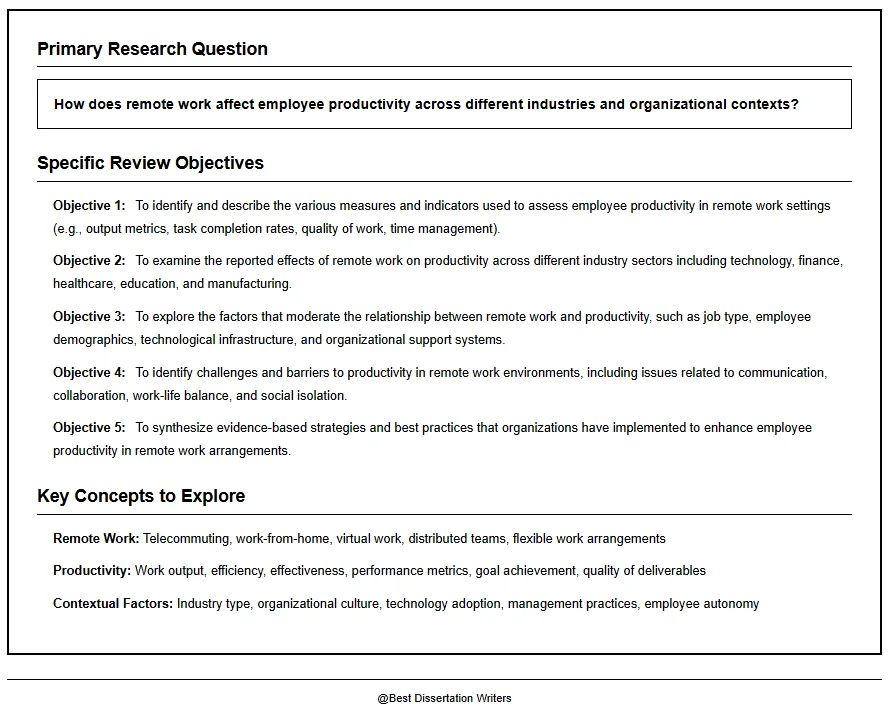
Step 2: Develop the Research Question and Objectives
- Each narrative review starts with a focused research question that defines what the review will provide.
- Formulate clear objectives that address existing literature and highlight factors that may influence the research process.
- Use recognized research guides to refine questions, ensuring they address a specific topic and contribute to the body of knowledge.
- Dr. Javeed Sukhera (FRCPC) from the Department of Psychiatry emphasizes that narrative reviews should connect current evidence with description and interpretation to inform future research.
