Introduction
This article presents a comprehensive 7-step guide for conducting narrative reviews and systematic reviews. Readers will gain valuable insights into a methodology that combines the strengths of both narrative and systematic reviews techniques. The guide outlines a structured process for synthesizing and analyzing existing literature, ensuring a thorough and unbiased examination of research findings.
By following these steps, researchers and academics can enhance the rigor and reliability of their literature reviews, leading to more robust and credible research outcomes. This guide is particularly useful for those seeking to navigate the complexities of literature review methodologies in various academic fields.
Dissertation Writing Help
Feeling overwhelmed by your dissertation? Best Dissertation Writers is your solution. Our tailored support ensures your unique voice shines through. Don’t go it alone—partner with us for unparalleled results!
What is a narrative review?
A narrative review is a qualitative approach to synthesizing relevant literature on a specific research question. Unlike systematic reviews, narrative reviews often lack strict guidelines for inclusion and exclusion criteria. Reviewers conducting a narrative review typically perform a comprehensive literature search across various databases, but the search strategy may be less rigorous than in systematic reviews.
The narrative review process involves appraising and synthesizing evidence-based information to provide an overview of the current state of knowledge on a topic. While narrative reviews may not be as systematic as other review types, they offer valuable insights and can highlight gaps for future research. Narrative reviews are particularly useful when exploring complex topics that may not fit neatly into the structured approach of systematic reviews, allowing for a more flexible and interpretative synthesis of the available literature.
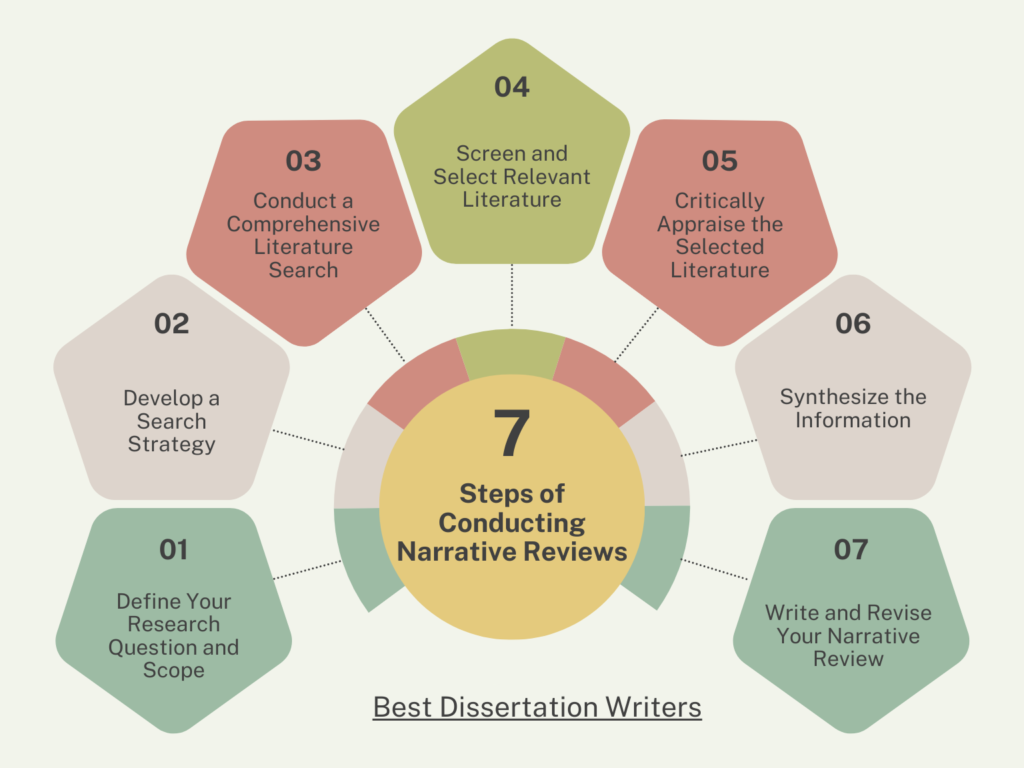
A 7-Step Guide for Conducting a Narrative Review
Narrative reviews provide a comprehensive overview of the literature on a topic, offering valuable insights and context for researchers, educators, and practitioners. Although narrative reviews may not follow the strict methodological guidelines of systematic reviews, they play a crucial role in synthesizing and interpreting complex bodies of knowledge. This guide outlines a 7-step process for conducting a thorough and informative narrative review.
Step 1: Define Your Research Question and Scope
Begin by clearly defining your topic of interest and the specific questions your review aims to address. Consider the various types of narrative reviews, such as traditional literature reviews, critical reviews, or meta-narrative reviews, to determine which best suits your research goals. Make sure you’re focused on a manageable scope that allows for a comprehensive review of the literature without becoming overwhelmed.
