What is an Argumentative Essay?
- Definition
- An argumentative essay is a type of academic essay that presents a clear argument on a contentious issue.
- The essay begins with an introduction that establishes the context, identifies the argumentative essay topics, and states a thesis statement.
- Unlike an expository essay, which only explains, an argumentative essay is persuasive and evaluative, requiring the writer to argue, discuss, and evaluate both sides of an argument.
- Key Features
- Logical structure: A clear five-paragraph or extended structure is common, where each paragraph builds toward the conclusion.
- Thesis and support: The thesis is defended with argument with evidence, citing research papers, surveys, and credible text.
- Counterarguments: The writer acknowledges strengths and weaknesses of opposing views and offers a rebuttal.
- Models of argumentation: Writers may use the Rogerian model (focusing on common ground) or the Toulmin model (claim, evidence, warrant).
- Guidelines for students: College students are expected to follow MLA or APA format when they write an argumentative essay and properly cite sources.
- Why It Matters for College Students
- Argumentative writing develops critical thinking, the ability to assess both sides of an argument, and skills in composition.
- Argumentative essay examples help students see how to introduce, develop, and defend a position on the topic while maintaining clarity and persuasiveness.
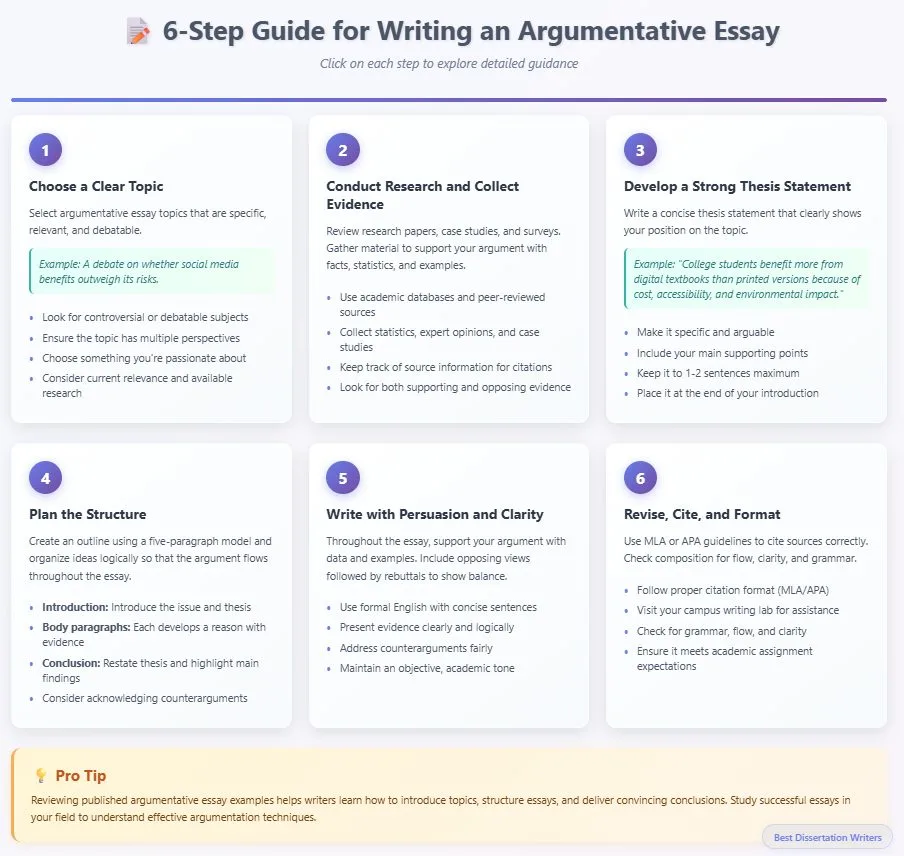
A 6-Step Guide for Writing an Argumentative Essay
- Choose a Clear Topic
- Select argumentative essay topics that are specific, relevant, and debatable.
- Example: a debate on whether social media benefits outweigh its risks.
- Conduct Research and Collect Evidence
- Review research papers, case studies, and surveys.
- Gather material to support your argument with facts, statistics, and examples.
- Develop a Strong Thesis Statement
- Write a concise thesis statement that clearly shows your position on the topic.
