Introduction to Blue Ocean Strategy
- The Blue Ocean Strategy is a revolutionary business approach introduced by Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne. It focuses on creating uncontested market space that makes competition irrelevant.
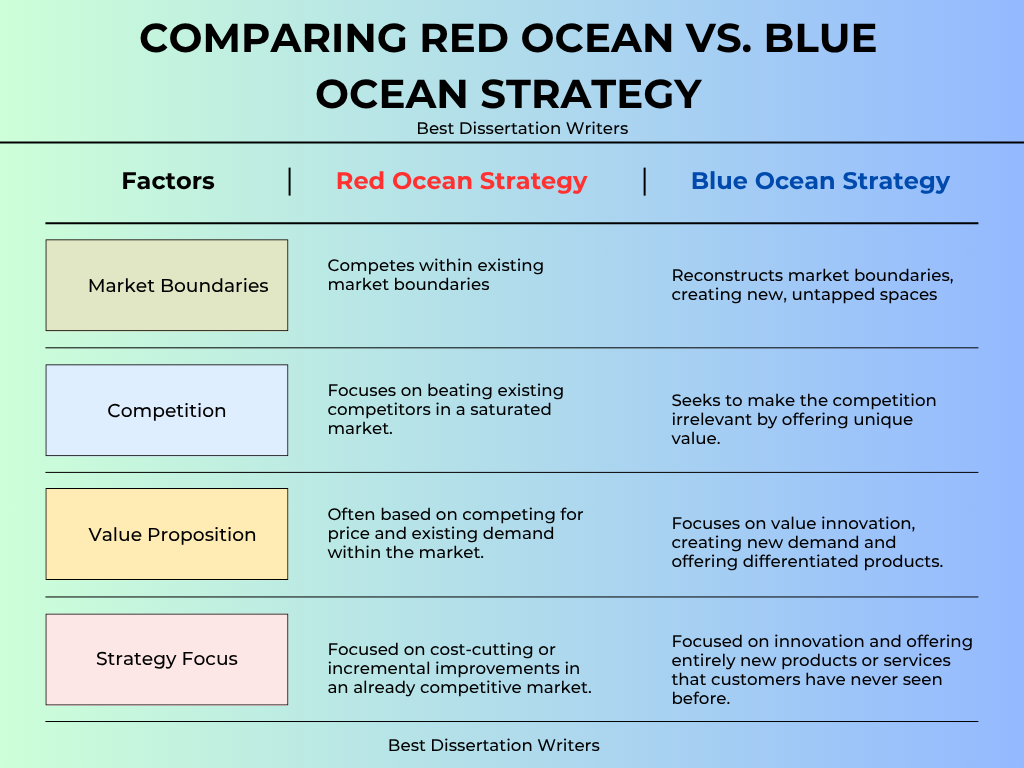
- The Blue Ocean Strategy contrasts with traditional approaches that often emphasize fighting over existing market space in a red ocean of competition.
- By using the Blue Ocean Strategy, businesses can create and capture new demand, offering innovative products or services that differentiate them from rivals.
- This strategic move aims to make the competition irrelevant by offering customers new and unique value propositions.
Professional Dissertation Writing Help
Get expert assistance from Best Dissertation Writers to craft a top-tier dissertation. Our team ensures high-quality, plagiarism-free work tailored to your requirements. Contact us today for reliable and timely service!
Defining Blue Oceans and Red Oceans
- Red Oceans represent the existing market space, where companies fight for market share in a saturated environment. The competition in a red ocean of rivals is intense, leading to price wars and limited growth.
- In contrast, Blue Oceans refer to untapped market spaces where demand is created, and companies innovate to make the competition irrelevant. This can be achieved by breaking traditional market boundaries and creating new demand.
- The Blue Ocean Strategy emphasizes that instead of competing in an already bloody red ocean, companies should create blue oceans where they can create new demand and attract new customers.
The Importance of Shifting from Red Ocean to Blue Ocean
- Shifting from a red ocean strategy to a blue ocean shift is vital for long-term success. By transitioning to blue oceans within the market, companies can avoid the constant battle with rivals and instead focus on differentiation and innovation.
- The concept of blue ocean highlights the need to reconstruct market boundaries, allowing businesses to tap into new opportunities where competition is minimal, and growth is more sustainable.
- The key to creating a blue ocean is identifying gaps in the market and offering a unique product or service that has not been fully explored. By doing so, companies don’t just beat the competition; they render it irrelevant.

