Understanding the Dissertation Outline and Its Importance
A dissertation outline is a structured plan that helps guide your dissertation writing process. It serves as a blueprint for organizing your ideas, arguments, and research findings into coherent chapters and sections. In this section, we will explore the significance of a dissertation outline, how to create one, and common mistakes to avoid.
Expert Dissertation Writing Help
Need top-quality dissertation writing assistance? Our team of Best Dissertation Writers is here to guide you through every step. Get professional support today and submit a dissertation that stands out!
What is a Dissertation Outline and Why is it Crucial?
- A dissertation outline is a roadmap for your entire dissertation. It helps you to visualize the flow of your research and organize it systematically.
- The dissertation outline gives your work structure and allows you to break the process into manageable tasks. This makes it easier to focus on each section, ensuring that you don’t miss important details.
- A dissertation outline is crucial because it helps in:
- Defining the dissertation topic and narrowing down your research question.
- Setting the order of the chapters and sections, including the methodology chapter, literature review, and conclusion.
- Organizing the data collection process and research design to ensure alignment with your goals.
- Highlighting key arguments and maintaining focus on your hypothesis or problem statement.
- Preventing writer’s block by giving you a clear direction to follow.
- Using a dissertation outline helps prevent common mistakes like misalignment between the chapters, lack of relevant literature, and plagiarism. By clearly defining headings and subheadings, it ensures the argumentative aspect of your work remains coherent and relevant throughout.
How to Organize Your Dissertation Outline Effectively
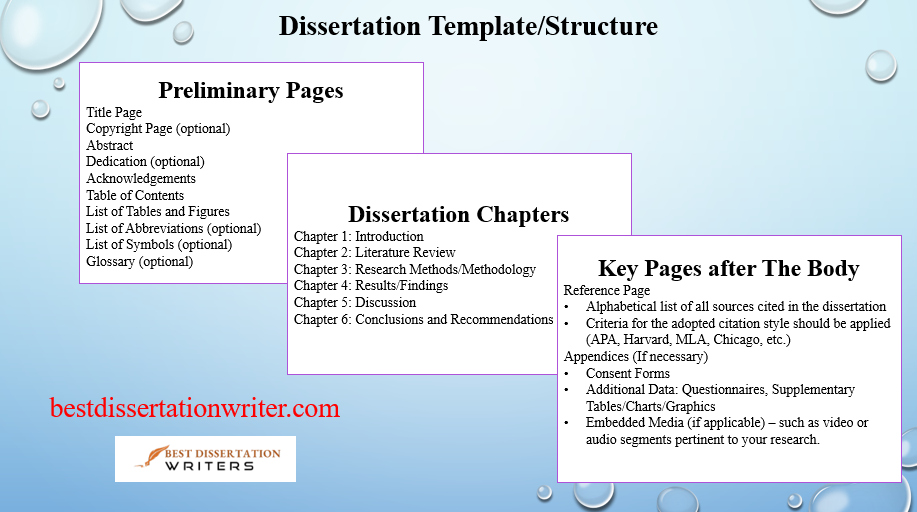
- Start with the Title Page:
- The first part of your dissertation outline should include your title page, which should have the dissertation title, your name, and the title of your supervisor or dissertation chair. Ensure the title is concise and clearly reflects the research topic.
- Abstract:
- Write a brief summary of your dissertation, including the research aim, methodology, and conclusions. The abstract in your dissertation outline will help you focus on the key aspects of your work.
- Table of Contents:
- This section is vital as it will outline all the chapters and subheadings of your dissertation, with appropriate page numbers. Use this section as a quick reference guide during writing.
- Introduction (Chapter 1):
- The introduction is the first chapter of your dissertation outline, where you introduce your problem statement and state the research question.
- The overview of your research and the aim of the dissertation should also be included in this chapter.
- This chapter sets the tone and context for the entire dissertation, explaining the relevance of the dissertation research in the field of study.
- Literature Review (Chapter 2):
- The literature review is a vital part of your dissertation outline as it summarizes and critically analyzes the relevant literature.
