Essential Steps to Writing Your Dissertation Introduction
Writing the dissertation introduction is a crucial step in framing your entire thesis or dissertation. The introduction provides an essential overview and sets the tone for the rest of the research. To effectively write a dissertation introduction, you must focus on several key elements that ensure clarity and coherence.
Writing the Introduction Chapter: Key Elements for Your Thesis
- Background Information: Begin your dissertation introduction by providing background information. This helps set the context of your study and allows readers to understand the landscape of your research topic.
- Clearly State the Research Topic: In this section, clearly state the research topic. A dissertation introduction should outline the specific focus of your research.
- Research Aims and Objectives: Present the aims and objectives of your research, specifying what you intend to achieve through your study. These should be concise, highlighting the research questions and what the research seeks to answer.
- Research Hypothesis: If applicable, include your research hypothesis, which will guide your study and establish your stance on the topic.
Expert Dissertation Writing Services
Need expert guidance on your dissertation? Get professional help from Best Dissertation Writers to ensure high-quality, well-structured work. Let us help you craft a compelling dissertation that meets academic standards. Contact us today!
Providing an Overview: Setting the Foundation for Your Dissertation
- Concise Overview of the Research: Offer a concise overview of the entire dissertation. This gives the reader an understanding of the study’s scope, structure, and direction.
- Overview of the Topic and Relevance: Provide an overview of the topic’s relevance and importance. Make sure to explain why your research is significant and what contribution it will make to the existing body of knowledge. This sets the foundation for the reader to understand the purpose of your research.
- Literature Review: Mention the literature review briefly in the introduction. This section summarises existing research and will lay the groundwork for the methodology chapter.
- Context of the Study: Explain the context of the study, outlining how your research fits within the current state of research. This helps to position your dissertation within the broader academic landscape.
Defining the Scope and Relevance of Your Research in the Introduction
- Scope of Your Research: Define the scope of your research. Be clear about what aspects of the research topic you are focusing on, and state any limitations or exclusions.
- Research Methods: Briefly explain the research methods you will be using, especially if your study is qualitative. This provides the reader with an understanding of how you will gather and analyse data to answer the research questions.
- Research Objectives: State your research objectives clearly. These should align with the aims of your dissertation and provide a roadmap for the methodology chapter.
- Relevance of Your Research: Demonstrate the relevance of your research, explaining why it matters to the field and how it contributes to existing research.
Crafting the Thesis Introduction: Effectively Stating Your Research
- Clearly State the Purpose of the Research: The dissertation introduction should clearly state the purpose of the research. What exactly are you investigating, and why is it important?
- Provide a Brief Overview of the Structure: Briefly outline the structure of your dissertation, providing an overview of what each chapter will cover. This gives the reader a clear guide to how your dissertation will unfold.
- Link to the Conclusion: The introduction should naturally link to the conclusion. By the end of the dissertation introduction, readers should understand how the research will be carried out and what to expect throughout the dissertation.
Quick Links to Introduction Chapter Resources – Learn More
- Discover how to write background section in your dissertation/research paper effectively by reading our article on Background of the Study Example | Top 6 Sections.
- Understand how to clearly write primary purpose of your study by reading our article on Example of Purpose of the Study | Purpose Statement.
- Learn how to write a compelling problem statement in your dissertation/research paper by reading our article on Write an Effective Problem Statement: A 5-Step Guide.
- Highlight the importance and contribution of your study by reading our article on How to Write Significance of the Study Example in 7 Steps.
- Learn how to develop smart objectives for your research by reading our article on What’re Research Objectives | 5 Step Guide for Good Research.
- Frame strong, answerable research questions by reading our article on Writing Strong Research Questions | 4 Steps in Dissertation.
By following these essential steps, you can ensure that your dissertation introduction effectively sets the foundation for your thesis. This will guide the reader through your research, helping them understand the context, relevance, and structure of your entire dissertation.