Overview of Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne’s Framework
- Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne are regarded as two of the most influential management thinkers in the world. Their framework, outlined in their iconic and impactful strategy book, “Blue Ocean Strategy,” offers a structured approach for businesses to create blue oceans.
- Their framework focuses on differentiation and low cost, combining elements that traditionally were seen as opposing strategies. This new strategy allows companies to achieve differentiation while keeping costs low, making it a blue ocean approach to business growth.
- In their research, Kim and Mauborgne examined how successful companies create new blue oceans and how they challenge the traditional notion of competing in the existing market.
- The Blue Ocean Strategy encourages businesses to reconstruct market boundaries, opening up new possibilities and allowing them to create and capture new demand. It’s a shift from competing in a bloody red ocean of rivals to exploring untapped blue oceans with immense growth potential.
Key Components of Blue Ocean Strategy
- The Blue Ocean Strategy emphasizes creating value in untapped market space, often referred to as blue ocean opportunities, where competition is irrelevant. This strategy goes beyond the typical red ocean of rivals fighting for market share and focuses on creating and capturing blue oceans of new demand.
Identifying Uncontested Market Space
- The principles of blue ocean strategy focus on identifying and exploring unknown market space that is untainted by existing competition.
- The Blue Ocean Strategy encourages businesses to look for blue ocean opportunities where there are few, if any, competitors. By identifying uncontested market space, companies can provide unique products or services that meet the needs of customers who are not currently being served.
- This approach is crucial for companies seeking to avoid the cutthroat competition found in the red ocean of rivals fighting for dominance in an overcrowded market.
- Real-world examples, such as Apple’s introduction of the iPhone, showcase how companies can gain uncontested market space by developing innovative products that open up entirely new markets.
Creating New Market Space and Making Competition Irrelevant
- The Blue Ocean Strategy helps companies create new market space that is untainted by competition, leading to a situation where competition is irrelevant.
- Rather than trying to beat the competition, the goal is to create a blue ocean idea that attracts new customers through differentiation, value, and innovation. The strategy focuses on breaking free from the limitations of the known market space to develop a new blue ocean that does not rely on battling with existing players.
- The strategy models in Harvard Business Review’s publication on the Blue Ocean Strategy suggest that companies should reconstruct the boundaries of their industries, challenging the red and blue ocean divide.
- By doing so, organizations can create another blue ocean, offering products or services that capture the attention of customers in new, innovative ways.
Value Innovation: The Cornerstone of Blue Oceans
- Value innovation is the cornerstone of the Blue Ocean Strategy. It involves creating a product or service that is both differentiated and cost-effective, thus providing value to the consumer while keeping production costs low.
- The core idea is to offer customers value that is different from what is currently available in the market. This approach allows businesses to create new demand and avoid competing with the red ocean of rivals.
- Harvard Business highlights that value innovation helps businesses tap into entirely new market segments, while strategy execution is key to ensuring that these opportunities are successfully captured. By focusing on both differentiation and cost leadership, companies can open up blue ocean opportunities where the competition is irrelevant.
Custom Essay Writing Services
Need help with your essays? Best Dissertation Writers offer custom, high-quality essays written to meet your specific guidelines. Get in touch now and ensure your academic success with our expert writing services!
Strategy Tools for Creating Your Blue Ocean
- The Blue Ocean Strategy offers various tools to help businesses create and capture blue oceans by identifying and implementing blue ocean opportunities. These tools focus on shifting away from the red ocean of rivals fighting and instead encourage companies to innovate and differentiate in uncontested market spaces.
- In business books such as “Blue Ocean Strategy” by Renée Mauborgne, the authors provide several strategies and frameworks designed to help businesses successfully navigate the blue ocean shift.
The Strategy Canvas: Mapping Your Competitive Landscape
- The Strategy Canvas is one of the key tools within the Blue Ocean Strategy. It provides a visual representation of the competitive landscape, helping businesses to understand where they currently stand in their market.
- This tool allows companies to identify the current factors that competitors focus on and spot opportunities for creating and capturing blue oceans. By analyzing the space and making the competition irrelevant, businesses can find areas where they can innovate and stand out.
- The Blue Ocean Strategy encourages companies to use the Strategy Canvas to map their value curve, which can highlight untapped potential and help create a blue ocean idea that breaks free from traditional competitive constraints.
The Four Actions Framework: Eliminate-Reduce-Raise-Create
- The Four Actions Framework is a key part of the Blue Ocean Strategy, guiding businesses to rethink their approach to industry factors. This framework asks companies to:
- Eliminate factors that the industry takes for granted but no longer add value.
