How to Write a 10000 Word Dissertation in 2 Weeks
- Writing a dissertation in two weeks is realistic only if you treat it like a short, intensive project with a strict timeframe and clear targets.
- Start writing on Day 1 by setting your word count goal (for example, a 10000 word dissertation in 2 weeks) and converting it into words a day so you know exactly what “progress” means.
- Build a simple daily routine: research block + writing block + short review block, and protect it from distraction (phone off, tabs closed, one task at a time).
- Beat procrastination by starting with the easiest section (often the literature review notes) and writing rough paragraphs fast—do not edit heavily yet.
- Use your outline to split the dissertation writing into manageable chunks by chapter and section, instead of attempting one sitting.
- Whether it is an undergraduate dissertation or late stage thesis, you must organise your time to write, keep clarity around the argument, and meet academic standards.
- If done correctly, you can complete your dissertation within days or less before the deadline and still have time to edit, proofread, and check every reference.
Understanding the Dissertation Writing Process
- A dissertation is a formal academic assignment that demonstrates you can investigate a problem, build an argument, and present evidence clearly while meeting academic standards.
- Writing a dissertation is not only “writing”; it is a full workflow that includes planning, research, drafting, referencing, and polishing.
- Most undergraduate dissertation and thesis projects follow a predictable structure, so you should use that structure to reduce confusion and increase clarity.
- The dissertation writing process is usually broken into these main parts (your sections may vary by department):
- Introduction: defines the topic, purpose, research questions, and why the study matters.
- Literature review: shows what is already known, identifies gaps, and positions your work.
- Methodology: explains how you collected and analyzed information (so it can be evaluated).
- Findings/analysis: presents results and interprets what they mean.
- Discussion: links findings back to the thesis and existing literature.
- Conclusion: summarizes contributions, limits, and recommendations.
- Each chapter has a job to do and must contribute directly to the thesis, otherwise you waste time and become unproductive.
- A big reason students struggle is they want to write without a clear outline, a working thesis, or a realistic timeframe—this leads to procrastination, distraction, and weak word count control.
- When you need a dissertation in two weeks, you must plan backwards from the deadline, then assign specific writing targets (for example, a 10000 word dissertation means a fixed number of words a day).
- Good execution also depends on technical accuracy: correct format, consistent subheadings, clean grammar and spelling, and a reliable reference system.
- Understanding “what comes next” in each section keeps productivity high, makes it easier to refine your draft, and helps you seek feedback early instead of panicking late stage.
Creating Your Detailed Plan
- A detailed plan is the difference between “want to write” and actually finishing a dissertation within a short time.
- Start by locking in three non-negotiables:
- Deadline (the exact day and time)
- Total word count (example: 10000)
- Required format/layout (your school template, margins, headings, reference style)
- Convert the total word dissertation target into daily output:
- 10000 word dissertation in 2 weeks = 14 days → aim for roughly 700–900 words a day (higher on writing days, lower on edit days).
- If you only have two weeks but need “days or less” flexibility, build a buffer by writing more in the first week.
- Make a schedule that breaks the dissertation writing into manageable chunks by chapter and section:
- Day 1–2: topic refinement + thesis clarity + confirm sources
- Day 3–6: literature review drafting (highest word count potential)
- Day 7: methodology draft + fix gaps
- Day 8–10: findings/analysis + discussion
- Day 11: write the introduction and conclusion (when you have full clarity)
- Day 12–13: edit + proofread + reference check + format cleanup
- Day 14: final polish + submission readiness
- Protect your writing time: schedule deep work blocks and remove distraction (notifications off, single-task writing).
- Plan for quality control, not just speed: reserve time to refine weak paragraphs, fix grammar and spelling, and confirm every reference matches the in-text citations.
- This approach helps you complete your dissertation fast while still meeting academic standards and producing a complete draft that can be improved efficiently.
Developing Your Outline
- Your outline is the tool that turns dissertation writing from a stressful “big task” into a clear step-by-step workflow.
- Start with your required structure (chapters and sections), then add subheadings under each chapter so you always know what to write next.