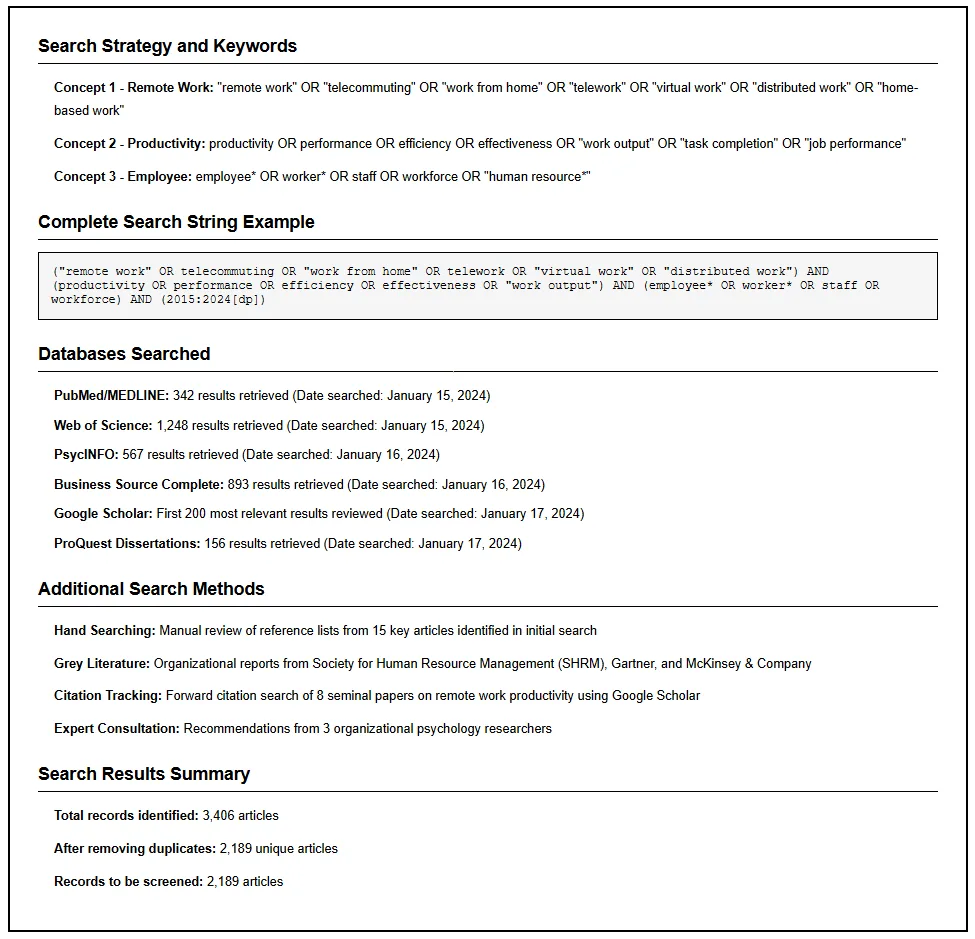
Step 3: Conduct a Comprehensive Literature Search
- Search databases such as PubMed, PMC, Google Scholar, and Scopus to find relevant literature.
- Include grey literature and traditional literature to capture a wide range of perspectives.
- A robust search strategy ensures inclusion of peer-reviewed and published research.
- Record search terms, time frames, and sources. Reviewers should ensure transparency in this review process.
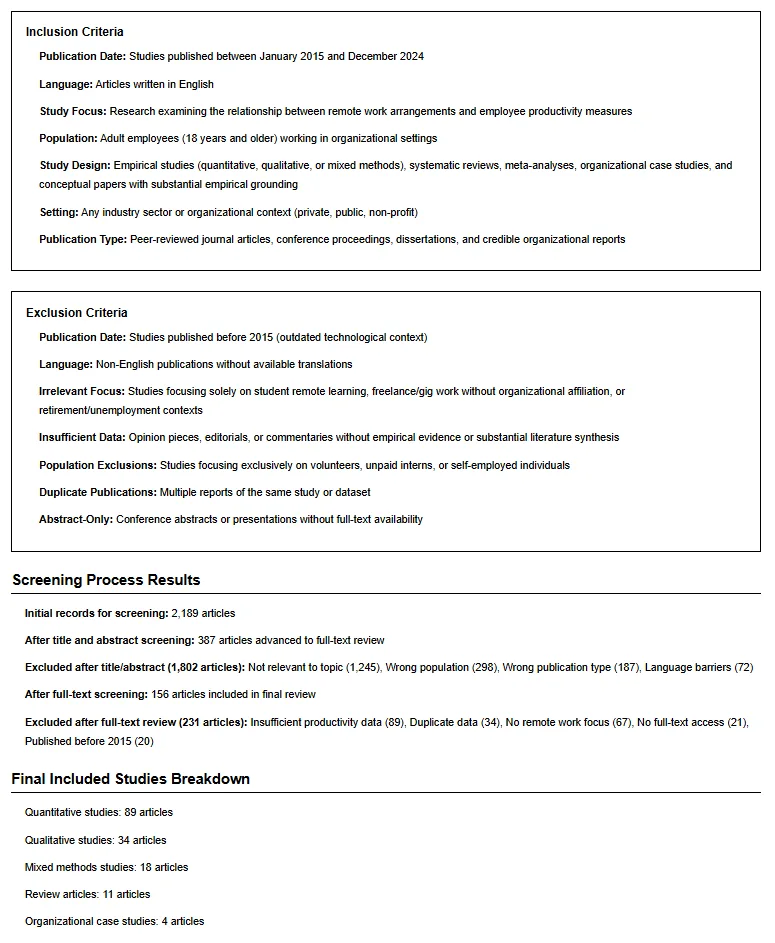
Step 4: Apply Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- Clearly define inclusion and exclusion criteria for your narrative review to maintain focus.
