What is the Expectancy Theory of Motivation?
What is the basic idea behind expectancy theory?
- The expectancy theory of motivation explains how individuals make decisions regarding their behavior based on the expected outcomes of their actions.
- This theory assumes that people are motivated to engage in certain behaviors when they believe that their effort will lead to a desired outcome.
- It suggests that motivation is a result of a rational calculation based on the belief that effort will lead to performance, and the performance will lead to the desired outcome.
- The expectancy theory model asserts that an individual’s effort, performance, and outcomes are all interrelated in determining their level of motivation.
- Victor Vroom’s expectancy theory highlights how an individual’s motivation depends on three key factors: expectancy, instrumentality, and valence.
Professional Dissertation Writing Help
Struggling with your dissertation? Let Best Dissertation Writers help you craft a high-quality, research-backed paper. Our experts ensure your success—get in touch today to start your journey toward academic excellence.
How does Victor Vroom define motivation?
- Victor Vroom’s expectancy theory defines motivation as the result of a cognitive process where individuals assess the probability that their efforts will lead to the desired performance and, in turn, result in an outcome they value.
- According to Vroom, motivation is a product of the individual’s belief that:
- Their effort will lead to improved performance.
- This performance will, in turn, lead to an expected outcome.
- The outcome is valued based on personal goals and incentives, which increases motivation.
- The motivational force is the product of these factors: expectancy, instrumentality, and valence.
- As Wiley and others suggest, the strength of an individual’s motivation is influenced by their perceived likelihood of success and the value they place on the outcome.
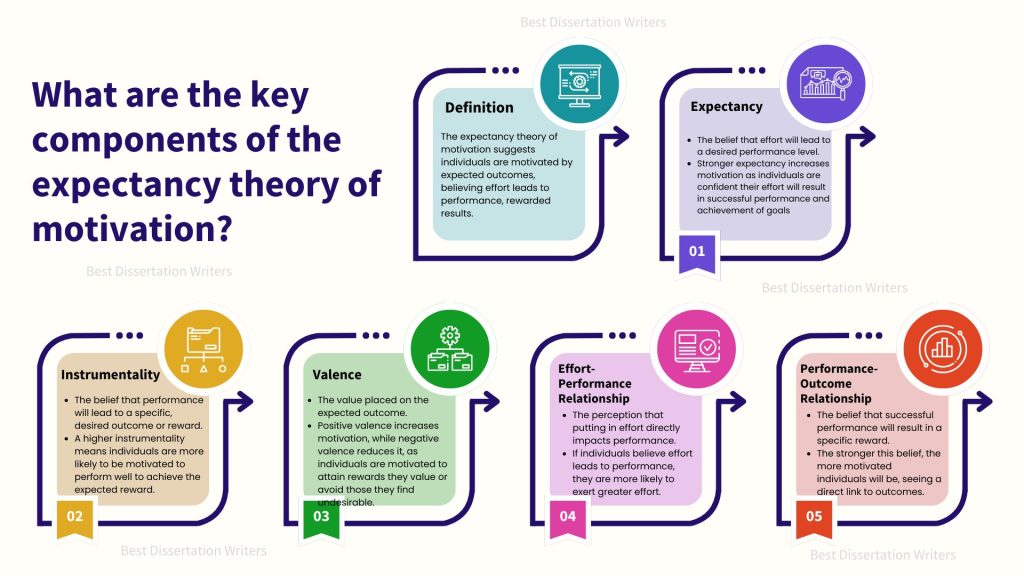
What are the key components of the expectancy theory of motivation?
- Expectancy: This is the belief that one’s effort will lead to performance. If a person believes that their effort will improve their performance, they are more likely to be motivated to engage in that activity.
- Instrumentality: This is the belief that good performance will lead to a particular outcome or reward. If individuals believe that their performance will lead to the desired results, they are more likely to exert effort.
- Valence: The value that a person places on the expected outcome. If the expected results of their performance align with their personal goals or rewards, the motivation to perform is stronger.
- Outcome expectancy: This refers to the belief that the effort will result in a particular outcome. If individuals expect a positive outcome from their efforts, their motivation will increase.
- Expectancy violations theory: This theory focuses on how deviations from expectations, such as an outcome that does not meet the anticipated result, can influence motivation.
The expectancy theory of motivation is often used in organizational settings to understand how managerial decisions can impact employee motivation and performance. By aligning individual goals with organizational goals, motivation theory can be applied to increase motivational efforts within businesses.