- This chapter should include a conceptual framework and a discussion of theoretical perspectives that support your research.
- Incorporate the relevant literature to establish the theoretical framework that grounds your research and justifies the study.
- Methodology (Chapter 3):
- In this chapter, define your methodology—whether it is qualitative or quantitative.
- Discuss the research design, data collection methods, and instrumentation used for your study.
- Include the justification for choosing the research method and outline how the research will be conducted and analyzed.
- Findings and Discussion (Chapter 4):
- This chapter will present your dissertation research results. You should include figures and tables that display your data findings.
- Discuss the findings in light of the existing literature and show how your results contribute to the problem statement and hypothesis.
- Conclusion (Chapter 5):
- The conclusion summarizes your research findings and reflects on the research topic.
- You should also discuss the limitations of the study and suggest areas for future research.
- Make sure to link the research findings to the initial research question and discuss the broader implications of your study.
- References and Citations:
- Ensure that your dissertation outline includes a section dedicated to references. List all sources cited in your dissertation, following APA style or the preferred citation format provided by your advisor.
- Appendices:
- Add any supplementary materials such as survey instruments, interview guides, or additional data that support your dissertation.
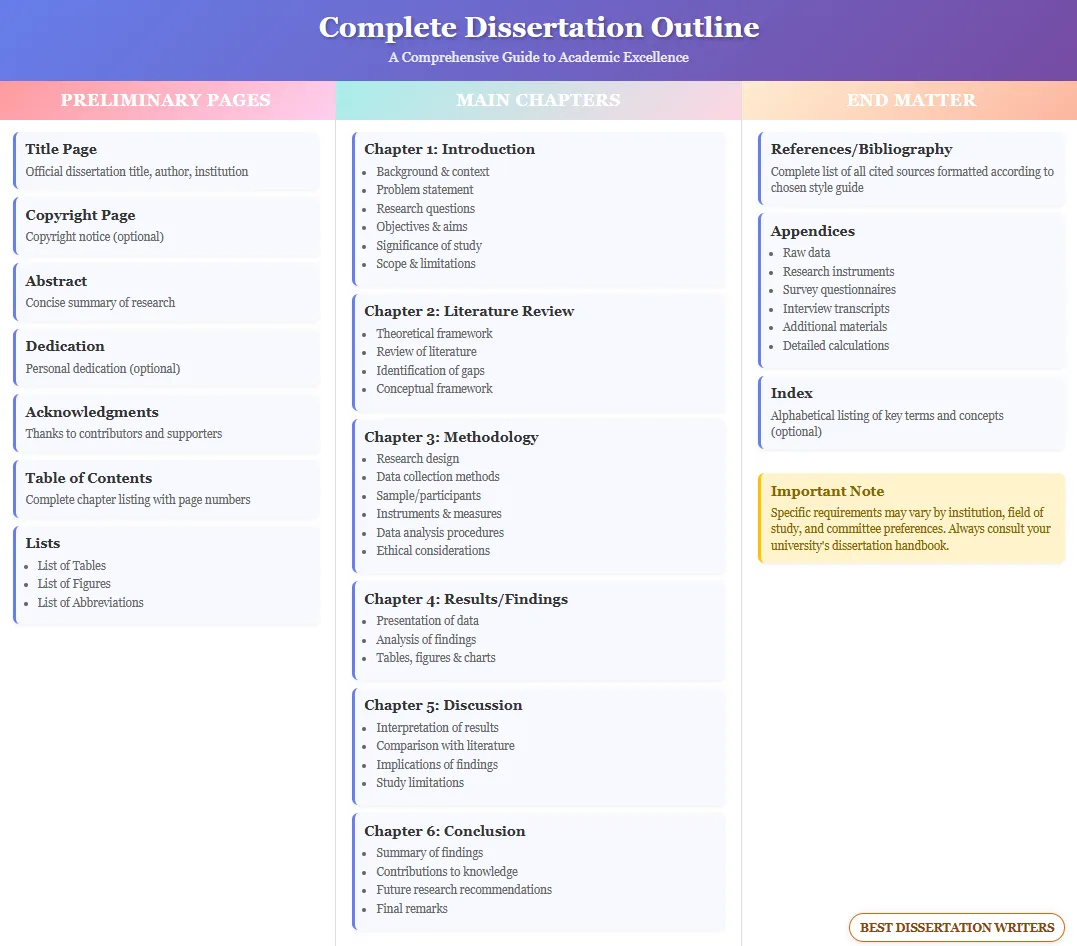
Important Chapters in Dissertation Structure
The core chapters in any dissertation outline include:
- Chapter 1: Introduction: Outlines the research background, statement of the problem, and research objectives.