- Unlike systematic reviews, narrative literature reviews may allow noncomprehensive coverage but must justify excluded materials.
- Criteria Examples:
- Include studies from peer-reviewed journals only.
- Exclude reports lacking evidence-based data or with unclear methodology.
- Keep a log for reviewers to track appraisal decisions and maintain best practice consistency.
Step 5: Appraise the Quality of the Literature
- Use an appraisal checklist (e.g., CASP or AMSTAR) to assess credibility and relevance.
- Each narrative review must judge available evidence for quality and bias.
- The review authors should appraise the scientific literature carefully, summarizing patterns and trends.
- This ensures that your narrative review builds an evidence-based foundation and informs the body of knowledge on your topic of interest.
- Narrative reviews may integrate expert opinions when research data are limited.

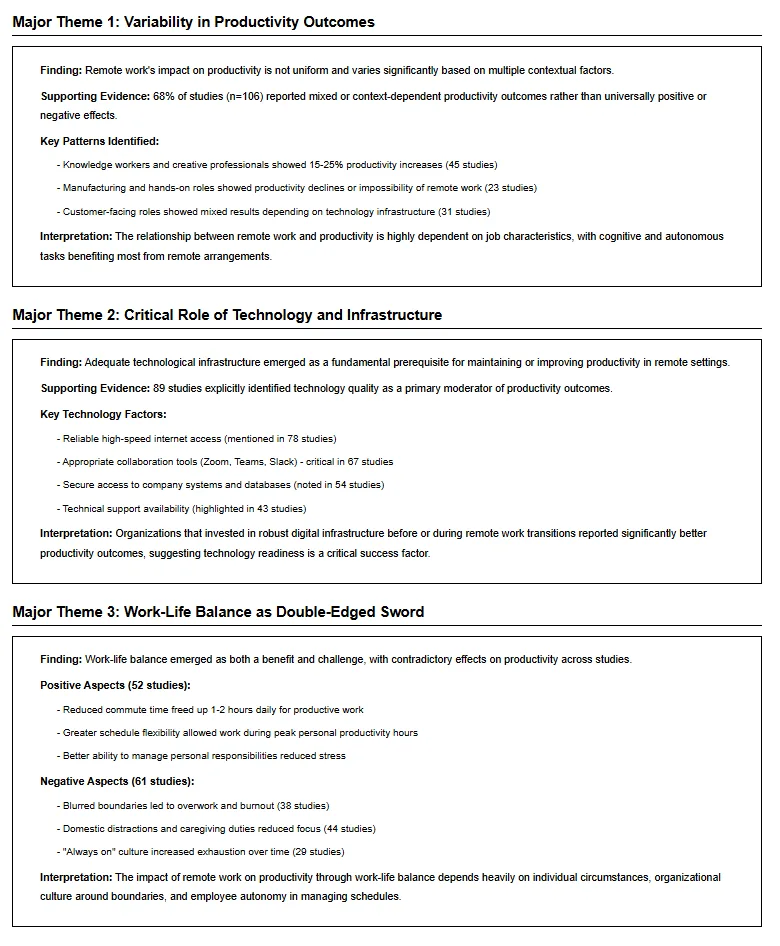
Step 6: Synthesize and Interpret Findings
- Conduct a narrative synthesis, combining results into thematic categories.