Step 2: Develop a Search Strategy
Create a robust search strategy to identify relevant literature. Utilize research guides and consult with librarians to optimize your search. Include both traditional literature sources and peer-reviewed databases such as PubMed and PMC. Consider incorporating grey literature to capture a broader range of perspectives. Your search strategy should be thorough enough to provide a representative sample of the current evidence on your topic.
Step 3: Conduct a Comprehensive Literature Search
Execute your search strategy across multiple databases and sources. Use a combination of keywords, subject headings, and Boolean operators to refine your results. Be sure to document your search process, including the databases searched, search terms used, and any inclusion or exclusion criteria applied. This documentation will help ensure transparency and allow others to understand the scope of your review.
Step 4: Screen and Select Relevant Literature
Review the titles and abstracts of the identified literature to determine relevance to your research question. Create a system for organizing and managing your selected articles, such as using reference management software. As you screen the literature, be mindful of potential biases and strive to include diverse perspectives. Remember that narrative reviews usually aim to provide a broad overview, so consider including a range of study types and methodologies.
Step 5: Critically Appraise the Selected Literature
Analyze and interpret the selected literature, paying attention to the quality and relevance of each source. Consider factors that may influence the reliability and validity of the findings, such as study design, sample size, and potential biases. As you appraise the literature, look for patterns, themes, and contradictions across studies. This critical analysis will form the foundation of your narrative synthesis.
Step 6: Synthesize the Information
Develop a narrative synthesis that integrates the findings from your selected literature. This step involves more than just summarizing individual studies; it requires analyzing and interpreting the literature as a whole to provide a cohesive overview of the current state of knowledge on your topic. Consider using frameworks or models to organize your synthesis, such as chronological, thematic, or conceptual approaches.
Step 7: Write and Revise Your Narrative Review
Begin drafting your narrative review, ensuring that you provide a clear and logical flow of information. Start with an introduction that sets the context for your research and clearly states your research question. In the main body of the review, present your findings in a structured manner, highlighting key themes, controversies, and gaps in the literature. Conclude with a summary of the current state of knowledge and implications for future research or practice.
Throughout the writing process, keep in mind the following considerations:
- Transparency: Clearly describe your methodology, including search strategies and selection criteria.
- Balance: Present different perspectives and conflicting evidence fairly.
- Critical analysis: Go beyond description to offer insightful interpretation and analysis.
- Relevance: Ensure that your review provides valuable context for your research and advances understanding in your field.
As you revise your draft, consider seeking feedback from colleagues or mentors. Review authors should also consult publication standards, such as the RAMESES publication standards for meta-narrative reviews, to ensure their work meets quality expectations.
Dissertation Writing Services
Achieve dissertation excellence with Best Dissertation Writers. Our seasoned academics are prepared to guide you through every challenge. Invest in your future—get in touch today and experience the difference!
While conducting your narrative review, it’s important to acknowledge both the strengths and limitations of this approach. Although narrative reviews offer flexibility in analyzing and interpreting the literature, they may be criticized for being noncomprehensive or potentially biased. Address these concerns by being transparent about your methodology and acknowledging any limitations in your review.
By following this 7-step guide, researchers can produce high-quality narrative reviews that contribute significantly to the body of knowledge in their field. Whether you’re a seasoned researcher like Dr. Javeed Sukhera (FRCPC) from the Department of Psychiatry or an emerging scholar, narrative reviews offer a valuable opportunity to synthesize and interpret the literature, providing essential context for future research and informing best practices in your discipline.
Remember that conducting a narrative review is an iterative process. As you progress through these steps, you may need to refine your research question, adjust your search strategy, or revisit earlier steps based on new insights gained during the review process. Embrace this flexibility, as it allows for a richer and more nuanced understanding of your topic of interest.
Main differences between a systematic review and a narrative review
The main differences between a systematic review and a narrative review lie in their methodological approaches and objectives. A systematic review follows a rigorous, predefined protocol with explicit inclusion and exclusion criteria, aiming to comprehensively identify and synthesize all relevant literature on a specific research question. In contrast, a narrative review typically adopts a more flexible approach, allowing for broader exploration of a topic without adhering to strict methodological guidelines.
Systematic reviews employ a highly structured search strategy across multiple databases, often involving multiple reviewers to minimize bias. Narrative reviews, while still comprehensive, may have a less exhaustive search process. The analysis in systematic reviews is often quantitative, whereas narrative reviews tend to be more qualitative and interpretative.
Systematic reviews are considered the gold standard for evidence-based research, while narrative reviews are valuable for providing a broader context and identifying research gaps. The choice between a systematic review and a narrative review depends on the research objectives and available resources.
Main differences between a systematic review and a scoping review
The main differences between a systematic review and a scoping review lie in their scope and objectives. A systematic review aims to answer a specific, well-defined research question by synthesizing and critically appraising all relevant studies. In contrast, a scoping review typically has a broader scope, mapping the key concepts, types of evidence, and research gaps in a particular field.