- For each section, write:
- The purpose (what this part must prove or explain)
- 3–6 key bullet points (main ideas and evidence to include)
- A target number of words (to control word count and avoid drifting)
- Keep the thesis visible at the top of the outline so every paragraph supports the argument and maintains clarity.
- Use the outline to prevent procrastination: when you sit down to start writing, you are not deciding what to do—you are executing.
- A strong outline also improves productivity because it reduces distraction and stops you from rewriting the same ideas.
- This is essential when you are aiming for a dissertation in two weeks, a dissertation in just two weeks, or a word dissertation in 2 weeks plan, because it helps you write a dissertation fast without sacrificing academic standards.
Want to learn how to write a dissertation? Start here, and if you need support, Best Dissertation Writers provides top-notch dissertation writing services.
Week One: Research and Initial Writing
- Week one is about building momentum and generating a solid draft, not perfection.
- Begin by confirming your thesis, research questions, and the exact dissertation format your department expects.
- Collect and organise sources immediately so you do not waste time later searching randomly under pressure.
- Create a simple reference system (one document or software library) and record every citation as you go to avoid late stage chaos.
- Focus your writing time on high word count chapters first, especially the literature review and early methodology, because they are easier to draft quickly from sources.
- Aim to hit your words a day target consistently; for a write a 10000 plan in two weeks, consistent output beats occasional “marathon” sessions.
- Avoid heavy edit work in week one—write fast, keep paragraphs simple, and leave polishing for week two.
- Reduce distraction by working in timed blocks, using your outline to guide each section, and stopping only after you complete a small chunk.
Writing Your Dissertation Introduction
- Your introduction tells the reader exactly what your dissertation is about and why it matters, so it must be clear and direct.
- Start with a focused background: define the topic area and the specific problem your dissertation addresses.
- State the purpose of the study and what you are trying to achieve (objectives).
- Present your thesis or central argument early so the reader understands your direction from the first page.
- Add your research questions (or hypotheses) in bullet form to create clarity and keep the scope controlled.
- Briefly explain what methods you used and why they are appropriate, without turning the introduction into a methodology chapter.
- End with a short “roadmap” sentence that tells the reader what each chapter covers.
- When writing a dissertation in two weeks, you can draft the introduction quickly now, then refine it later once the full draft is complete—this helps you save time to write while still meeting academic standards.
Building Your Thesis Statement
- Your thesis is the central claim or argument that the entire dissertation must support.
- A strong thesis gives clarity, prevents unproductive detours, and keeps your word count focused.
- Write your thesis in one or two sentences that clearly state:
- What your study is about
- What position you are taking or what relationship you are examining
- What you expect to show through evidence
- Test your thesis with a quick check: every chapter and section should answer “How does this support the thesis?”
- If a paragraph does not support the thesis, remove it or move it to notes—this saves time to write and reduces editing later.
- When writing a dissertation fast, keep your thesis visible (top of your outline or document) so you stay organised and avoid distraction.
- You can refine the thesis after the analysis chapter is drafted, but you must keep a working thesis from Day 1 to complete your dissertation within a short timeframe.
Week Two: Complete Your Dissertation
- Week two is about finishing the remaining chapters, tightening the argument, and preparing a complete dissertation for submission.
- Start by completing any unfinished sections from week one, then move in order: analysis/findings, discussion, conclusion, and final updates to the introduction.
- Protect your writing time daily and keep hitting your words a day target, but shift your focus from “creating” to “completing.”
- Use your outline to check that every chapter links back to the thesis and stays within the correct word count.
- Avoid adding new sources unless absolutely necessary; too much new research in week two causes distraction and slows progress.
- Reserve dedicated blocks to edit and proofread, fix grammar, confirm spelling, and check that every reference is correctly matched to in-text citations.
- This is the stage where format and layout must be cleaned up: headings, subheadings, page numbers, spacing, and required academic standards.
- By the end of week two, you should be able to say you complete your dissertation within the deadline, not just “almost done.”
Writing a Dissertation Fast
- Writing a dissertation fast is not about rushing blindly; it is about using a controlled system that protects quality while meeting a short timeframe.
- First, set your non-negotiables: the deadline, the required format, and the total word count (example: 10000 for a 10000 word dissertation).