- Reduce factors that are over-emphasized in the industry.
- Raise factors that are underappreciated but could create significant value.
- Create factors that the industry has never offered before, creating new demand.
- By applying this framework, companies can differentiate themselves and craft a new blue ocean, where competition is irrelevant.
- The Four Actions Framework aligns with the overarching goal of the Blue Ocean Strategy: to break free from the red ocean of competition and focus on innovation to develop a unique value proposition.
Utilizing the Buyer Utility Map
- The Buyer Utility Map is another essential tool in the Blue Ocean Strategy, designed to help businesses understand how they can deliver greater value to customers.
- This map focuses on the entire buyer experience, from the point of purchase to post-purchase use, allowing companies to identify areas where they can improve customer satisfaction and provide new utility.
- By identifying and capitalizing on blue ocean opportunities, companies can innovate in ways that competitors have overlooked. The map highlights where businesses can offer new utility and create a blue ocean that offers consumers more value than existing solutions in the market.
- With Renée Mauborgne’s insights from the Blue Ocean Strategy, the Buyer Utility Map can be used to reconstruct market boundaries and make the competition irrelevant by meeting unmet customer needs and creating entirely new market spaces.
Practical Tips for Implementing Blue Ocean Strategy
- The Blue Ocean Strategy is a powerful tool for businesses aiming to create and capture new demand by shifting from the red ocean of competition to blue oceans of untapped market space. To implement this strategy effectively, it is essential to approach it with a systematic plan. Below are practical tips for businesses looking to apply the Blue Ocean Strategy successfully.
Conducting Market Research to Identify New Market Opportunities
- The Blue Ocean Strategy begins with thorough market research to uncover opportunities in untapped market space. Understanding customer needs, preferences, and gaps in existing offerings is key.
- By analyzing current market trends, businesses can identify areas where competition is weak or non-existent, thus revealing blue ocean opportunities.
- Research should focus on uncovering blue ocean opportunities that competitors have overlooked, allowing businesses to create blue oceans that offer unique value.
- Businesses must look beyond the red ocean of rivals fighting for market share and focus on innovative ideas that can attract entirely new customers and create new demand.
Engaging Stakeholders in the Strategy Development Process
- One of the key components of the Blue Ocean Strategy is engaging stakeholders throughout the strategy development process. This ensures that everyone is aligned with the vision of creating new, uncontested market space.
- Renée Mauborgne and Chan Kim, in their impactful strategy book, emphasize that involving stakeholders in the creation of a blue ocean idea allows for the integration of diverse perspectives and expertise, which enhances the development of innovative solutions.
- Engaging stakeholders from various levels of the organization also helps in overcoming resistance to change and ensures strategy execution is smoother and more efficient.
- By working collaboratively, businesses can avoid being trapped in the red ocean of competitors and instead focus on creating value that makes the competition irrelevant.
Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators for Blue Oceans
- To successfully implement the Blue Ocean Strategy, businesses must set clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure progress and success.
- These KPIs should focus on growth metrics such as market share in the new space, customer acquisition rates, and the level of differentiation compared to existing competitors.
- The goal is to track whether the company is moving away from the red ocean of traditional competition and establishing a new blue ocean.
- Metrics should also assess how effectively a company has differentiated its offerings and whether it is meeting previously unmet customer needs, thus achieving the value innovation that the Blue Ocean Strategy is known for.
- Harvard Business highlights the importance of tracking both short-term and long-term success in the new market space to ensure that strategy execution is aligned with the ultimate goal of making the competition irrelevant.
By focusing on these practical tips, businesses can successfully implement the Blue Ocean Strategy and open up entirely new market spaces that deliver lasting success.
Examples of Blue Ocean Strategy in Action
- The Blue Ocean Strategy has been implemented by various companies to escape the red ocean of fierce competition and create uncontested market spaces. Below are some real-world examples that demonstrate how this strategy has been applied successfully, as well as insights into where it has failed.
Case Study: Cirque du Soleil as a Blue Ocean Example
- Cirque du Soleil is one of the most well-known examples of the Blue Ocean Strategy in action. Instead of competing in the traditional circus industry, which was heavily constrained by the red ocean of competition (other circuses), Cirque du Soleil created a new market space by blending circus arts with theater and live music.
- By eliminating the traditional elements of a circus, such as animals, and focusing on adult audiences with more sophisticated performances, Cirque du Soleil was able to create blue oceans where it could thrive without the need to compete with other circuses. This strategic move made the competition irrelevant.