- Chapter 2: Literature Review: Reviews and discusses previous research in the field, identifies gaps, and establishes the theoretical base.
- Chapter 3: Methodology: Details the methods used for data collection, analysis, and justification for the chosen methods.
- Chapter 4: Results and Discussion: Presents the findings, discusses them with reference to previous studies, and highlights their significance.
- Chapter 5: Conclusion: Summarizes the entire research, evaluates the findings, and provides suggestions for future research.
Each chapter in your dissertation outline must be well-defined and consistent. Ensure that each chapter logically flows from the previous one, providing a seamless structure.
Download the MS Word Version of Our Dissertation Outline: Get a fully editable MS Word version of our dissertation outline. Download now and start crafting your perfect dissertation structure with ease!
Download the PDF Version of Our Dissertation Outline: Prefer a ready-to-go format? Download our PDF version of the dissertation outline and view a professionally structured template to guide your writing process.
Dissertation Outline Examples for Structuring Your Thesis
- Example 1:
- Title Page
- Abstract
- Table of Contents
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Literature Review
- Chapter 3: Methodology
- Chapter 4: Results and Discussion
- Chapter 5: Conclusion
- References
- Appendices
- Example 2:
- Title Page
- Acknowledgements
- Abstract
- Table of Contents
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Literature Review
- Chapter 3: Methodology
- Chapter 4: Data Collection and Analysis
- Chapter 5: Findings
- Chapter 6: Conclusion
- References
- Appendices
Common Mistakes to Avoid While Writing a Dissertation Outline
- Inconsistent Chapter Titles:
- Ensure all chapters are named consistently in your dissertation outline. Each section should align with the overall dissertation format.
- Missing Key Components:
- Always include the title page, abstract, literature review, and methodology chapter in your dissertation outline.
- Lack of Justification:
- Failing to justify your research methodology and design in the dissertation outline can lead to confusion and weak arguments.
- Overly Complicated Structure:
- Keep the dissertation outline clear and straightforward. Avoid making it too detailed or complicated, as this can hinder the writing process.
- Not Adhering to Guidelines:
- Follow the format and structure provided by your dissertation chair or university guidelines. Not adhering to these could lead to your outline being rejected or needing major revisions.
A well-organized dissertation outline is essential to the success of your dissertation. It serves as a blueprint for your research, ensuring that all chapters and sections are logically structured and aligned with your research goals. Properly planning your dissertation outline will save time and effort and increase the quality of your final submission.
Key Sections of a Dissertation Outline and How to Write Them
A dissertation outline is an essential tool for organizing your dissertation writing process. It helps break down the complexity of your research into manageable tasks and ensures that all necessary components are covered. Below, we will discuss how to craft key sections of your dissertation outline and offer tips on writing them effectively.
How to Craft an Impressive Table of Contents in Your Dissertation Outline
- Table of Contents is one of the first sections in your dissertation outline and acts as a roadmap for your readers.
- It provides an organized list of all chapters and subheadings, ensuring that your dissertation outline is well-structured.
- Include page numbers for each section, allowing easy navigation.
- Key Sections to Include in the Table of Contents:
- Abstract: A brief summary of your dissertation’s aims, methodology, and conclusions.
- Chapter 1: Introduction: Introduction to your research topic, research question, and objectives.
- Chapter 2: Literature Review: Overview of the relevant literature, including key concepts and theories.
- Chapter 3: Methodology: Details of the methodology and data collection methods used in your research.
- Chapter 4: Results and Discussion: Presentation of your findings and analysis.