- Convert the goal into daily output: if you are aiming for a dissertation in two weeks, you must commit to consistent words a day and treat writing time like scheduled work.
- Use “draft-first” rules to beat procrastination:
- Write rough paragraphs quickly without stopping to edit
- Use subheadings to keep each section focused
- Mark gaps with placeholders and continue (do not freeze)
- Reduce distraction to protect productivity:
- One tab for sources, one document for writing
- Notifications off, phone away
- Timed writing blocks with short breaks
- Avoid “one sitting” perfection attempts; fast completion comes from repeated focused sessions, not a single marathon.
- Keep your thesis visible to maintain clarity and prevent unproductive detours that inflate word count without improving argument strength.
- Track progress daily: chapter completed, section drafted, number of words produced, references added.
- If you are in a late stage push, prioritize completion first, then return to edit and proofread for grammar, spelling, and academic standards.
- This approach is the practical way to complete your dissertation and get your dissertation finished as a word dissertation in 2 weeks plan—especially if you need a dissertation within days or less before submission.
The Complete Writing Phase
- The complete writing phase is where you turn separate drafts into one coherent dissertation that meets academic standards.
- Your goal here is not to “add more,” but to make the dissertation read like a single connected argument from introduction to conclusion.
- Start by checking structure and flow:
- Does every chapter connect back to the thesis?
- Do section transitions make sense, or do they feel like unrelated notes?
- Are subheadings consistent and aligned with your outline?
- Control word count deliberately:
- Remove repeated explanations and filler paragraphs
- Tighten long sentences that reduce clarity
- Keep each section close to its target number of words
- Strengthen the argument:
- Add topic sentences that clearly state the point of each paragraph
- Ensure evidence is explained, not just listed
- Link findings to the literature instead of leaving them isolated
- Protect quality while moving fast:
- Avoid rewriting everything from scratch (this becomes unproductive)
- Fix the biggest issues first: missing sections, weak logic, unclear thesis alignment
- Keep referencing accurate:
- Every claim that needs support should have a reference
- Confirm the reference list matches in-text citations exactly
- Confirm format and layout early:
- Headings, spacing, page numbers, tables/figures if used
- Required institutional style rules for the dissertation
- This phase is essential for a dissertation in just two weeks because it prevents late stage confusion and helps you complete your dissertation within the deadline instead of submitting an unfinished draft.
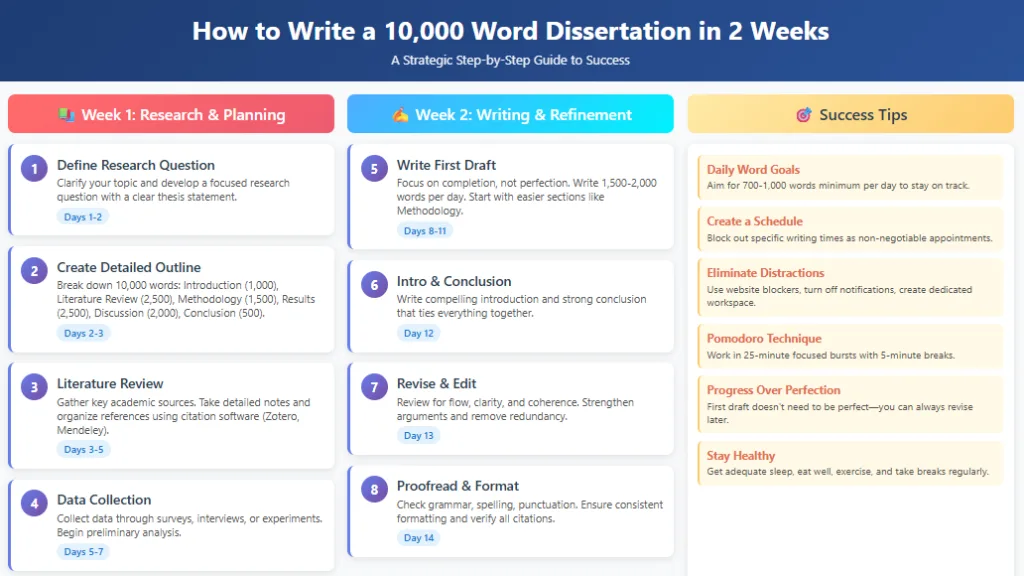
Strategies for Completing Your Dissertation in Two Weeks
- To complete your dissertation in two weeks, you need a repeatable system that prevents procrastination and protects productivity.