- As Renée Mauborgne and Chan Kim discuss in their impactful strategy book, “Blue Ocean Strategy,” Cirque du Soleil innovated and differentiated itself in ways that allowed it to gain uncontested market space in the entertainment sector, fundamentally changing how people viewed and engaged with live performances.
Innovative Companies Pioneering New Market Spaces
- Many innovative companies have successfully embraced the Blue Ocean Strategy to pioneer new market spaces. For example:
- Apple revolutionized the music and mobile phone industries with its introduction of the iPod and iPhone, creating entirely new market spaces where competition was minimal. By combining differentiation with value innovation, Apple made the competition irrelevant.
- Tesla is another prime example. Instead of competing with traditional automakers in the crowded red ocean of the automobile market, Tesla created a blue ocean by pioneering electric vehicles that offered unique features like longer battery life and autonomous driving capabilities.
- Amazon changed the retail industry by creating a new market space through e-commerce and cloud computing, offering services that were innovative and distinct from existing retail models.
Lessons Learned from Failed Blue Ocean Strategies
- While the Blue Ocean Strategy can lead to incredible success, it is important to recognize that not all attempts to create blue oceans succeed. Some companies have failed to effectively execute the strategy due to various factors.
- One example is Kodak, which failed to fully embrace digital photography in time, despite having the technology. Kodak’s slow adoption of blue ocean opportunities allowed competitors to take the lead, leaving Kodak stuck in the red ocean of traditional film.
- Another example is Blockbuster, which missed the opportunity to innovate and move into the online streaming space, allowing companies like Netflix to create a blue ocean and make the competition irrelevant in the video rental industry.
- These examples highlight the importance of strategy execution and timely recognition of blue ocean opportunities. Without careful planning and market research, companies may fail to shift from the red ocean to a blue ocean, missing the chance to innovate and lead in new markets.
By studying these examples, businesses can learn how the Blue Ocean Strategy can lead to success when properly executed, and also recognize the risks associated with failing to adapt to blue ocean opportunities.
Conclusion: Embracing the Blue Ocean Mindset
- The Blue Ocean Strategy offers businesses an invaluable approach to escaping the red ocean of competition and finding uncontested market spaces. By adopting the blue ocean mindset, companies can shift from merely trying to beat the competition to creating innovative, value-driven solutions that make the competition irrelevant.
- Embracing this mindset requires companies to look beyond traditional industry boundaries and reimagine their products, services, and customer experiences in ways that have not been explored. Renée Mauborgne and Chan Kim’s framework, outlined in one of the most impactful strategy books ever written, empowers businesses to make bold strategic moves and create and capture new demand.
The Future of Business Strategy
- The future of business strategy lies in continuous blue ocean shifts—finding and capitalizing on blue ocean opportunities before competitors even see them. As markets become more saturated, businesses that cling to traditional models may struggle, while those embracing the Blue Ocean Strategy will be the ones that innovate, thrive, and lead in new sectors.
- The future of business strategy will require organizations to not just be reactive to competition, but proactive in identifying blue ocean spaces where they can introduce new demand, redefine industries, and make the competition irrelevant.
- In a world of increasing technological advancements and global connectivity, the ability to create new market spaces and solve previously unmet needs will become the hallmark of successful businesses.
Trusted Dissertation Support
Struggling with your dissertation? Best Dissertation Writers provides comprehensive, professional writing services to help you succeed. Our experts deliver exceptional work that meets all your academic needs. Reach out for assistance today!
Final Thoughts on Creating Uncontested Market Space
- Creating uncontested market space is more than just a strategic goal; it is a transformative approach to business that prioritizes innovation, differentiation, and value creation. The Blue Ocean Strategy offers businesses a pathway to not just survive but thrive in environments where competition is fierce and traditional approaches no longer work.
- By implementing the principles of the Blue Ocean Strategy, companies can discover new demand that sets them apart and propels them into the future, leaving behind the bloody red ocean of rivals.
Encouragement to Shift Towards Blue Oceans
- It’s time for businesses to take the leap and shift towards blue oceans. The strategies outlined in the Blue Ocean Strategy have been proven to work, and companies that embrace this mindset will not only make the competition irrelevant, but will also create lasting, impactful success.
- The blue ocean mindset calls for companies to be bold, embrace innovation, and remain agile as they explore new opportunities. For those ready to embark on this journey, the Blue Ocean Strategy offers the tools, frameworks, and inspiration to leave the red ocean behind and lead in untapped, profitable markets.
By embracing the Blue Ocean Strategy, companies can craft their future, find fresh opportunities, and redefine the way they engage with customers.