The expectancy theory explains that individuals are motivated when they believe their efforts will lead to successful outcomes that help them achieve their goals. According to the Yale School of Management, understanding expectancy theory helps managers create environments where employees believe their hard work will result in positive rewards.
How do the Three Components of Expectancy Theory Work?
What is expectancy in Vroom’s model as a management theory?
- Expectancy in Vroom’s model, as part of the expectancy theory of motivation, refers to the belief that one’s effort will lead to a specific level of performance.
- The expectancy theory of motivation states that if an individual believes their effort will result in successful performance, they are more likely to put in the necessary effort to achieve that goal.
- In management, ensuring that employees believe their effort will lead to positive performance is crucial to increasing motivation and productivity.
- Victor H. Vroom developed the expectancy theory of motivation, which suggests that individuals will be motivated if they perceive a direct connection between their effort and the expected outcome.
- To enhance expectancy, managers should provide employees with the necessary tools and resources, utilizing business intelligence and information systems to track progress and feedback.
How does instrumentality influence motivation?
- Instrumentality refers to the belief that successful performance will lead to a valued outcome. According to the expectancy theory of motivation, instrumentality influences motivation by linking performance with rewards.
- If an individual believes their performance will directly result in a reward, their motivation will increase. However, instrumentality is low when employees feel that their efforts won’t be recognized or rewarded appropriately.
- The expectancy theory of motivation emphasizes that the performance leads to rewards only when employees perceive a clear connection between their actions and the rewards they will receive.
- Managers can boost instrumentality by ensuring that rewards are tied directly to specific behavior and performance expectations, creating clearly defined goals and reward systems.
- The model includes a system of tracking performance and providing transparent feedback, so employees understand how their performance expectation is met and what rewards to expect.
- Edward Lawler and other scholars have conducted meta-analysis on instrumentality, showing that employees are more motivated when the instrumentality of rewards is high.
What role does valence play in achieving desired outcomes?
- Valence refers to the value or desirability of the outcome. The expectancy theory of motivation states that if individuals place high valence on an outcome, they will be more motivated to achieve it.
- Valence and instrumentality are closely related—individuals choose actions based on the perceived value of the outcome and the belief that their actions will lead to it. The higher the valence, the more likely the behavior will lead to a motivational force.
- If the reward is positive, employees are more likely to be motivated. If the reward is negative or terrible, they may not put in the effort needed to achieve the desired performance.
- Managers should consider what employees value, and ensure that rewards align with those desires. By co-creation of goals and rewards, managers can increase valence, making outcomes more desirable.
- The expectancy theory of motivation suggests that individuals perceive rewards differently, and the performance expectation must align with what the person values for motivation to be effective.
- By understanding the desirability of rewards, managers can optimize motivation by offering rewards that are both valued outcomes and aligned with employees’ performance expectations.
The expectancy theory of motivation works by linking effort, performance, and outcomes through the components of expectancy, instrumentality, and valence. Managers can apply this theory by ensuring that employees perceive a clear connection between their effort and performance and are offered valued outcomes for their success.
How Can the Expectancy Theory of Motivation Be Applied in Management?
How can managers use expectancy theory to motivate employees?
- Expectancy theory of motivation provides a framework for managers to increase motivation by focusing on the relationship between effort, performance, and rewards.
- Managers should use systems that clearly link an employee’s effort to expected performance, and performance to desired outcomes.
- By ensuring that individuals may believe their effort-performance relationship is achievable, managers can increase the motivation to perform well.
- Expectancy theory suggests that when employees perceive a high likelihood that their efforts will lead to a positive outcome, they are more likely to be motivated to work hard.
- Managers can improve instrumentality by ensuring that rewards are guaranteed for achieving specific performance goals, making it clear that performance leads to the desired outcome.
- VIE theory (Valence, Instrumentality, Expectancy) suggests that managers should provide positive reinforcement for desired behavior and create rewards that align with individuals’ goals and values.
- By understanding Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, managers can align rewards with employees’ personal values, ensuring that the reward is something they find desirable.
- Managers can motivate employees by understanding how individuals choose their actions based on the anticipated rewards and intended performance.
What insights can leaders gain from Vroom’s expectancy theory?
- Vroom’s expectancy theory provides key insights into organizational behavior theories by focusing on how individuals’ beliefs about effort, performance, and rewards shape their motivation.