- Use this step-by-step approach:
- Step 1: Lock the scope — confirm your thesis, research questions, and chapter requirements so you do not expand the project late stage.
- Step 2: Plan backwards — build a detailed plan from the deadline and assign each day a chapter or section target.
- Step 3: Hit daily output — set words a day targets based on the number of words needed (example: a 10000 word dissertation in 2 means daily writing must be consistent).
- Step 4: Draft fast, then refine — separate drafting from editing so you do not get stuck rewriting early paragraphs.
- Use “minimum viable draft” rules to stay moving:
- Write the main idea first, then add evidence, then tighten language later
- Use placeholders for missing citations and return to fix them
- Keep each section aligned to word count to avoid over-writing
- Reduce distraction aggressively:
- Work in timed blocks
- Use a clean workspace and a single writing document
- Limit internet browsing to planned research windows
- Prioritize the highest-impact chapters:
- Literature review and analysis typically drive more words quickly
- Save introduction polishing for after the body is drafted
- Build accountability:
- Track your word dissertation progress daily
- Use a checklist: chapter drafted, references added, section complete
- Plan quality checks inside the timeframe:
- Reserve time to edit, proofread, fix grammar and spelling, and confirm reference accuracy
- These strategies help you complete your dissertation within a short time and make a dissertation in just two weeks realistic—even if you need it done days or less before submission.
The Edit and Proofread Stage
- The edit and proofread stage is where your draft becomes a submission-ready dissertation that meets academic standards.
- Separate editing into layers so you do not waste time fixing small issues while bigger problems remain:
- Layer 1: Structure and clarity (edit first)
- Confirm every chapter supports the thesis and answers the research questions
- Check that each section follows a logical order and does not repeat points
- Ensure subheadings match your outline and guide the reader clearly
- Remove unproductive paragraphs that do not add evidence or analysis
- Layer 2: Argument strength (refine next)
- Strengthen topic sentences so every paragraph has a clear purpose
- Improve transitions between sections so the dissertation reads smoothly
- Add explanation after evidence (do not “drop” quotes or studies without linking them to your point)
- Layer 3: Technical accuracy (proofread last)
- Correct grammar, spelling, and punctuation
- Check consistency in terms, tense, and academic tone
- Ensure formatting and layout follow department rules (margins, headings, spacing, numbering)
- Confirm word count targets are met across sections and chapters
- Reference checks (non-negotiable)
- Every in-text citation must appear in the reference list
- Every reference list entry must be cited in the text
- Ensure citation style is consistent across the dissertation
- For a dissertation in two weeks, do not attempt to rewrite everything during editing. Focus on high-impact improvements that increase clarity and quality quickly.
- A careful edit and proofread phase is what makes a 10000 word dissertation in 2 weeks believable and professional, not rushed.
Tips for Dissertation in Two Weeks Success
- Success with a dissertation in two weeks depends more on discipline than intelligence. You must execute daily, even when motivation is low.
- Use these practical tips to stay consistent and avoid procrastination:
- Protect your writing time
- Block a fixed time to write every day and treat it like an appointment
- Remove distraction: phone away, notifications off, only essential tabs open
- Use timed work sessions to maintain productivity
- Stay organised and clear
- Keep your outline visible so you always know the next section to write
- Keep your thesis visible so every paragraph supports the main argument
- Track progress by chapter, section, and word count so your work feels measurable
- Control word count and pace
- Set words a day targets based on the number of words needed (example: write a 10000 plan requires consistent output)
- Avoid over-writing early chapters; stay within your target number of words
- If you fall behind, recover by adding small extra blocks, not all-nighters
- Avoid perfection traps
- Draft first, then refine—do not edit heavily while drafting
- Accept that the first draft will be imperfect, but it must be complete
- Use placeholders and return later to fix missing citations or unclear lines
- Improve quality efficiently
- Reserve time to edit and proofread for grammar, spelling, and consistency
- Read sections aloud to catch awkward sentences and weak clarity
- Seek feedback on the highest-risk parts only (thesis, argument logic, structure)
- With determination and a detailed plan, you can complete your dissertation within a short time and still meet academic standards—even if you are working late stage and the deadline is close.