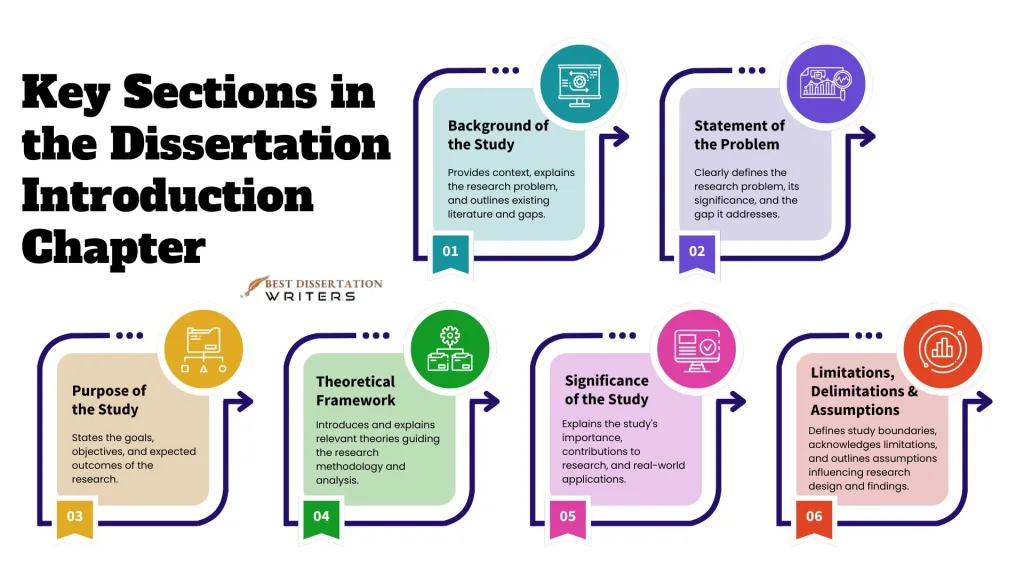
| Dissertation Introduction Chapter Sections | Description |
| Background of the Study | Contextualise the research. Identify the research problem and its significance. Summarise existing literature and identify research gap. Formulate research questions. |
| Statement of the Problem | Clearly state the research problem. Provide a brief summary of the problem’s context. Discuss the relevance of the problem. Link the problem to research objectives. |
| Purpose of the Study | State the study’s purpose and goals. Define the research aims and objectives. Discuss the study’s contribution to existing research. Outline the scope of the study. |
| Theoretical Framework | Introduce the theoretical framework. Explain key theories or concepts. Link the framework to research questions. Explain how the framework guides the study. |
| Significance of the Study | Articulate the importance of the study. Discuss the contribution to academic research and practical applications. Identify stakeholders who will benefit. |
| Limitations, Delimitations, and Assumptions | Outline the limitations of the study. Discuss the delimitations (boundaries of the study). Acknowledge assumptions made during research. |
| Definitions and Key Terms | Define key terms and concepts used throughout the dissertation. Provide a clear and concise explanation for specialised language. |
| Organization of the Dissertation | Provide an overview of the dissertation’s structure. Briefly summarise each chapter. Explain how the chapters link to the overall research. |
Dissertation Introduction Chapter Outline
The dissertation introduction chapter is a critical component of your dissertation. It sets the stage for the entire study, providing a roadmap for your readers to follow. The introduction chapter of your dissertation should include several key elements that help contextualise your research, state your purpose, and outline the structure of the dissertation. Below is a detailed outline for writing an effective dissertation introduction, ensuring that all critical elements are covered.
Background of the Problem
- Contextualise Your Research: Begin the dissertation introduction by providing the background to your study. This helps your readers understand the broader context in which your research is situated.
- Identify the Research Problem: In this section, highlight the specific problem your dissertation addresses. Be sure to explain why the problem is significant and what makes it worthy of investigation.
- Overview of Existing Literature: Provide a brief summary of key findings from the study of existing literature. This will help your reader understand the research gap you aim to fill with your work.
- Research Questions: Formulate your research questions in a clear and concise manner. This will help guide the direction of your dissertation and ensure that your dissertation introduction provides a framework for your research objectives.
Statement of the Problem
- Clearly State the Problem: In the dissertation introduction, clearly articulate the research problem. The problem statement should explain the core issue that your research will address and why it is important.
- Brief Summary of the Problem’s Context: Provide a brief summary of the background that leads to the problem. This helps readers gain a clear understanding of the issue at hand.
- Problem’s Relevance: Discuss why the problem matters in your field. This will help contextualise your research and show the relevance of the study.
