What is Social Learning Theory?
- Social Learning Theory is a psychological concept that explains how people learn from one another through observation, imitation, and modeling. It suggests that learning can occur in a social context, without the need for direct reinforcement or punishment. The theory emphasizes the importance of cognitive processes in learning, showing how individuals can acquire new behaviors and skills by observing others.
Who developed Social Learning Theory?
- Albert Bandura, a Canadian-American psychologist, developed social learning theory in the 1960s. His work led to the creation of Bandura’s Social Learning Theory, which has significantly influenced organizational behavior theories and various learning processes. Bandura’s social learning theory suggests that humans can learn through observing others, especially in social environments, rather than only through direct personal experiences.
- Bandura’s research highlighted the role of observational learning, which is central to social learning theory. He demonstrated that people do not need to experience events firsthand in order to learn new behaviors—seeing others perform behaviors can be enough.
Professional Dissertation Help
Get expert assistance from Best Dissertation Writers to craft a top-quality dissertation. Our team provides tailored support at every stage, ensuring your success. Contact us today for reliable dissertation writing services!
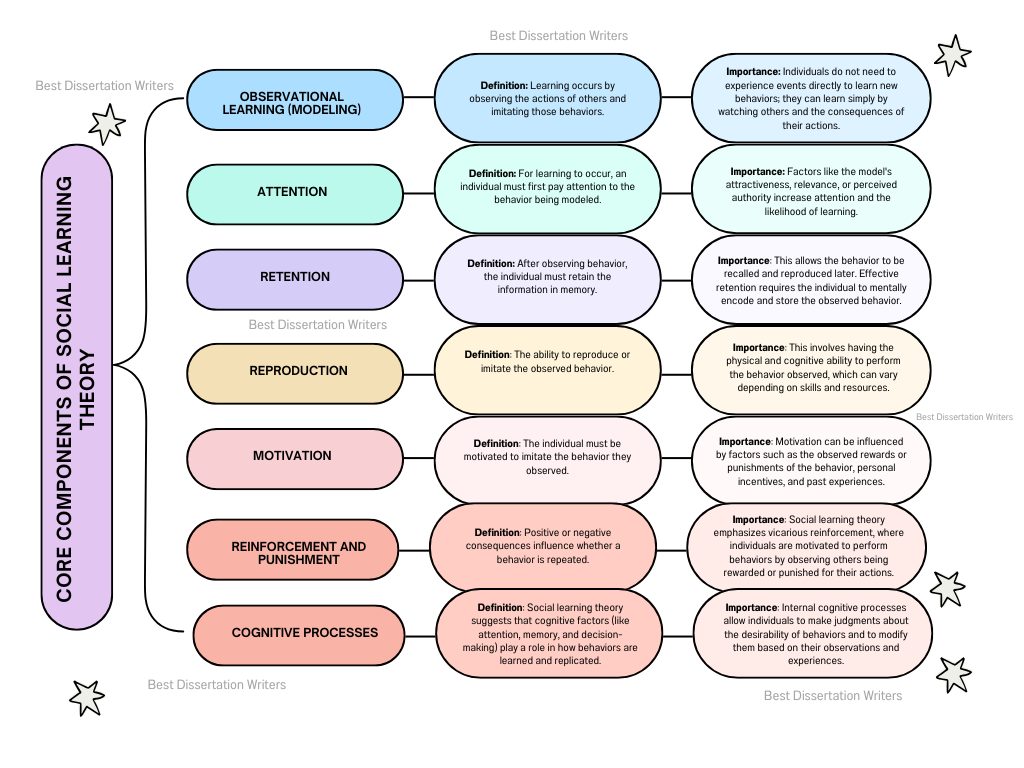
What are the core components of Social Learning Theory?
- Observational Learning: Central to social learning theory, observational learning occurs when an individual observes the actions of others and imitates their behavior. This process is often referred to as learning and imitation. In this context, the social environment plays a significant role, as individuals tend to learn from the people they interact with.