- Chapter 5: Conclusion: Summarizes the results and discusses the broader implications.
- Your dissertation outline will also include an appendices section for any supplementary material.
- The Table of Contents should be easy to update as you finalize each chapter.
Creating Clear and Detailed Dissertation Chapters in Your Outline
- Each chapter in your dissertation outline should have a clear, descriptive title and provide enough detail about what will be discussed in that section.
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- This chapter describes the problem statement, research question, and the aim of your research.
- Ensure that your dissertation outline highlights why the topic is relevant and important.
- The introduction should also provide a brief overview of the research design and methodologies used.
- Chapter 2: Literature Review
- The literature review chapter outlines the existing research and theories related to your topic.
- In your dissertation outline, identify key theories, concepts, and authors that will be discussed.
- Make sure to show how your research fills a gap in the existing body of work.
- Chapter 3: Methodology
- The methodology chapter in your dissertation outline describes the research approach you will use (qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods).
- Provide details about how data will be collected, analyzed, and presented.
- Include the research design, data collection instruments, and any manuals or instruments that will be used.
- Chapter 4: Results and Discussion
- In this chapter, outline the methods for presenting your data and how you plan to analyze it.
- Your dissertation outline should clarify whether you will use analytical techniques like statistical analysis or thematic analysis.
- Discuss how the results will be interpreted and linked to the research objectives.
- Chapter 5: Conclusion
- This chapter should provide a summary of the findings, discussing the implications of your research and how it contributes to your field.
- In your dissertation outline, highlight areas for future research or any gaps in knowledge your study has uncovered.
- The conclusion should also revisit the research question and hypothesis presented earlier in the outline.
Thesis Statement and Introduction: Essential Sections in the Outline
- Thesis Statement: The thesis statement is a crucial part of your dissertation outline and guides the entire dissertation. It presents the central argument or focus of your research in a concise way.
- It should be clear, direct, and specific, explaining the main point of your research.
- Ensure that your dissertation outline presents a thesis statement that aligns with your research question and objectives.
- Introduction: The introduction in your dissertation outline sets the stage for your research.
- Clearly state the research problem and outline why it is important to address it.
- Your dissertation outline should also include a brief overview of the structure of your dissertation, giving readers an idea of what to expect.
- This section must also provide an overview of your methodology, so the reader understands how you will answer your research question.
Dissertation Outline Templates: Streamlining Your Writing Process
- Dissertation Outline Templates are pre-made structures that help you organize your work efficiently.
- Using a dissertation outline template streamlines the process by guiding you through each chapter and section, ensuring no critical component is missed.
- Benefits of Using Dissertation Outline Templates:
- Consistency: Templates ensure that your dissertation outline follows a consistent format, making it easier to structure your work.
- Time-Saving: Templates save you time by providing a ready-made framework, allowing you to focus on content rather than formatting.
- Focus: Templates help maintain your focus by providing headings and subheadings that guide your writing.
- Elements to Include in a Dissertation Outline Template:
- Title Page: Include a place for the title of your dissertation, your name, and the name of your dissertation advisor.
- Abstract: A section for summarizing the dissertation’s main aim and findings.
- Chapter Breakdown: Clearly marked chapters for introduction, literature review, methodology, results, and conclusion.
- Page Numbers: Include space to add page numbers to each section in the template.
- References and Citation: Add a space to list sources, adhering to your required citation style (e.g., APA style).
- Appendices: If applicable, include space to list any supporting materials like questionnaires, interview guides, or survey results.
- Dissertation Outline templates can be customized to fit the specific requirements of your doctoral dissertation or any doctoral programs.
By using a dissertation outline template, you streamline the writing process, ensuring that all sections are clearly defined and logically organized. This approach allows you to focus on the content of your dissertation rather than worrying about structure. It also provides a clear plan for meeting deadlines and submitting drafts.
Developing a detailed dissertation outline is an essential first step in the dissertation process. It helps ensure that each section of your work is carefully thought out and well-organized, allowing you to meet academic expectations and submit a cohesive, high-quality dissertation.