- Leaders can gain insight to impact employee behavior by understanding that motivation is not just about rewarding good performance but ensuring that employees perceive the connection between effort and rewards.
- By applying the expectancy theory of motivation, leaders can develop systems where employees perceive clear effort-performance and performance-reward relationships.
- Leaders can gain insight into the behavioral intentions of their teams, understanding that individuals will be motivated to engage in behaviors because of their expected outcomes.
- This insight can help managers adjust their leadership approach to address gaps in instrumentality or expectancy and to improve overall motivation within their teams.
- Understanding decision to act in response to perceived rewards helps managers tailor their approach based on the individuals may differ in what they value.
- Leaders should use the expectancy theory of motivation to foster a motivational environment by aligning individual goals with organizational rewards.
What are the challenges likely to be faced by managers and leaders when using Vroom’s expectancy theory?
- Managers may face challenges in ensuring that the effort-performance relationship is clear and realistic for all employees.
- Some individuals might have different perceptions of what is achievable, leading to misalignments in motivation.
- If instrumentality is low, employees might not see a clear connection between their performance and rewards, resulting in decreased motivation.
- Managers should use systems that provide ongoing feedback and communication to address these gaps and help employees understand how their effort leads to performance and rewards.
- Perceived difficulty of tasks can also create a barrier. If the task seems too difficult or if employees believe their effort will not lead to a successful outcome, their motivation can decline.
- The theory states that behavior will lead to outcomes only if individuals perceive that the effort required is within their capabilities. Addressing behavioral change through training and support is essential for leaders to overcome this barrier.
- Employees may be motivated to study or pursue personal goals, but managers must ensure that the performance expectation is met with realistic rewards that align with the employee’s values.
- The expectancy theory of motivation can be terrible it must be applied without understanding individual differences, so managers should ensure they recognize unique motivational drivers within their teams.
- Vroom’s theory also highlights the need for co-creation of goals and rewards to keep motivation high and maintain performance expectations.
What are the Implications of Vroom’s Theory for Client Success?
How does understanding expectancy lead to client satisfaction?
- The expectancy theory of motivation helps organizations understand how to align client expectations with the services they deliver. When clients expect that their needs will be met efficiently, they are more likely to be satisfied.
- According to Vroom’s theory, when clients believe that their effort (or their engagement with a service or product) will lead to a positive outcome, their satisfaction increases. This understanding can guide how businesses interact with clients to build trust and provide value.
- Managing director at the decision lab suggests that understanding expectancy allows businesses to create clear expectations for clients, ensuring they know what outcomes to expect and how their needs will be addressed.
- By choosing one clear path for delivering services and managing expectations effectively, businesses can improve client engagement and satisfaction based on the expectancy theory of motivation.
- Clients are more likely to engage with services or products if they believe that their efforts will lead to a favorable outcome. In essence, the effort-performance connection directly impacts client trust and satisfaction.
What strategies can organizations implement based on the expectancy theory?
- The expectancy theory of motivation highlights that individuals make decisions based on the belief that effort will lead to success. Organizations can apply this by ensuring their services and products align with client expectations.
- Co-founder and managing director of several successful startups suggests that businesses must create clear, achievable goals and promises for clients to ensure they feel their efforts will lead to the desired outcomes.
- Organizational behavior theories indicate that aligning product quality with client expectations will ensure that businesses see repeat engagement. When clients see that the company’s promises are met, they feel their involvement was worth the effort.
- Organizations can use the expectancy theory of motivation to implement strategies like customer education, transparent communication, and tailored experiences to ensure clients believe their investments (whether time or money) will yield results.
- By ensuring that outcomes align with expected results, businesses can avoid positive or negative surprises and foster long-term client loyalty.
What are Common Misunderstandings about Expectancy Theory?
What myths exist around Victor Vroom’s theory?
- A common misunderstanding about the expectancy theory of motivation is that it only applies to employee motivation, when in fact it can be applied to client behavior as well.
- Some believe that expectancy theory assumes all people are motivated solely by rewards, overlooking the choices among intrinsic and extrinsic motivations, which the theory does take into account.
- Myth: People think that Vroom’s theory is simply about setting goals for clients, but in reality, it’s about aligning effort with expected outcomes. The theory suggests that motivation is a decision-making process where people evaluate effort, performance, and rewards.
- Another misconception is that expectancy theory only deals with performance, when it is equally concerned with perceived difficulty and how achievable a goal is for the individual or group.