- Example: “College students benefit more from digital textbooks than printed versions because of cost, accessibility, and environmental impact.”
- Plan the Structure
- Create an outline using a five-paragraph model:
- Introduction – introduce the issue and thesis.
- Body paragraphs – each one develops a reason, presents evidence, and may acknowledge counterarguments.
- Conclusion – restate thesis and highlight main reason and findings.
- Organize ideas logically so that the argument and showing of evidence flows throughout the essay.
- Create an outline using a five-paragraph model:
- Write with Persuasion and Clarity
- Throughout the essay, support your argument with data and examples.
- This can be done using a thematic writing approach.
- Include proponent and opposing views, followed by a rebuttal to show balance.
- Maintain formal English language, with concise sentences.
- Revise, Cite, and Format
- Use MLA or APA guidelines to cite sources correctly.
- Check composition for flow, clarity, and grammar.
- Many students use their campus writing lab to polish essays before submission.
- Ensure the essay follows academic assignment expectations and reflects proper argumentation.
- Tip: Reviewing published argumentative essay examples helps writers learn how to introduce topics, structure essays, and deliver convincing conclusions.
- To see how examples connect to broader ideas, explore our complete guide on thematic essays for deeper insights.
- Beyond debates, you may also explore clear and factual expository essay topics for building strong informative essays.
- If you’re interested in capturing detail instead of debate, try exploring our engaging list of descriptive essay topics created to boost your success.
- Looking for personal storytelling instead of structured debate? Explore our collection of narrative essay topics.
Best Argumentative Essay Format
- Introduction
- Begin with context and a hook to engage the reader.
- Introduce the contentious issue and position on the topic.
- End with a strong thesis statement.

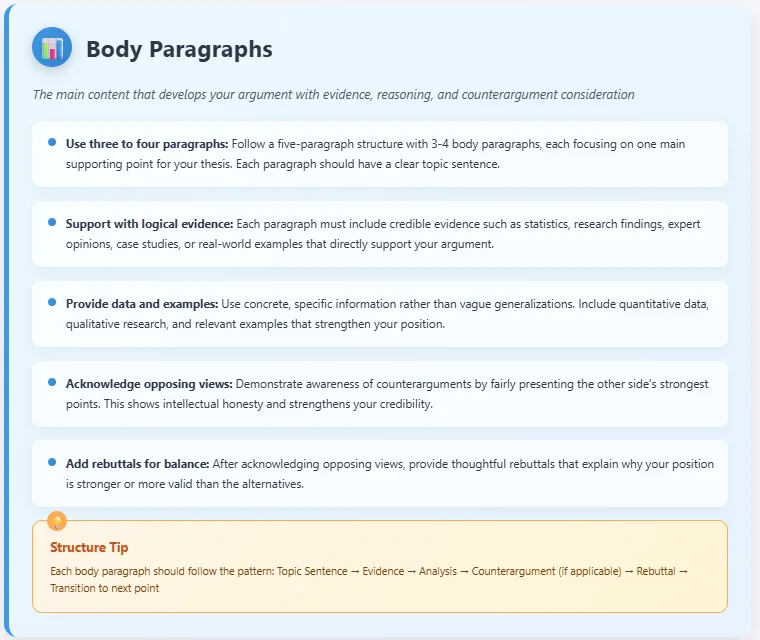
- Body Paragraphs
- Use three to four paragraphs in a five-paragraph structure.
- Each paragraph should support your argument with logical evidence, data, or examples.
- Acknowledge opposing views and add a rebuttal for balance.