- A narrative review should synthesize insights across research studies, linking theoretical and practical implications.
- Use qualitative reasoning to analyze literature addressing your research question and explain emerging patterns.
- A comprehensive review of the literature, identifying relationships, contradictions, and patterns and trends.
- Identify the forms of narrative approaches—such as traditional literature reviews, critical reviews, and meta-narrative reviews—and discuss how each contributes to understanding of a topic.
Step 7: Report and Disseminate the Review
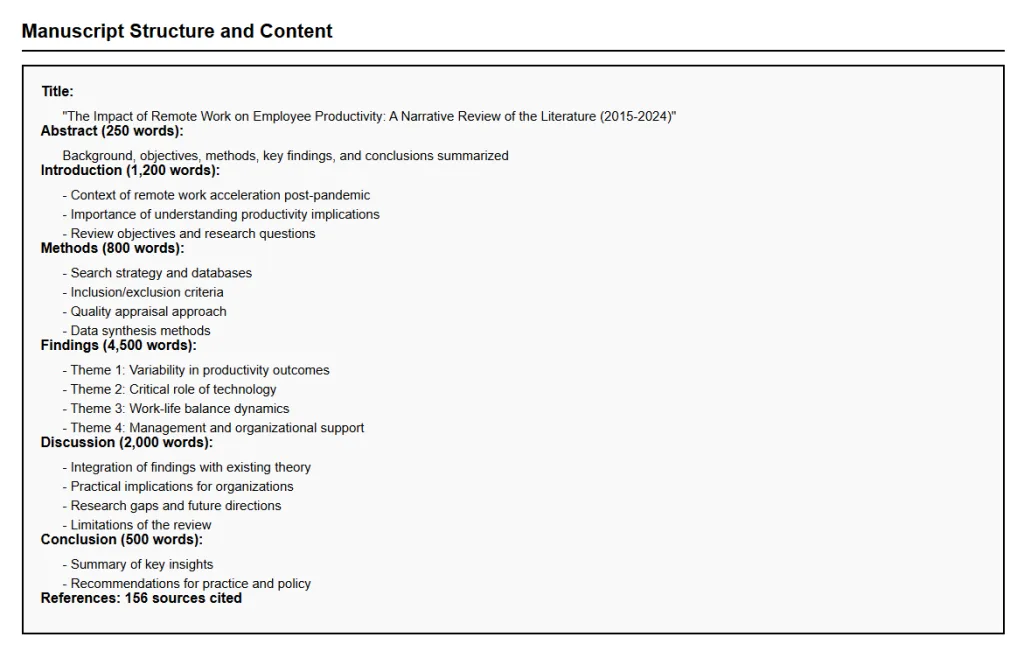
- Present findings in sections: Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion.
- Highlight subtypes of narrative reviews and explain which type of review fits your topic of interest.
- Report methods clearly to support reproducibility and best practice.
- Include corresponding author details and affiliations, such as “Department of Psychiatry, Javeed Sukhera, FRCPC,” as required by journals.
- Follow RAMESES publication standards to ensure clarity, transparency, and ethical reporting.
- A high-quality narrative review enhances understanding of a topic, supports future research, and contributes to the global body of knowledge.
Key Takeaways
- A narrative review is a flexible and insightful form of literature review that allows researchers to synthesize and interpret findings from the scientific literature on a specific topic.
- Unlike a systematic review or a scoping review, a narrative review focuses on description and interpretation rather than strict inclusion and exclusion criteria or statistical analysis.
- It helps educators and researchers build an evidence-based understanding of complex issues, identify patterns and trends, and suggest future research directions.
- The narrative review process involves planning, defining the research question, conducting a literature search, appraising the available evidence, and presenting a coherent narrative synthesis.
- By following best practices and adhering to RAMESES publication standards, authors can produce high-quality narrative literature reviews that inform practice, policy, and theory, making them a vital part of the research process and an essential bridge between existing literature and new discoveries.