Working with a Dissertation Writer
- Working with a dissertation writer can be helpful when the timeframe is tight, especially if you are aiming for a dissertation in two weeks or a dissertation in just two weeks.
- The safest and most effective use of a writer is support-based, so you still produce your own work and meet academic standards.
- What a dissertation writer can help with (appropriate support)
- Clarifying your thesis and improving overall clarity of the argument
- Building a detailed plan and helping you organise the writing schedule
- Refining your outline, subheadings, and the structure of each section
- Reviewing chapter flow and identifying gaps or repetition
- Helping you improve grammar and spelling through feedback
- Checking format and layout consistency and pointing out missing elements
- Providing guidance on how to write with stronger academic style and logic
- How to work with a writer efficiently in two weeks
- Share your outline, required word count, and the exact deadline from Day 1
- Ask for targeted feedback on the highest-impact areas (introduction, thesis, and argument structure)
- Submit one chapter at a time for review to keep the workflow moving
- Use the feedback to refine your draft quickly rather than rewriting everything
- Important quality controls
- Ensure every reference and citation is accurate and consistent
- Do not allow last-minute edits to change meaning or introduce errors
- Keep version control so you do not lose the most recent draft
- A good writer support system can reduce unproductive cycles and help you complete your dissertation within a short time, but you still must start writing early, follow your schedule, and commit to edit and proofread before submission.

Finalizing Your Complete Dissertation
- Finalizing is the last quality-control stage where you confirm your dissertation is complete, coherent, and submission-ready.
- Treat this as a checklist process, not a rewriting session, especially if you are finishing a dissertation in two weeks.
- Confirm completeness and structure
- Ensure every required chapter is present and clearly labeled
- Check that each section follows the outline and uses consistent subheadings
- Verify the introduction matches what the dissertation actually does
- Confirm the conclusion answers the research questions and reflects the thesis
- Word count and pacing checks
- Review total word count and confirm it meets requirements (example: 10000)
- Check the number of words per chapter so one chapter does not dominate
- Cut repeated points to improve clarity and keep the dissertation within target limits
- Reference and citation audit (critical)
- Ensure every in-text citation appears in the reference list
- Ensure every reference list entry is cited in the text
- Check consistency in citation style and formatting
- Verify quotations, page numbers (if required), and author dates are correct
- Edit and proofread final pass
- Fix grammar, spelling, punctuation, and formatting inconsistencies
- Confirm numbering (pages, tables, figures, headings) is correct
- Review layout requirements: margins, spacing, font, and title page rules
- Submission readiness
- Save your final file in the correct format (for example, PDF or Word)
- Name the file correctly based on your institution’s rules
- Do a final read-through of the first and last page for professionalism
- This step ensures you do not submit a draft that looks rushed. It is what turns a 10000 word dissertation in 2 weeks into a polished final product that meets academic standards and feels complete.
Conclusion
- A dissertation in two weeks is demanding, but it is achievable when you follow a structured system instead of relying on last-minute pressure.
- The fastest path to success is to start writing early, organise your tasks, and use an outline to break the writing process into manageable chunks.
- If your target is a 10000 word dissertation, you must control word count daily by setting words a day goals and protecting your time to write from distraction.
- Draft first, then refine: complete each chapter, then edit and proofread for clarity, grammar, spelling, and consistent reference use.
- Stay disciplined, follow your schedule, and avoid unproductive perfectionism that slows progress.
- Whether you are completing an undergraduate dissertation or late stage thesis work, the same rule applies: clear planning plus consistent execution leads to completion.
- If you apply these steps, you can complete your dissertation within a short timeframe and submit a complete, professional dissertation in just two weeks—often with days or less to spare before the deadline.