How can these misconceptions impact work motivation?
- Misunderstandings around the expectancy theory of motivation can negatively impact work motivation because employees or clients may feel their efforts will not be adequately rewarded or recognized.
- If people do not understand that the theory emphasizes effort-performance relationships, they may become disengaged because they perceive their efforts are futile or too difficult to achieve.
- When instrumentality (the belief that performance will lead to rewards) is misunderstood, employees or clients might feel that their work or engagement will not lead to the expected rewards, lowering their motivation and satisfaction.
- People ask if expectancy theory is too simplistic, but it is important to recognize the complexity of aligning both intrinsic and extrinsic motivations.
What’s Next After Learning About Expectancy Theory?
What resources are available for those eager to learn more?
- After learning about the expectancy theory of motivation, there are many resources to dive deeper, including academic journals, books, and case studies that explore how this theory has been applied in various industries.
- One great starting point is Vroom’s original work on the expectancy theory of motivation, which explores its theoretical underpinnings. Resources like BCom in decision-making courses and organizational behavior theories workshops also provide valuable insights.
- The latest in technology and topics in places like online platforms and research databases offer accessible readings and video content explaining how VIE theory applies in modern workplaces.
How can you apply these insights to achieve your goals?
- To apply the insights from Vroom’s expectancy theory, individuals can start by choosing one clear, measurable goal to focus on. Understanding how effort-performance expectations are aligned with personal or organizational goals helps improve motivation and success.
- As you move forward, it’s essential to directly correlate your efforts with achievable outcomes and adjust strategies if the expected results aren’t met. This will improve both personal and organizational performance.
- Use the expectancy theory of motivation to manage expectations, focus on clear rewards, and enhance your work behavior. This approach can help achieve a 52-week performance goal or similar long-term objectives in both professional and personal settings.
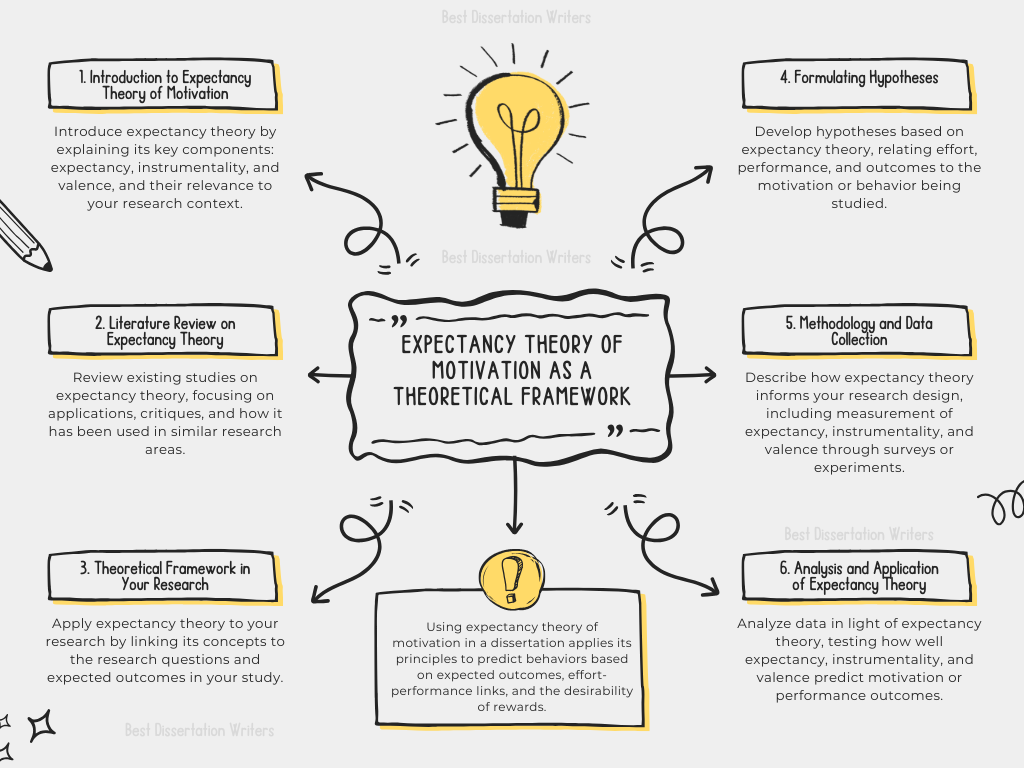
Using Expectancy Theory of Motivation as a Theoretical Framework in a Dissertation
Using the Expectancy Theory of Motivation as a theoretical framework in a dissertation involves applying the principles of the theory to understand, explain, and predict the behaviors of individuals (or groups) within a particular context. The Expectancy Theory of Motivation, proposed by Victor Vroom, asserts that people are motivated to act based on the expected outcomes of their behavior, the desirability of those outcomes, and the likelihood that effort will lead to successful performance. Below is an outline on how to structure this framework in your dissertation:
1. Introduction to Expectancy Theory of Motivation
- Definition: Start by introducing the Expectancy Theory of Motivation, providing a brief explanation of its key components: expectancy, instrumentality, and valence.