- Connection to Research Objectives: Ensure that the problem statement connects to your research aims and objectives, providing clarity for the reader throughout your dissertation.
Purpose of the Study
- State the Purpose: In this section of the dissertation introduction, state the purpose of the study. What do you intend to achieve with your research? Be clear and concise in stating your objectives.
- Research Goals and Aims: Define the goals of your research, ensuring that they align with the problem you’ve stated. These should reflect the purpose of your study and the impact it will have on the field.
- Contribution to Existing Research: Discuss how your research will contribute to the academic writing body in your discipline. Outline how your research aims to fill the gap identified in the problem statement.
- Overview of Research Scope: Provide a brief overview of your research scope. Discuss what is included and what is excluded from the study, which will help define the limits of your dissertation.
Theoretical Framework
- Introduce the Theoretical Framework: In your dissertation introduction, introduce the theoretical framework that will guide your study. This framework will serve as the foundation for your research methods, analysis, and interpretation of data.
- Explain Key Theories: Outline the key theories or concepts you are working with and explain how they apply to your study.
- Connection to Research Questions: Ensure that the theoretical framework connects clearly to your research questions. This will help maintain focus and provide a solid foundation for your research.
- How Theory Guides the Study: Briefly explain how the theoretical framework will guide your analysis, findings, and conclusions. This section should offer a clear understanding of how your theoretical background shapes your research.
Significance of the Study
- State the Study’s Significance: Clearly articulate the importance of your study. Why is it significant? What impact will it have on your field or discipline? Ensure that this section is clear and concise.
- Potential Contribution to Existing Research: Discuss how your research will contribute to existing research in your field. Be specific about how your findings could help advance knowledge or offer solutions to practical problems.
- Relevance to Practice: Highlight the practical applications of your research findings. This will show how your study is relevant beyond academia.
- Benefits for Stakeholders: Identify who will benefit from your research and how, such as policymakers, educators, or specific communities. This section helps readers understand the wider impact of your study.
Limitations, Delimitations, and Assumptions of the Study
- State the Limitations: Every research project has limitations. In the dissertation introduction, clearly outline the limitations of your study, such as the sample size, time constraints, or methodological restrictions.
- Discuss Delimitations: Delimitations refer to the boundaries or scope you have set for your research. Be sure to explain what you will not include in your study and why these decisions were made.
- Acknowledge Assumptions: Discuss any assumptions you’ve made in your research process. For example, you may assume that certain conditions remain constant throughout the study or that certain data will be available.
- Transparency and Honesty: Addressing these aspects openly in your dissertation introduction helps build credibility and shows that you are aware of the study’s limitations.
Definitions and Key Terms
- Define Key Terms: It’s important to define terms and concepts that will be used throughout your dissertation. This ensures that readers have a clear understanding of any specialised language or terminology.
- Provide a Brief Overview: Offer a brief overview of the key terms that are critical to your research. This section should be easy to follow, providing clarity for your readers.
- Clarify Complex Concepts: If your dissertation involves complex or technical terms, make sure to provide definitions so that readers can easily follow your academic writing.
- Consistency in Terminology: Ensure that key terms are used consistently throughout your dissertation, maintaining clarity and preventing confusion.
Organization of the Dissertation
- Outline the Structure: In your dissertation introduction, provide an overview of your dissertation’s structure. This should include a brief summary of each chapter in your dissertation.
- Chapter Breakdown: Provide a clear and concise breakdown of each chapter of your dissertation, outlining the purpose and focus of each. This will guide your readers and help them understand how the dissertation is organised.
- Linking Chapters Together: Explain how each chapter connects to the overall research. This will help contextualise your research and show how each section contributes to answering your research questions.
- Introduction and Conclusion: Briefly mention how the introduction and conclusion of your dissertation will tie together your research findings and results.
By following this comprehensive outline for your dissertation introduction, you will lay a strong foundation for your entire dissertation. The introduction will provide your readers with the necessary context, clear understanding, and direction to follow throughout your study. The dissertation introduction not only helps clarify your research purpose and scope but also ensures that your dissertation is structured in a logical, coherent manner.
Here is the PDF version of the dissertation introduction chapter. Please read it to get detailed understanding on how this chapter should be written.