- Imitation and Modeling: Social learning theory also highlights how people imitate the behaviors of others they observe. This concept emphasizes that learning occurs when individuals replicate observed behaviors, often mimicking those actions within the same social or work environment.
- Reinforcement and Punishment: While social learning theory doesn’t require direct rewards for learning, Bandura’s social learning theory suggests that reinforcement can influence the likelihood of a behavior being repeated. If a behavior is followed by positive reinforcement, an individual is more likely to repeat it, while punishment may reduce the behavior’s frequency.
- Cognitive Learning: Bandura’s work also suggests that cognitive processes are essential in understanding how learning occurs. Social learning theory emphasizes how individuals think about the behaviors they observe, and this cognitive aspect impacts the likelihood of learning a new behavior.
How does Albert Bandura’s work influence this theory?
- Albert Bandura’s Social Learning Theory has had a lasting impact on learning theorists and the field of psychology. His work in 1977 further shaped the development of social learning theory and its application in various fields, including education, therapy, and organizational behavior.
- Bandura’s theory works by showing how individuals can learn from social behavior around them. He proposed that learning is an active process where individuals not only observe but also process the information and make decisions about whether or not to imitate the behavior they’ve observed.
- Bandura’s social learning theory suggests that learning and behavior are influenced by factors like attention, retention, reproduction, and motivation. His theory also highlights how social workers and educators can use social learning to help individuals develop new skills or change unwanted behaviors.
Social learning theory offers a comprehensive approach to understanding how individuals learn within a social context, with significant contributions from Albert Bandura’s research on observational learning, imitation, and the cognitive aspects of the learning process.
How Does Observational Learning Fit into Social Learning Theory?
- Observational learning is a central concept in social learning theory. It suggests that learning occurs through watching the actions of others, particularly in a social context. This form of learning doesn’t require direct interaction with the environment, but instead relies on observing others’ behaviors and their outcomes. It highlights the importance of observational learning in understanding human behavior and its role in social learning theory.
What is the process of Observational Learning?
- Observational learning, also known as vicarious learning, involves four main processes:
- Attention: The individual must first pay attention to the behavior being demonstrated. This is influenced by factors like the observer’s interest or the observer’s relationship to the person performing the action.
- Retention: After observing a behavior, the individual must retain the information in memory in order to reproduce the behavior later. This process involves cognitive functions and memory.
- Reproduction: The individual must have the ability to reproduce the observed behavior. This means the person must have the physical and mental capability to perform the action.
- Motivation: The individual is more likely to imitate a behavior if there is a perceived reward or reinforcement. Learning theory suggests that people are motivated to engage in behaviors based on the outcomes they have observed.
Can you provide examples of Observational Learning?
- Social learning theory is visible in everyday life, and examples of observational learning include:
- Children learning to speak: Children observe and imitate the language used by their parents or peers, demonstrating how social learning theory helps individuals acquire complex skills like communication.
- Workplace learning: Employees often observe colleagues to learn job tasks or social behaviors, showcasing examples of social learning theory within organizational behavior theories.
- Media influence: Watching characters in TV shows or movies can lead individuals to imitate certain behaviors, especially when these behaviors are reinforced or result in positive outcomes.
How do people learn through observation in social contexts?
- Social learning theory emphasizes that people learn through social interactions. According to Bandura, human learning often takes place in a social environment, where individuals absorb knowledge from observing others.
- Role of social context: Learning theory proposes that individuals learn by interacting within social and cultural contexts. For instance, in social work or psychological theory, the social environment influences learning and behavior patterns.
- Bandura’s theory posits that the social support and feedback from others are crucial in determining whether the learned behavior will be adopted. This interaction shapes the individual’s response and actions, reinforcing the learning process.
- Learning and behavioral outcomes: The theory shows that learning can lead to changes in both social behavior and cognitive development. Learning theory suggests that observation allows individuals to assess the consequences of behavior before trying them themselves.