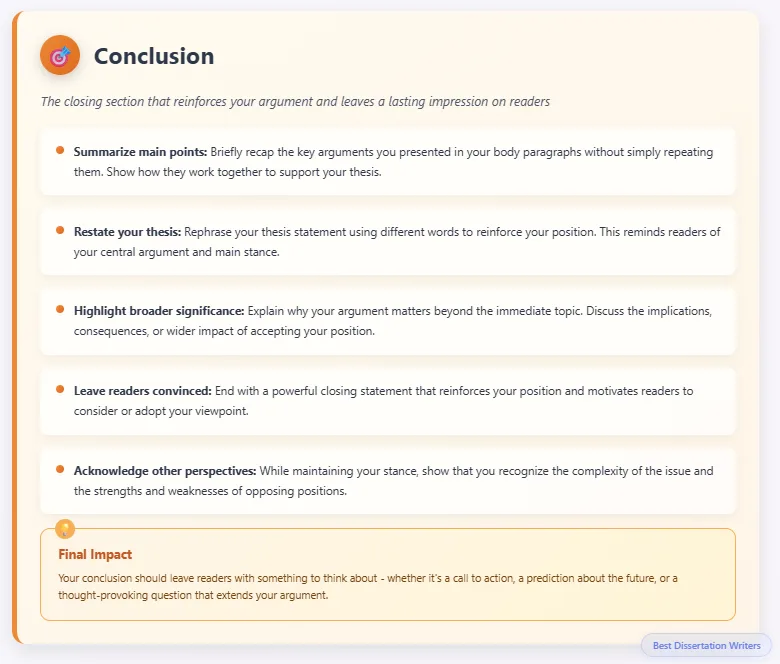
- Conclusion
- Summarize main points, restate thesis, and highlight the broader significance of the issue.
- The conclusion should leave readers convinced of your stance while recognizing the strengths and weaknesses of other positions.
- Formatting and Style
- Follow either MLA or APA style when referencing.
- Keep the composition concise, persuasive, and professional.
- Ensure proper grammar, smooth structure, and academic tone.
- Why Format Matters
- The format ensures clarity and flow throughout the essay.
- Proper formatting makes an essay easier to grade, present, or publish in academic settings.
- Practical Example
- Most argumentative essay examples use the Toulmin model for logical reasoning or the Rogerian model when aiming for compromise.
- Either model ensures that the argument with evidence is strong, balanced, and persuasive.
- After reviewing this example, you may also want to explore our full list of argumentative essay topics to inspire your next paper.
- If you’d like to compare persuasive writing with explanatory styles, check out our detailed expository essay examples.
- Want to see how vivid details can strengthen arguments? Browse our descriptive essay examples for your inspiration.
- Persuasive writing often draws from stories — view our narrative essay examples to see how storytelling enhances arguments.
Assorted Argumentative Essay Examples
MLA Argumentative Essay Example
Do Social Media Platforms Do More Harm Than Good?
In the digital age, social media platforms have become essential tools for communication, entertainment, and information sharing. However, their rapid growth has raised pressing concerns about their impact on individuals and society. While social media has undeniable benefits, such as global connectivity and rapid information exchange, it ultimately does more harm than good by encouraging misinformation, fostering mental health challenges, and weakening real-life social interactions.
One of the primary harms of social media is its role in spreading misinformation. Platforms such as Facebook and Twitter allow information to circulate instantly, but not all information is factual. In the 2016 U.S. presidential election, false news stories often outperformed accurate journalism in engagement, demonstrating how misinformation thrives online (Allcott and Gentzkow 213). Social media algorithms prioritize engagement over accuracy, creating an environment where false or misleading content spreads rapidly. Although fact-checking tools exist, they often arrive too late, after harmful narratives have already reached millions.
Another major concern is the link between social media use and mental health struggles. Studies consistently show that heavy use of platforms like Instagram and TikTok correlates with higher levels of anxiety, depression, and loneliness among young people. According to Jean Twenge, social media contributes to a culture of constant comparison, where adolescents measure their self-worth against curated images of peers and celebrities (102). This constant exposure to idealized lifestyles fosters insecurity and a fear of missing out, leading to long-term negative psychological effects.
Additionally, social media weakens authentic, face-to-face social interactions. While these platforms claim to bring people together, they often replace meaningful communication with shallow digital exchanges. Sherry Turkle argues that constant online connectivity paradoxically makes individuals feel “alone together,” as relationships are reduced to likes, shares, and emojis (Turkle 19). Instead of enhancing community, social media fosters isolation, as users substitute genuine conversation with digital affirmation.
Defenders of social media argue that these platforms provide essential benefits, such as political mobilization and global awareness. The Arab Spring, for example, demonstrated how platforms like Twitter can empower citizens to challenge oppressive governments. While these benefits are noteworthy, they do not outweigh the broader harms. Positive examples remain exceptions rather than the rule, and harmful effects such as misinformation and mental health crises impact far larger populations on a daily basis.