- Expectancy: The belief that effort will lead to a desired level of performance.
- Instrumentality: The belief that good performance will lead to a specific reward or outcome.
- Valence: The value placed on the expected outcome.
- Theory Background: Discuss Victor Vroom’s contribution and the significance of this theory in understanding human motivation, especially in organizational settings.
- Relevance to Dissertation: Explain why this theory is a suitable framework for your dissertation topic. Highlight how it can help to understand the motivations behind particular behaviors or outcomes relevant to your study.
2. Literature Review on Expectancy Theory
- Foundations of the Theory: Provide an in-depth review of literature regarding the development of the Expectancy Theory of Motivation and its evolution over time. Mention key research papers, studies, and critiques of the theory.
- Applications in Various Fields: Showcase how the theory has been used in diverse areas such as organizational behavior, employee motivation, leadership, and even in client motivation (depending on your research focus).
- Key Studies and Models: Analyze key studies that have applied expectancy theory in similar contexts. Highlight the results and conclusions drawn from these studies to set a foundation for your dissertation.
Expert Essay Writing Services
Need an exceptional essay? Best Dissertation Writers provides custom essays tailored to your requirements. Our experienced writers deliver top-notch content. Reach out now and get your essays done by professionals!
3. Theoretical Framework in Your Research
- Contextualizing the Theory: Discuss how the Expectancy Theory of Motivation will apply to your research context (e.g., employee behavior, organizational practices, consumer behavior, etc.). For example, if your dissertation is about organizational behavior, explain how expectancy theory can predict employees’ motivation levels based on the effort-performance and performance-outcome relationships.
- Formulating Hypotheses: Use expectancy theory to formulate hypotheses related to your research objectives. For example:
- Hypothesis 1: Higher levels of expectancy will lead to higher motivation among employees.
- Hypothesis 2: A strong perception of instrumentality will increase the likelihood of employees performing well.
- Hypothesis 3: A higher valence attached to the outcome will improve overall motivation and performance.
4. Methodology and Data Collection
- Research Design: Explain how the expectancy theory of motivation will guide your research design. Whether you’re using qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods, discuss how you will measure key components such as effort, performance, and outcomes.
- Measurement Tools: Use surveys, interviews, or experiments to collect data. Develop questions or instruments that assess expectancy, instrumentality, and valence in relation to your study’s context.
- Sample Selection: Describe how you will select your sample (e.g., employees, consumers) and justify why this group is appropriate for testing the theory.
5. Analysis and Application of Expectancy Theory
- Data Analysis: Explain the methods you will use to analyze the data, such as statistical tools for hypothesis testing, thematic analysis, etc.
- Interpretation of Results: After collecting the data, interpret the results in light of expectancy theory. Analyze whether the relationships between effort, performance, and outcomes hold true in your specific research context.
- Linking Back to Theory: Discuss how the findings support, refute, or extend the expectancy theory of motivation. Show how your results contribute to existing literature and what new insights they provide.
6. Conclusion
- Summary of Findings: Summarize how the application of expectancy theory has contributed to answering your research questions and achieving your dissertation objectives.
- Practical Implications: Based on your findings, discuss the practical implications of using expectancy theory in your area of research (e.g., managerial practices, policy recommendations, customer engagement strategies).
- Limitations and Future Research: Identify any limitations in using expectancy theory as a framework and suggest areas for future research to extend or refine the theory’s application.
By effectively incorporating expectancy theory into your dissertation, you can provide a robust theoretical foundation to analyze motivation in a variety of contexts, whether it’s employee behavior, customer satisfaction, or other areas where motivation plays a significant role.