- Social learning theory in 1977 laid the foundation for understanding how human learning is mediated by social experiences, emphasizing the importance of social context in the learning process.
Observational learning plays a pivotal role in social learning theory, which explains how individuals learn by observing the behaviors of others in their social environment. Whether in everyday life, work settings, or media consumption, social learning theory provides valuable insights into the mechanisms of learning.
What are the Principles of Social Learning According to Albert Bandura?
- Social learning theory, developed by psychologist Albert Bandura, is one of the most influential theories in psychology. The theory explains how individuals learn from their social environment through observation, imitation, and modeling. Below, we explore the core principles of social learning theory as proposed by Bandura.
What does social learning theory propose about behavior?
- Social learning theory proposes that behavior is learned through social interaction, rather than solely through personal experience or environmental stimuli, as suggested by behaviorist learning theories.
- According to Bandura, people learn new behaviors by observing others, particularly role models. This is a significant aspect of social learning theory.
- Learning theory suggests that people learn by watching others and noting the consequences of those behaviors, which may lead them to imitate or avoid certain actions based on their observations.
- Social learning theory explains that behaviors can be acquired without the learner directly experiencing the consequences. Instead, they can observe social behavior and internalize it.
- Bandura’s theory highlights the importance of cognitive learning in this process, where individuals process and understand the behaviors they observe before deciding whether to replicate them.
How do social interactions influence learning?
- Social learning theory emphasizes that learning from our social experiences is essential for personal and cognitive development. Learning theory in everyday life often occurs within the social environment, where individuals witness and engage with various behaviors.
- According to Bandura, social interactions play a vital role in how people learn because they provide models for behavior. Social interactions allow individuals to understand the consequences of actions in a social context.
- The role of social interactions is highlighted in social learning theory as individuals imitate behaviors they observe within their environment, whether at home, work, or school.
- Social learning theory in 1977 further emphasizes that social contexts and relationships significantly affect learning. People are more likely to imitate behavior from individuals they find important or influential in their social circles.
What role does reinforcement play in learning theory?
- Reinforcement is a central concept in Bandura’s social learning theory, though the theory suggests that social learning is not immediate. Instead, reinforcement serves to strengthen or weaken the likelihood of a behavior being repeated in the future.
- Reinforcement can come in two forms:
- Direct reinforcement: The individual is directly rewarded for their behavior, which increases the likelihood that they will repeat the action.
- Vicarious reinforcement: An individual observes someone else being rewarded for a behavior, and this influences the observer to imitate that behavior, even without direct reinforcement.
- Social learning theory explains that both positive reinforcement (rewards) and punishment can shape behavior. However, Bandura noted that individuals might also choose to replicate behaviors that are not immediately reinforced if they anticipate future rewards.
- This principle of reinforcement shows the power of social influences in shaping behavior, where individuals learn from social experiences and anticipate consequences through observation.
Social learning theory by Albert Bandura provides an understanding of how people learn through social interactions, reinforcement, and observing others. It remains a foundational concept in psychology, explaining how we acquire behaviors based on the social environment and social experiences. This theory also has practical applications in social work and various fields, offering insights into human behavior and learning mechanisms.
How is Social Learning Theory Applied in Social Work?
- Social learning theory offers a valuable framework for understanding how individuals acquire behaviors and skills within a social environment, making it particularly useful in social work. By applying social learning theory, social workers can develop strategies that encourage positive behavior change and provide interventions that are based on social experiences and observational learning.
What are the practical implications of Social Learning Theory in social work?
- Social learning theory helps social workers understand how clients learn behaviors from their social environment. By recognizing the importance of social interactions, social workers can apply social learning theory principles to improve treatment outcomes.
- Learning theory suggests that people learn through social and cultural experiences, so social workers can use social learning theory to design interventions that focus on the social contexts of their clients. This can include fostering positive social networks and relationships that promote healthy behaviors.
- Social learning theory provides a way for social workers to use social learning theory to promote change through modeling behaviors. For example, social workers can model healthy coping strategies, communication skills, or problem-solving techniques for clients to observe and imitate.