Systematic reviews follow a strict, predefined protocol and often include a quantitative synthesis of results. Scoping reviews, while still methodical, allow for more flexibility in the inclusion criteria and synthesis process. The purpose of a systematic review is to provide a comprehensive summary of the best available evidence on a specific question, whereas a scoping review aims to identify the nature and extent of research evidence on a broader topic.
While both types of reviews involve a systematic search strategy, the depth of analysis and critical appraisal is typically more rigorous in systematic reviews compared to scoping reviews.
When to use narrative reviews
- Broad overview of a topic: Narrative reviews are ideal when you need to provide a comprehensive overview of the scientific literature on a specific topic, including both published research and grey literature.
- Complex or multifaceted subjects: Use narrative reviews when exploring topics that are too complex or diverse for systematic reviews or meta-analyses.
- Identifying patterns and trends: Narrative reviews excel at highlighting patterns and trends across different studies and research traditions.
- Providing context: They are useful for establishing a theoretical framework and providing context for future research.
- Exploring evolving fields: Narrative reviews are particularly valuable when examining emerging or rapidly changing areas of study.
Strengths of narrative reviews over other types of reviews
- Flexibility: Narrative reviews offer greater flexibility in analyzing and interpreting literature, allowing for a more nuanced exploration of complex topics.
- Broad scope: They can incorporate a wide range of research studies and methodologies, providing a more comprehensive view of the literature.
- Contextual understanding: Narrative reviews excel at synthesizing information to offer rich context and deeper understanding of a topic.
- Expert insights: They allow authors to draw on their expertise and perspectives, providing valuable insights that may not be captured in more structured review forms.
- Versatility: Narrative reviews can incorporate elements from different review types, making them adaptable to various research needs.
Limitations of narrative reviews compared to other types of reviews
- Potential for bias: The subjective nature of narrative reviews can lead to bias in the selection and interpretation of literature.
- Lack of reproducibility: Without strict protocols, it can be challenging for other researchers to replicate the findings or verify the conclusions.
- Incomplete coverage: Narrative reviews may miss important studies or fail to adequately address conflicting evidence due to less rigorous search strategies.
- Difficulty in quantifying evidence: Unlike meta-analyses, narrative reviews struggle to quantify the strength of evidence or magnitude of effects.
- Less structured methodology: The flexible approach of narrative reviews can make it harder to establish definitive best practices or make strong recommendations.
By understanding these points, researchers can make informed decisions about when to use narrative reviews and how to interpret their findings in the context of other review types.
Best Dissertation Writers
Struggling with your dissertation? Let Best Dissertation Writers ease your burden. Our professional writers are standing by to deliver top-quality, custom-tailored work. Elevate your research—reach out now!
Frequently asked questions about narrative reviews
What is the narrative review method?
The narrative review method is a qualitative approach to synthesizing literature on a specific topic. It involves critically analyzing and interpreting existing research to provide a comprehensive overview of current knowledge. Unlike systematic reviews, narrative reviews offer more flexibility in literature selection and synthesis, allowing for broader exploration and interpretation of complex subjects.
What is a narrative review vs. systematic review?
A narrative review and a systematic review differ in methodology and scope. Narrative reviews provide a qualitative synthesis of literature, offering a broad overview of a topic with more flexibility in source selection and interpretation. They are useful for exploring complex issues and identifying research gaps.
Systematic reviews, conversely, follow a rigorous, predefined protocol to answer specific research questions. They employ comprehensive search strategies, explicit inclusion/exclusion criteria, and often include quantitative analysis. Systematic reviews aim to minimize bias and provide a more objective synthesis of evidence.
While narrative reviews offer deeper contextual understanding, systematic reviews are considered more robust for evidence-based decision-making due to their structured approach and reproducibility.
What is the narrative literature review?
A narrative literature review is a comprehensive, critical analysis of existing research on a specific topic. It synthesizes findings from various sources to provide an overview of current knowledge, identify trends, highlight gaps, and offer new perspectives. This method allows for a more interpretative and flexible approach compared to systematic reviews.
What is the difference between narrative and descriptive review?
Narrative and descriptive reviews are both forms of literature synthesis, but they differ in their approach and depth of analysis. Narrative reviews provide a critical, interpretative synthesis of literature, offering insights into patterns, controversies, and gaps in research. They involve in-depth analysis and often present new perspectives or theoretical frameworks.
Descriptive reviews, on the other hand, focus on summarizing and describing existing literature without extensive critical analysis or interpretation. They aim to provide an overview of available research on a topic, often categorizing studies based on characteristics like methodology or findings.
While narrative reviews offer more in-depth analysis and interpretation, descriptive reviews provide a more straightforward summary of existing literature.