In conclusion, although social media offers opportunities for connection and advocacy, its harmful consequences outweigh its benefits. By encouraging misinformation, worsening mental health issues, and eroding authentic relationships, social media ultimately does more harm than good. Society must address these challenges by implementing stronger regulations and promoting digital literacy. Only then can social media shift from a harmful force to a tool for positive change.
Works Cited
- Allcott, Hunt, and Matthew Gentzkow. “Social Media and Fake News in the 2016 Election.” Journal of Economic Perspectives, vol. 31, no. 2, 2017, pp. 211–236.
- Turkle, Sherry. Alone Together: Why We Expect More from Technology and Less from Each Other. Basic Books, 2011.
- Twenge, Jean M. iGen: Why Today’s Super-Connected Kids Are Growing Up Less Rebellious, More Tolerant, Less Happy—and Completely Unprepared for Adulthood. Atria Books, 2017.
APA Argumentative Essay Example
Should Universal Basic Income (UBI) Be Implemented to Address Economic Inequality?
Economic inequality remains one of the most pressing challenges in modern societies, with wealth concentrated in the hands of a small minority while millions struggle to meet basic needs. One proposed solution is the implementation of a Universal Basic Income (UBI), a policy that guarantees all citizens a fixed income regardless of employment status. Supporters argue that UBI can reduce poverty, support human dignity, and adapt economies to technological changes. Critics, however, contend that it is costly, potentially discourages work, and may fail to address structural inequities. Despite these concerns, evidence suggests that UBI is a viable and necessary policy to combat inequality.
First, UBI has the potential to reduce poverty and promote financial stability. By guaranteeing a basic income, UBI ensures that every citizen can afford essentials such as food, housing, and healthcare. Experiments conducted in Finland revealed that recipients of basic income reported higher levels of well-being and financial security, even if employment rates were minimally affected (Kangas et al., 2021). This demonstrates that UBI can provide stability and reduce stress caused by economic precarity.
Second, UBI can serve as a buffer against the challenges posed by automation and technological unemployment. As artificial intelligence and robotics increasingly replace human labor, many industries face potential job losses. According to Frey and Osborne (2017), nearly 47% of U.S. jobs are at risk of automation in the coming decades. A guaranteed basic income would provide citizens with the financial security to adapt, retrain, or pursue entrepreneurial ventures, ensuring that societies remain resilient in the face of technological disruption.
Furthermore, UBI upholds the principle of human dignity. Unlike welfare programs that often involve complex eligibility requirements, UBI eliminates stigma and bureaucratic inefficiency. By providing unconditional support, it treats citizens equally and fosters trust in government institutions. This aligns with the idea that all individuals deserve a foundation of economic security regardless of circumstances.
Critics argue that UBI is financially unsustainable and may disincentivize work. However, pilot studies demonstrate that UBI does not significantly reduce labor participation. In fact, many participants use the income to pursue education, caregiving, or part-time work that aligns better with personal goals (Banerjee et al., 2019). While large-scale implementation would require careful tax reform, the long-term benefits of reduced poverty, lower healthcare costs, and stronger social cohesion may offset initial expenses.
In conclusion, Universal Basic Income represents a practical and ethical response to growing economic inequality. By reducing poverty, adapting to technological change, and upholding human dignity, UBI offers a pathway to a more equitable society. While challenges remain regarding funding and implementation, the evidence suggests that UBI should be pursued as a transformative policy for the 21st century.
References
- Banerjee, A., Niehaus, P., & Suri, T. (2019). Universal Basic Income in the developing world. Annual Review of Economics, 11(1), 959–983. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-economics-080218-030243
- Frey, C. B., & Osborne, M. A. (2017). The future of employment: How susceptible are jobs to computerisation? Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 114, 254–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2016.08.019
- Kangas, O., Jauhiainen, S., Simanainen, M., & Ylikännö, M. (2021). Evaluation of the Finnish Basic Income Experiment 2017–2018. Ministry of Social Affairs and Health. https://urn.fi/URN:ISBN:978-952-00-4035-2
Harvard Argumentative Essay Sample
Is Climate Change the Greatest Global Threat of the 21st Century?
Climate change is increasingly recognized as one of the defining issues of the 21st century, raising urgent questions about humanity’s future. While some argue that other global challenges, such as pandemics or geopolitical conflicts, pose greater immediate risks, climate change stands apart due to its scale, persistence, and multifaceted consequences. This essay argues that climate change is indeed the greatest global threat of the century, given its impact on ecosystems, economies, and human survival.