- Theory in action: In social work, social learning theory can be applied in therapeutic settings where clients learn from observing others. This can include group therapy or peer support programs, where individuals share experiences and model constructive behaviors.
- Social workers can use social learning examples to help clients understand the impact of their actions on others and how social reinforcement can shape future behavior.
How can practitioners use Albert Bandura’s insights?
- Bandura’s insights into social learning theory are pivotal for social workers looking to facilitate behavior change. His social cognitive theory emphasizes the role of cognitive processes, which can be integrated into treatment plans for clients.
- Social learning theorists like Sears and Albert Bandura propose that behaviors are influenced by observing others, and this insight can help social workers focus on social support systems that can serve as positive role models.
- Social workers can apply Bandura’s social learning theory by encouraging clients to observe and interact with positive role models who exhibit constructive behavior. This creates an environment where direct social reinforcement plays a significant role in improving client outcomes.
- Social workers can also use Bandura’s insights to educate clients on how learning theory is based on the observation of others’ actions and the consequences that follow. This can help clients understand their ability to change through modeling and reinforcement.
What are the challenges of applying Social Learning Theory in social work?
- Social learning theory is not without its challenges in social work. One challenge is that learning theory is that learning through observation is not always immediate, and it may take time for clients to internalize and replicate desired behaviors.
- Differential association theory within social learning theory suggests that people learn from the social environment, but if clients are exposed to negative role models, this could reinforce undesirable behaviors instead of encouraging change.
- Social workers can use social learning theory effectively, but they must carefully consider the areas of social influences, such as family dynamics or peer groups, which may undermine progress.
- Psychoanalytic theory may also compete with the social learning theory in some social work contexts, especially when clients have deeply ingrained emotional issues that cannot be addressed through simple observation or modeling alone.
Social learning theory is an important theory in social work, offering valuable tools for promoting positive change through social support, modeling, and reinforcement. However, social workers face challenges when applying the theory, particularly when clients’ social environments do not support constructive behaviors. By understanding and overcoming these challenges, practitioners can use social learning theory to effectively address behavioral issues and promote lasting change in clients’ lives.
What are the Criticisms of Social Learning Theory?
- Social learning theory has been widely influential, but like any psychological theory, it has faced several criticisms. Below are some of the main critiques and limitations of Bandura’s social learning theory.
What are the main critiques of Bandura’s theory?
- Overemphasis on observational learning: One major critique of social learning theory is that it places too much emphasis on observational learning. Critics argue that learning theory should also account for other aspects of learning, such as cognitive processes or emotional development, which may not always be captured by simply observing others.
- Simplification of human behavior: Social learning theory simplifies human behavior by focusing primarily on social and environmental influences. Some critics believe that this neglects the complexity of human internal processes, such as motivation, emotions, and individual decision-making, which are crucial in understanding behavior.
- Limited focus on biological factors: Social learning theory largely ignores biological factors and genetic predispositions that can play a significant role in human behavior. This limitation makes it less comprehensive when compared to other theories, such as learning theory and behavioral theories, which often emphasize the interaction between biological, cognitive, and environmental factors.
- **Lack of emphasis on intrinsic motivation: Social learning theory tends to emphasize extrinsic motivation (such as rewards and punishments), potentially overlooking intrinsic motivation—the natural desire to engage in a behavior for its own sake. Critics argue that this is a significant limitation in understanding how people learn.
How does Social Learning Theory compare to other learning theories?
- Comparison with behaviorism: Unlike behaviorist learning theories, which focus solely on stimulus-response mechanisms and external reinforcement, social learning theory incorporates cognitive processes, suggesting that people learn through observation and imitation. This introduction to social learning theory offers a broader view of learning.
- Comparison with cognitive learning theories: While social learning theory shares some principles with cognitive learning theories, such as the role of internal processes in learning, it differs by emphasizing the social environment. The theory argues that learning theory comes from psychology, especially by incorporating the idea that people learn by seeing and imitating others. Social learning theory focuses more on behavioral aspects, while cognitive theories focus on internal mental processes, such as memory and perception.
- Social theory versus psychoanalytic theory: Psychoanalytic theory delves into unconscious processes and childhood experiences, which are not a significant focus in social learning theory. Critics argue that social learning theory oversimplifies behavior by not accounting for deep-seated psychological processes.
What limitations exist in social learning theory?
- Not applicable to all types of behavior: Social learning theory has been criticized for not accounting for behaviors that are difficult to explain through observation and imitation alone. For example, many social behaviors that stem from deep-seated personal experiences may not be easily explained by the principles of social learning theory.
- Limited applicability in real-world settings: Social learning theory is often criticized for its limited applicability in real-world situations, especially in social work and community settings. Although social learning theory in everyday life can be observed in many contexts, some behaviors are deeply ingrained and may require more than just observational learning to change.
- Challenges in measurement: Social learning theory is difficult to measure objectively, as social learning theory often focuses on internal cognitive processes that cannot be directly observed. This can create difficulties when trying to quantify or measure the learning theory in terms of tangible outcomes or behaviors.
- Theory goes beyond what is observable: Some argue that social learning theory does not adequately explain why certain behaviors are learned in different social settings. It assumes that all learning is a result of social interactions, but does not always consider other factors like individual experience or genetic predisposition.
While social learning theory provides valuable insights into how we learn through social environments, it is not without its criticisms. Its focus on observation and imitation has been challenged for oversimplifying human behavior and ignoring biological and emotional factors. However, social learning theory remains an influential important theory in psychology and social theory, especially in understanding the role of social environments in shaping behavior.
How Can We Apply Social Learning in Our Daily Lives?
- Social learning theory offers valuable insights into how we can learn from others through observation, modeling, and interaction. By understanding the principles of social learning theory, we can apply these ideas to improve our daily lives, whether in personal development, professional growth, or social interactions.
What strategies can enhance learning experiences?
- Leverage observational learning: Social learning theory suggests that people can learn by watching others. To enhance your learning experiences, surround yourself with individuals who exhibit behaviors you want to model, whether in work, relationships, or personal habits.
- Modeling positive behavior: According to Bandura, we tend to replicate behaviors that we observe in others, especially if those behaviors result in positive outcomes. So, it’s important to find role models who embody the qualities you wish to develop, like strong communication skills or healthy habits.
- Create a supportive environment: By fostering a social environment where learning can take place, you can benefit from the power of social learning theory. Engaging with peers or mentors who encourage positive behaviors helps create a dynamic where growth is more likely.
How can social observation benefit personal development?
- Social observation is a powerful tool for personal development because it allows you to learn not just through direct experience, but also through observing the behaviors of others.
- Learning from mistakes and successes: Social learning theory shows that we can learn by watching others succeed or fail. For example, by observing how someone manages a difficult situation or handles stress, you can adopt similar strategies to improve your own response.
- Increase self-awareness: Observing others in social settings helps you reflect on your own behavior. Social learning theory emphasizes the role of self-regulation in learning, which includes evaluating how your behaviors align with the outcomes you desire.
- Benefit from social modeling: Bandura’s social learning theory shows that social observation helps individuals develop critical thinking and emotional intelligence by watching how others handle various social situations, offering important theory for managing personal and professional relationships.
What are effective ways to learn through observation?
- Identify effective role models: The first step in learning through observation is finding individuals who exhibit behaviors or skills you admire. This can include mentors, leaders, or even peers.
- Actively engage with social interactions: Instead of simply observing, engage in conversations and situations where you can learn. Social learning theory suggests that active participation helps strengthen the connection between observation and imitation.
- Analyze and reflect: After observing a behavior or situation, take time to reflect on what you learned. What made the behavior effective or not? Social learning theory emphasizes the importance of processing observed behaviors and understanding their consequences.
- Apply and adjust: Once you observe something valuable, implement it in your own life. Learning theory suggests that learning is more likely to be retained when individuals actively apply observed behaviors and adjust them as necessary.