One of the most alarming aspects of climate change is its effect on ecosystems and biodiversity. Rising global temperatures, caused largely by greenhouse gas emissions, disrupt weather patterns, leading to habitat destruction and species extinction. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC, 2022), approximately one million species are currently at risk due to climate-related changes in ecosystems. Unlike regional conflicts or short-term crises, climate change threatens the very foundation of life on Earth, making it unparalleled in severity.
Climate change also has devastating economic consequences. Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and wildfires, increasingly strain national economies. The World Bank (2021) estimates that climate change could push over 130 million people into poverty by 2030, primarily due to declining agricultural productivity and rising food prices. These effects are not confined to developing countries; advanced economies also face infrastructure damage and resource scarcity, highlighting the universal nature of the threat.
Furthermore, climate change exacerbates global inequalities and fuels geopolitical instability. Rising sea levels threaten low-lying nations such as Bangladesh and the Maldives, creating millions of climate refugees. According to Homer-Dixon (2019), resource scarcity linked to climate stress can trigger conflicts over water and arable land, increasing the likelihood of wars in already fragile regions. This demonstrates how climate change magnifies existing vulnerabilities, making it a multiplier of global insecurity.
Critics may argue that other challenges, such as nuclear proliferation or pandemics like COVID-19, pose more immediate threats. However, these risks, while severe, are episodic and potentially containable through coordinated global action. Climate change, by contrast, is cumulative, long-term, and irreversible if not addressed urgently (IPCC, 2022). Its effects will persist for centuries, shaping every aspect of human society and the natural world.
In conclusion, climate change is the greatest global threat of the 21st century because it undermines ecosystems, destabilizes economies, and heightens geopolitical tensions. While other global issues demand attention, none match the scope and permanence of climate change. Addressing this crisis requires unprecedented international cooperation, urgent policy reforms, and collective commitment to sustainability. Humanity’s survival in the 21st century depends on recognizing and acting against this unparalleled threat.
References
- Homer-Dixon, T. (2019) Commanding hope: The power we have to renew a world in peril. Toronto: Alfred A. Knopf.
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (2022) Climate change 2022: Impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- World Bank (2021) Climate change action plan 2021–2025. Washington, DC: World Bank.
What People Also Ask About Argumentative Essays
What is an argumentative essay?
An argumentative essay is a type of academic writing where the writer takes a clear position on a controversial topic and defends it using logic, evidence, and reasoning. Unlike descriptive or expository essays, its purpose is to persuade readers to accept or understand the writer’s viewpoint. It requires presenting strong claims, supporting them with credible research, addressing counterarguments, and offering rebuttals. This type of essay is common in colleges to develop critical thinking, debate, and persuasive writing skills.
What is the structure of the argumentative essay?
The structure of an argumentative essay is designed for clarity and persuasion. It begins with an introduction that hooks the reader, provides context, and states the thesis. The body follows, usually in three or more paragraphs, where each presents a reason with supporting evidence. Counterarguments are then acknowledged and refuted to show balance. Finally, the conclusion restates the thesis, summarizes key points, and emphasizes the significance of the argument. This logical structure helps readers follow and evaluate the reasoning.
What are the 4 parts of the argumentative essay?
The four main parts of an argumentative essay are the introduction, thesis statement, body paragraphs, and conclusion. The introduction sets up the topic and engages the reader. The thesis statement clearly states the writer’s position. Body paragraphs present arguments with evidence while addressing opposing views through rebuttals. The conclusion reinforces the thesis and summarizes the key arguments. These four interconnected parts ensure the essay flows logically, persuades effectively, and demonstrates a clear stance supported by reasoning and credible sources.
What are the five elements of an argumentative essay?
The five elements of an argumentative essay are claim, evidence, counterargument, rebuttal, and conclusion. The claim is the central argument or position. Evidence, drawn from research and examples, supports the claim. A strong essay also presents counterarguments, showing awareness of opposing views. Rebuttals respond directly to those counterarguments, strengthening the original stance. Finally, the conclusion ties everything together by restating the thesis and emphasizing why the argument matters. These five elements work together to create a persuasive and balanced essay.