Social learning theory offers powerful tools for learning from others through observation and modeling. By applying strategies like observing effective role models, engaging in meaningful social interactions, and reflecting on observed behaviors, we can enhance personal development and foster growth in various areas of life. This approach is not only grounded in psychological theory, but also practical for improving our daily experiences and interactions.

How to Use Social Learning Theory as a Theoretical Framework in a Dissertation
Using social learning theory as a theoretical framework in a dissertation provides a structured approach to examining how people learn from their social environment. Below is a guide on how to effectively use social learning theory in your dissertation:
1. Introduction to Social Learning Theory
- Define social learning theory: Start by explaining what social learning theory is and its relevance to your dissertation topic. You can describe how the theory, originally proposed by Albert Bandura, explains how people learn behaviors, attitudes, and social norms through observation, imitation, and modeling.
- Connect to your research: Introduce how social learning theory will guide your research and why it is an appropriate theoretical framework for your study. For example, if your dissertation involves understanding behavior change, social learning theory provides insights into how individuals learn new behaviors through social interactions.
2. Literature Review
- Review past research: Explore how social learning theory has been used in previous studies relevant to your dissertation topic. This could include research on behavior change, education, social work, or psychology. You can also include examples of social learning theory in everyday life and its application in different contexts.
- Identify gaps: Highlight areas where the theory has not been fully explored or where there is room for further application, which your dissertation will address.
3. Concepts and Constructs of Social Learning Theory
- Introduce key concepts: Describe the main concepts of social learning theory, such as:
- Observational learning: Learning through observing others.
- Modeling and imitation: Copying behaviors seen in role models.
- Reinforcement: How behaviors are strengthened or weakened through rewards or punishments.
- Cognitive processes: How mental processes influence learning from observation.
- Explain relevance: Clarify how these concepts will inform your analysis and help in interpreting your findings.
4. Application of Social Learning Theory in Your Research
- Research questions: Frame your research questions or hypotheses around social learning theory. For example, if your dissertation focuses on the impact of social interactions on behavior change, you could use social learning theory to explore how observing others’ behavior influences individual decisions.
- Methodology: Explain how you will collect data that aligns with social learning theory. For example, if you’re studying behavior in a social group, you might use qualitative methods like interviews or observations to understand how participants learn from their peers. Quantitative methods could involve surveys to assess the impact of observed behaviors.
- Analysis: Analyze how participants’ behaviors can be explained through the lens of social learning theory. Look for patterns of imitation, modeling, reinforcement, and cognitive processing. You could use Bandura’s work on the role of observational learning in shaping behavior to guide your analysis.
Top-Notch Essay Writing
Need a well-written essay? Best Dissertation Writers offers expert essay writing services that guarantee high-quality, plagiarism-free content. Let us help you impress your professors—reach out now for customized writing solutions!
5. Discussion of Findings
- Interpret findings through the theory: Once you have collected and analyzed data, discuss your findings in relation to social learning theory. For example, did participants model the behaviors of individuals with high social influence? Did reinforcement play a role in the behavior change? How do your findings align with or contradict Bandura’s social learning theory?
- Implications: Discuss how your research contributes to the understanding of learning within a social context and how it extends or challenges existing social learning theory literature.
6. Limitations of Social Learning Theory
- Critiques and limitations: Acknowledge the criticisms and limitations of social learning theory, such as its focus on external behaviors and the possible neglect of internal psychological factors like intrinsic motivation or emotions. Address how these limitations might impact your research.
7. Conclusion
- Summary of contributions: Conclude by summarizing how social learning theory provided a robust theoretical framework for your research and how it helped explain the observed behaviors or phenomena. Discuss how your findings contribute to the broader field of social learning theory.
By following this structure, you will effectively incorporate social learning theory as a theoretical framework in your dissertation. This approach will ensure your research is grounded in established theory, while also allowing you to explore new insights in your chosen field.
